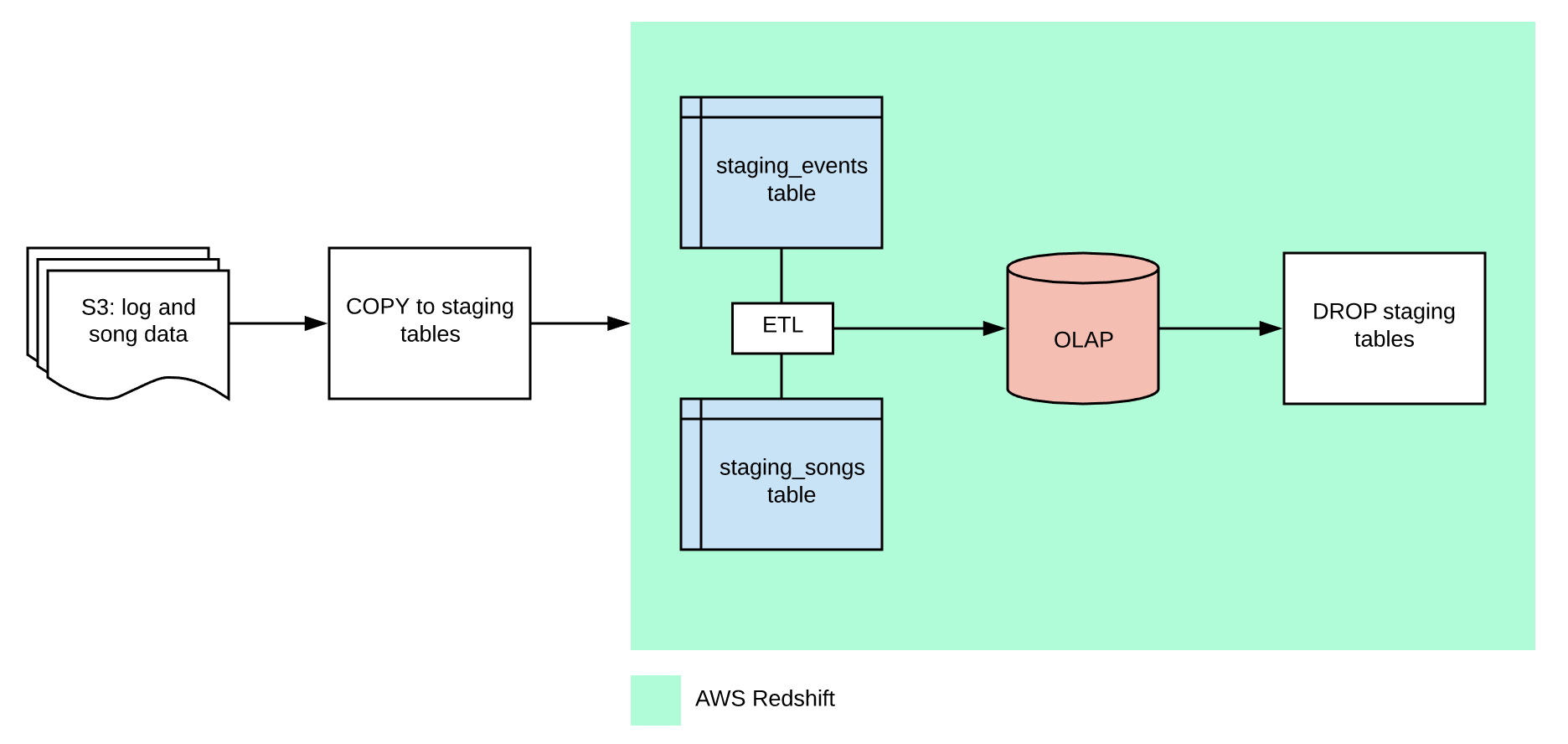
Previously, we helped a music streaming start-up called Sparkify grow and scale their analytics capabilities. The company has now elected to move the data contained in their on-premise databases to the cloud. For this project, we will build ETL pipelines that extract Sparkify's data (already in S3), stage them in Redshift, and transform data into a set of dimensional tables for their analytics team to continue deriving insights.
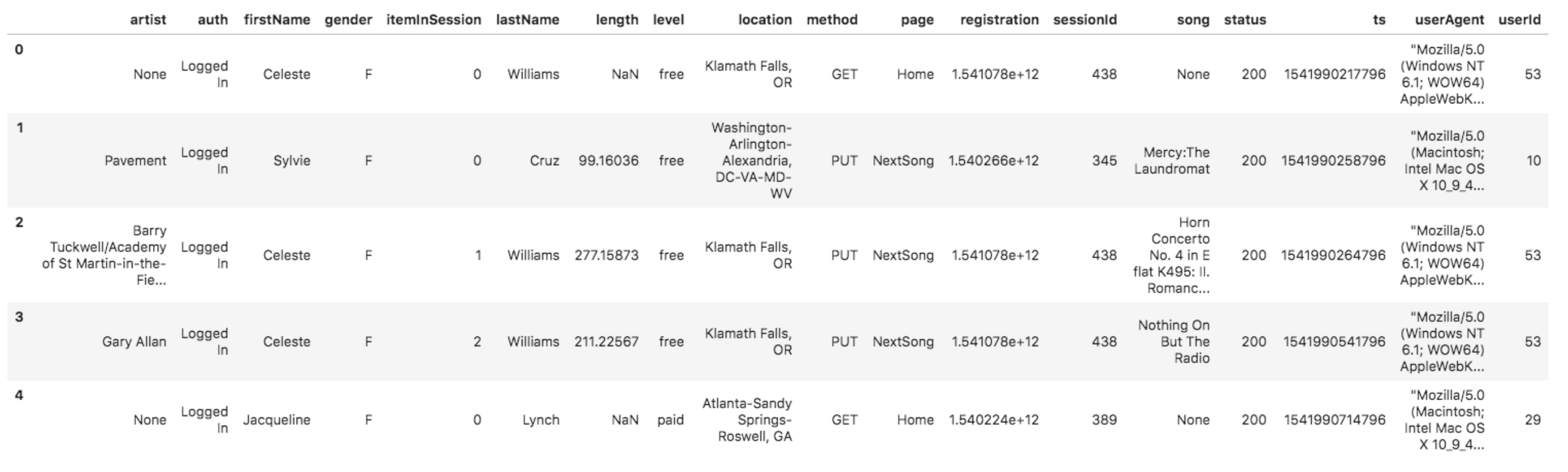
The raw data in S3 is contained in json format. There are two different types of data, logs and songs. Logs contain song play data; below is a an example of a log file.
Likewise, below is an example of a song data file.
{"num_songs": 1, "artist_id": "ARJIE2Y1187B994AB7", "artist_latitude": null, "artist_longitude": null, "artist_location": "", "artist_name": "Line Renaud", "song_id": "SOUPIRU12A6D4FA1E1", "title": "Der Kleine Dompfaff", "duration": 152.92036, "year": 0}
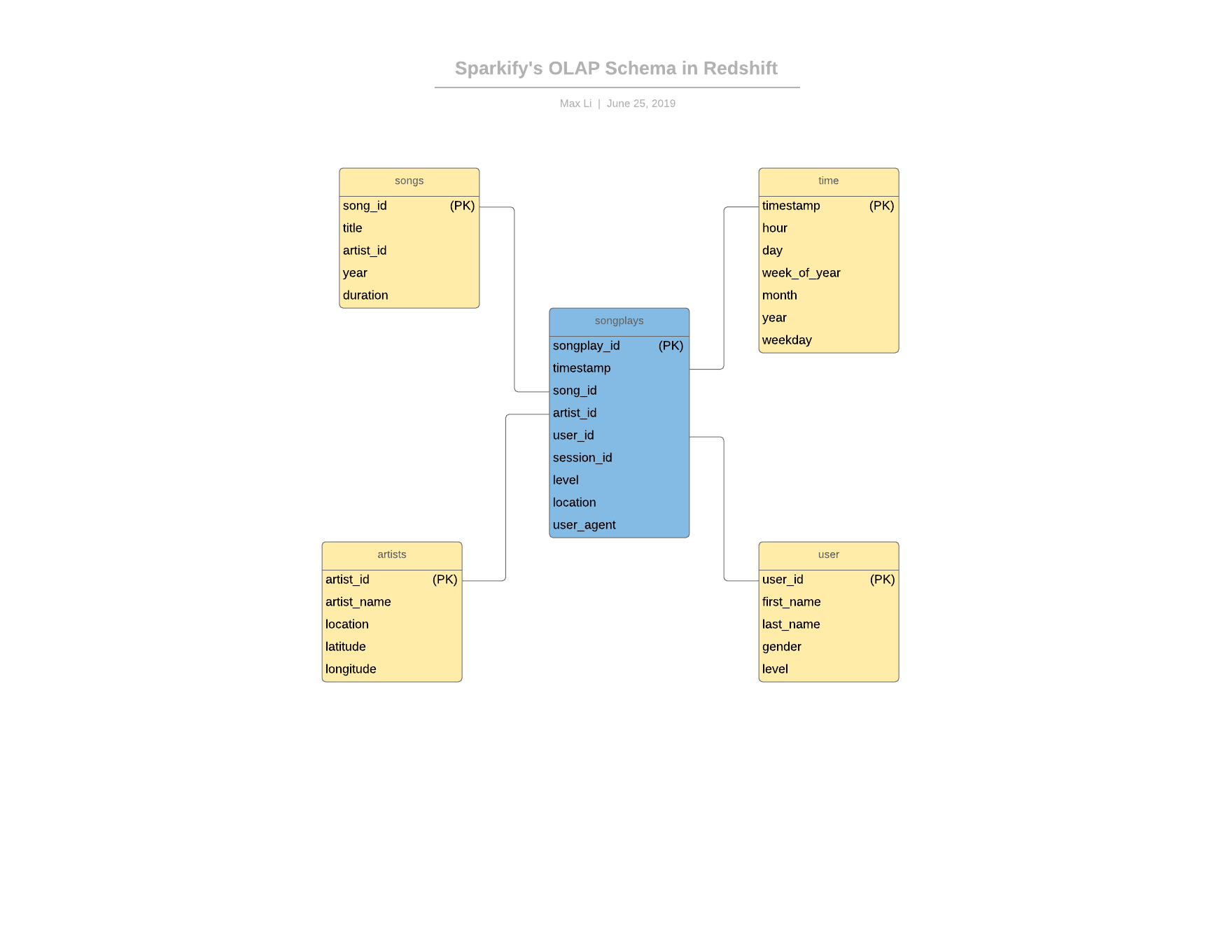
Below is a schematic of the ETL process, as well as the OLAP star schema on Amazon Redshift.
Some additional architectural notes.
-
Keys
distkey:
Used a distkey on the
song_idcolumn to avoid data shuffling in Redshift. We suspect that this will be a common key to join on.sortkey:
Used a sortkey on the
timestampvariable in both thesongplaysfact table and thetimedimensional table. This makes logical sense as it is common for tables to be sorted on timestamps. -
Distribution Style
Used DISTSTYLE ALL for the
artiststable because we suspect that this table will be pretty small compared to the others. Its growth should also be linear. -
INSERT statement for songplays table.
We create the
songplaystable by joining thestaging_eventsandstaging_songstables. We also filtered out any rows wherepagewas not equal to "NextSong", as other values do not represent a song listening action by the user.
- Run
python create_tables.pyin the root directory to create tables. - Run
python etl.pyin the root directory to initiate ETL process.
See test_etl_notebook.ipynb