The image dataset tool (IDT) is a CLI app developed to make it easier and faster to create image datasets to be used for deep learning. The tool achieves this by scraping images from several search engines such as duckgo, bing and deviantart. IDT also optimizes the image dataset, although this feature is optional, the user can downscale and compress the images for optimal file size and dimensions. A sample dataset created using idt that contains a total amount of 23.688 image files weights only 559,2 megabytes.
I am proud to announce our newest version! 🎉🎉
What changed
- Added auto duplicate images remover
- Added longer side resize method. With this option, the image is resized to its longer side.
- Added shorter side resize method. With this option, the image is resized to its shorter side.
- Added Smart Crop. This method tries to crop and resize exactly the main subject of the image. The algorithm is based on SmartCrop.js and SmartCrop.py.
- Removed verbose mode. This was used in earlier stages of development but now don't add value to the experience.
- The official documentation is almost ready. A link will be available soon
You can install it via pip or cloning this repository.
user@admin:~$ pip3 install idt
OR
user@admin:~$ git clone https://github.com/deliton/idt.git && cd idt
user@admin:~/idt$ sudo python3 setup.py install
The quickest way to get started with IDT is running the simple "run" command. Just write in your favorite console something like:
user@admin:~$ idt run -i apples This will quickly download 50 images of apples. By default it uses the duckgo search engine to do so. The run command accepts the following options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -i or --input | the keyword to find the desired images. |
| -s or --size | the amount of images to be downloaded. |
| -e or --engine | the desired search engine (options: duckgo, bing, bing_api and flickr_api) |
| --resize-method | choose a resize method of images. (options: longer_side, shorter_side and smartcrop) |
| -is or --image-size | option to set the desired image size ratio. default=512 |
| -ak or --api-key | If you are using a search engine that requires an API key, this option is required |
IDT requires a config file that tells it how your dataset should be organized. You can create it using the following command:
user@admin:~$ idt initThis command will trigger the config file creator and will ask for the desired dataset parameters. In this example let's create a dataset containing images of your favorite cars. The first parameters this command will ask is what name should your dataset have? In this example, let's name our dataset "My favorite cars"
Insert a name for your dataset: : My favorite carsThen the tool will ask how many samples per search are required to mount your dataset. In order to build a good dataset for deep learning, many images are required and since we're using a search engine to scrape images, many searches with different keywords are required to mount a good sized dataset. This value will correspond to how many images should be downloaded at every search. In this example we need a dataset with 250 images in each class, and we'll use 5 keywords to mount each class. So if we type the number 50 here, IDT will download 50 images of every keyword provided. If we provide 5 keywords we should get the required 250 images.
How many samples per search will be necessary? : 50The tool will now ask for and image size ratio. Since using large images to train neural networks is not a viable thing, we can optionally choose one of the following image size ratios and scale down our images to that size. In this example, we'll go for 512x512, although 256x256 would be an even better option for this task.
Choose images resolution:
[1] 512 pixels / 512 pixels (recommended)
[2] 1024 pixels / 1024 pixels
[3] 256 pixels / 256 pixels
[4] 128 pixels / 128 pixels
[5] Keep original image size
ps: note that the aspect ratio of the image will not be changed,
so possibly the images received will have slightly different size
What is the desired image size ratio: 1And then choose "longer_side" for resize method.
[1] Resize image based on longer side
[2] Resize image based on shorter side
[3] Smartcrop
ps: note that the aspect ratio of the image will not be changed,
so possibly the images received will have slightly different size
Desired Image resize method: : longer_side
Now you must choose how many classes/folders your dataset should have. In this example, this part can be very personal, but my favorite cars are: Chevrolet Impala, Range Rover Evoque, Tesla Model X and (why not) AvtoVAZ Lada. So in this case we have 4 classes, one for each favorite.
How many image classes are required? : 4Afterwards, you'll be asked to choose between one of the search engines available. In this example, we'll use DuckGO to search images for us.
Choose a search engine:
[1] Duck GO (recommended)
[2] Bing
[3] Bing API
[4] Flickr API
Select option:: 1Now we have to do some repetitive form filling. We must name each class and all the keywords that will be used to find the images. Note that this part can be later changed by your own code, to generate more classes and keywords.
Class 1 name: : Chevrolet ImpalaAfter typing the first class name, we'll be asked to provide all the keywords to find the dataset. Remember that we told the program to download 50 images of each keyword so we must provide 5 keywords in this case to get all 250 images. Each keyword MUST be separated by commas(,)
In order to achieve better results, choose several keywords that will
be provided to the search engine to find your class in different settings.
Example:
Class Name: Pineapple
keywords: pineapple, pineapple fruit, ananas, abacaxi, pineapple drawing
Type in all keywords used to find your desired class, separated by commas: Chevrolet Impala 1967 car photos,
chevrolet impala on the road, chevrolet impala vintage car, chevrolet impala convertible 1961, chevrolet impala 1964 lowrider
Then repeat the process of filling class name and its keywords until you fill all the 4 classes required.
Dataset YAML file has been created successfully. Now run idt build to mount your dataset!Your dataset configuration file has been created. Now just rust the following command and see the magic happen:
user@admin:~$ idt buildAnd wait while the dataset is being mounted:
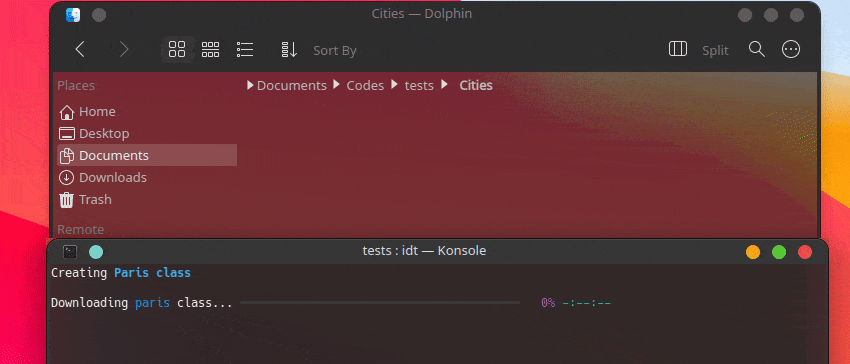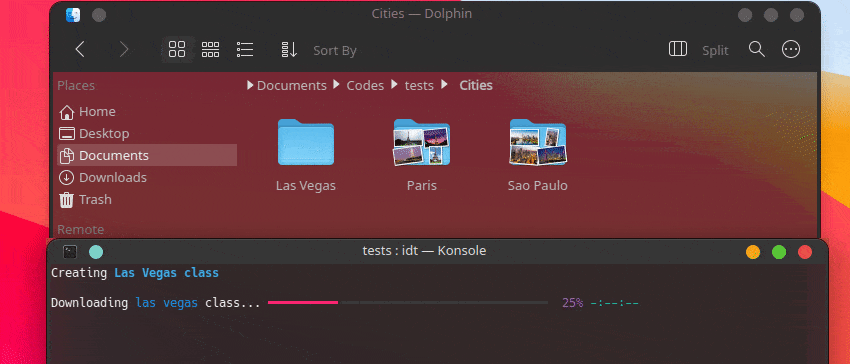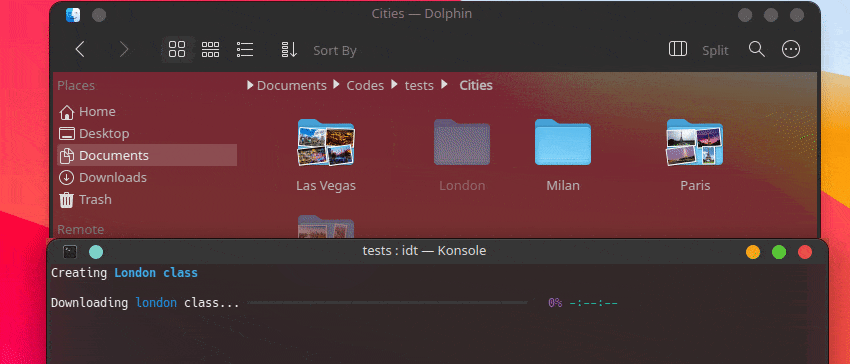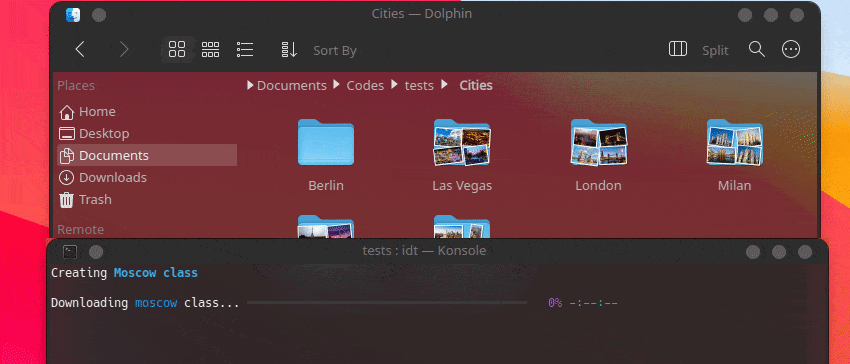
Creating Chevrolet Impala class
Downloading Chevrolet Impala 1967 car photos [#########################-----------] 72% 00:00:12
At the end, all your images will be available in a folder with the dataset name. Also, a csv file with the dataset stats are also included in the dataset's root folder.
Since deep learning often requires you to split your dataset into a subset of training/validation folders, this project can also do this for you! Just run:
user@admin:~$ idt splitNow you must choose a train/valid proportion. In this example I've chosen that 70% of the images will be reserved for training, while the rest will be reserved for validation:
Choose the desired proportion of images of each class to be distributed in train/valid folders.
What percentage of images should be distributed towards training?
(0-100): 70
70 percent of the images will be moved to a train folder, while 30 percent of the remaining images
will be stored in a validation folder.
Is that ok? [Y/n]: yAnd that's it! The dataset-split should now be found with the corresponding train/valid subdirectories.
This project is being developed in my spare time and it still needs a lot of effort to be free of bugs. Pull requests and contributors are really appreciated, feel free to contribute in any way you can!