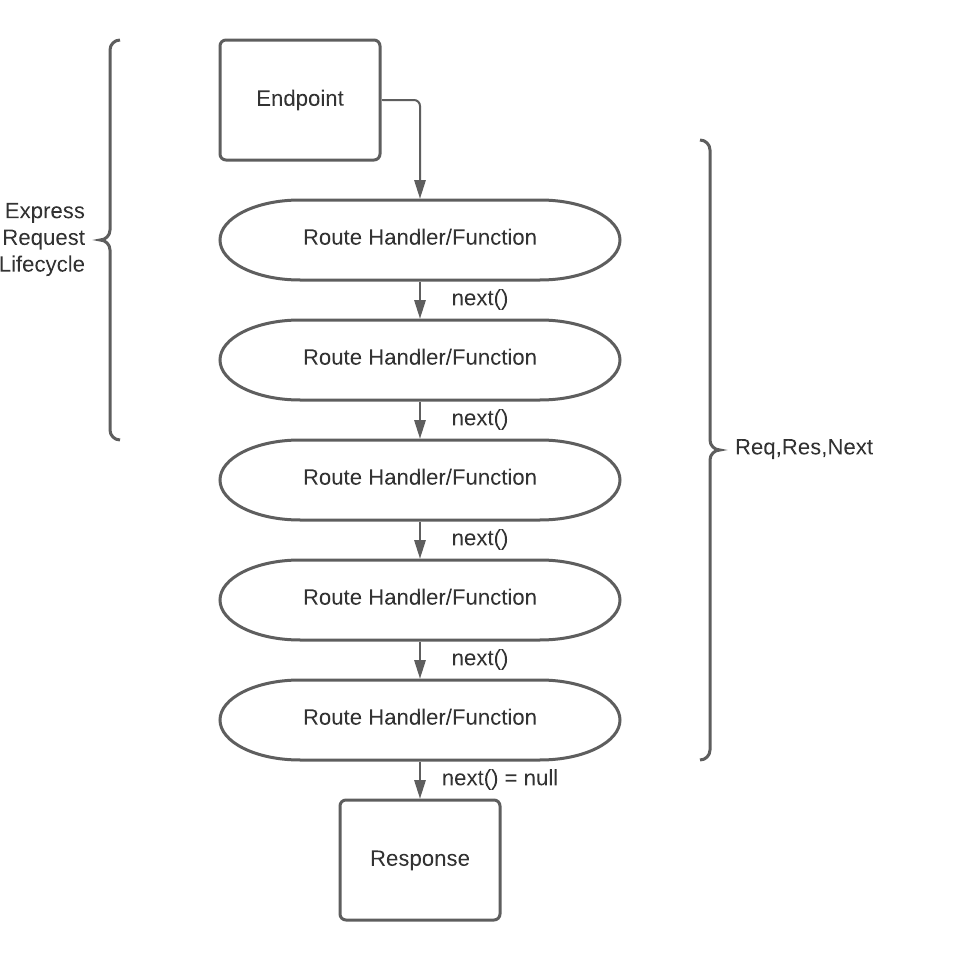
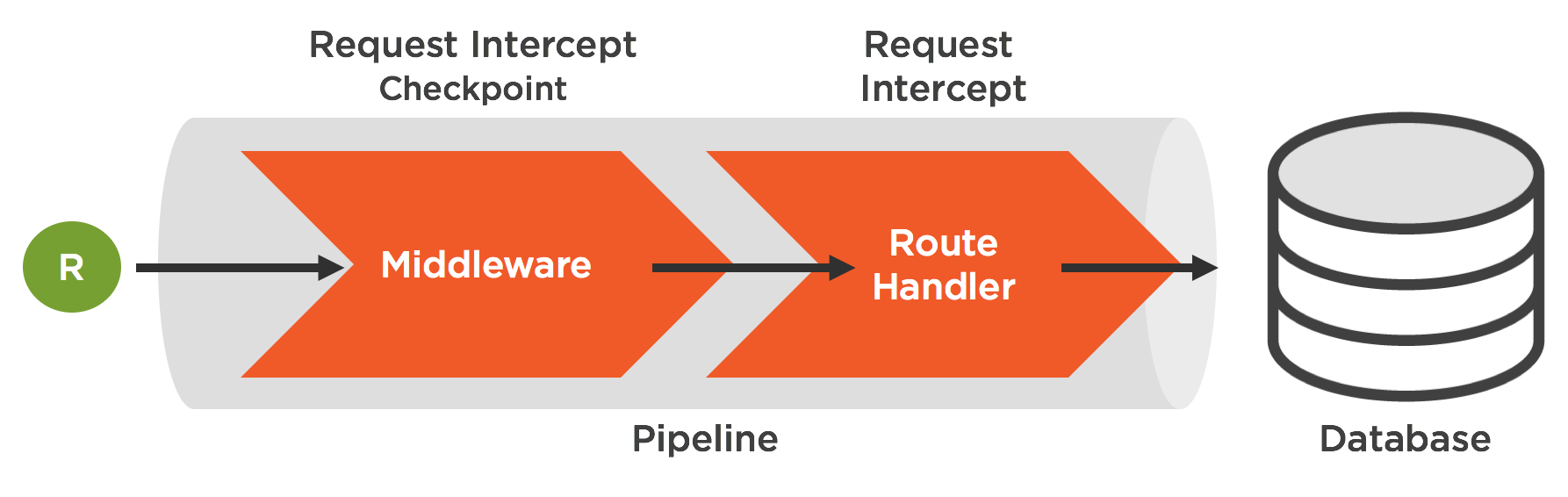
In this lesson we'll learn how to use functions called middleware. Middleware is a core concept of Express and allow us great flexibility in building and structuring our servers. Middleware helps us handle different conditions during the request/response lifecycle and assists us with making our code more modular.
- Implement Server middleware
- Use 3rd party middleware
- Build your own middleware
- Fork And Clone this repository
npm iornpm installto install the dependencies.npm run devto check your installation completed successfully.- Have Insomnia ready to go! A basic Express app has been provided for you.
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3001
// Your Code Here
// Your Code Ends Here
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`App listening on port: ${PORT}`)
})Middleware can be described as a function that run's in the middle of a request or before. From the Express documentation:
Middleware functions are functions that have access to the request object (req), the response object (res), and the
nextmiddleware function in the application’s request-response cycle. The next middleware function is commonly denoted by a variable named next.Middleware functions can perform the following tasks:
- Execute any code.
- Make changes to the request and the response objects.
- End the request-response cycle.
- Call the next middleware function in the stack.
Let's install a depedency that we will use as middleware.
npm install corsOnce the dependency finishes installing, we'll need to require it in our app.js.
const express = require('express')
const cors = require('cors')
const app = express()
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3001
// Your Code Here
// Your Code Ends Here
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`App listening on port: ${PORT}`)
})Now that we have access to this packages we can utilize it in our express app.
Luckily Express makes it super easy for us to incorporate middleware.
Express provides us with a .use() function that allows us to incorporate 3rd party packages.
Add the following to your app.js in the your code goes here section.
app.use(cors())
// the following middleware comes out of the box with express...
app.use(express.json())
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }))By invoking the .use() method, we are telling our Express app to use these packages.
The cors package enables cross origin resource sharing for our app.
Feel free to look this up on your own time.
The json method allows us to send json information to our server and the urlEncoded method allows us to send encoded forms to our server.
We've successfully implemented 3rd party middleware with our app!
Below our 3rd party middleware, create a GET route for a /middleware endpoint:
app.get('/middleware')After the url, create a function and pass in 3 parameters, request, response and next.
app.get('/middleware', (request, response, next) => {})next is a function that tells express to call or invoke the next function.
Inside of this function let's add a console.log and log this is a middleware function and invoke the next function.
app.get('/middleware', (request, response, next) => {
console.log('this is middleware')
next()
})Now let's add the final function in our route. In this function, pass in the request and response parameters and we'll send back a reponse with the string request completed.
app.get(
'/middleware',
(request, response, next) => {
console.log('this is middleware')
next()
},
(req, res) => {
res.send('response completed')
}
)Test this endpoint with insomnia and you'll see our console.log in the terminal and a response returned to your HTTP client.
You've just built your own middleware!
Create 4 routes, one for each HTTP method. Each route should have their own middleware function that console.log's the type of HTTP method the route is for. Create a function after your middleware that sends a response saying: the HTTP type of {httpType} request is complete.
In this lesson we built and utilized middleware. We implemented 3rd part middleware like cors. We also built our own middleware functions.
Remember middleware functions are functions that execute as long as there is a next function in the request stack.