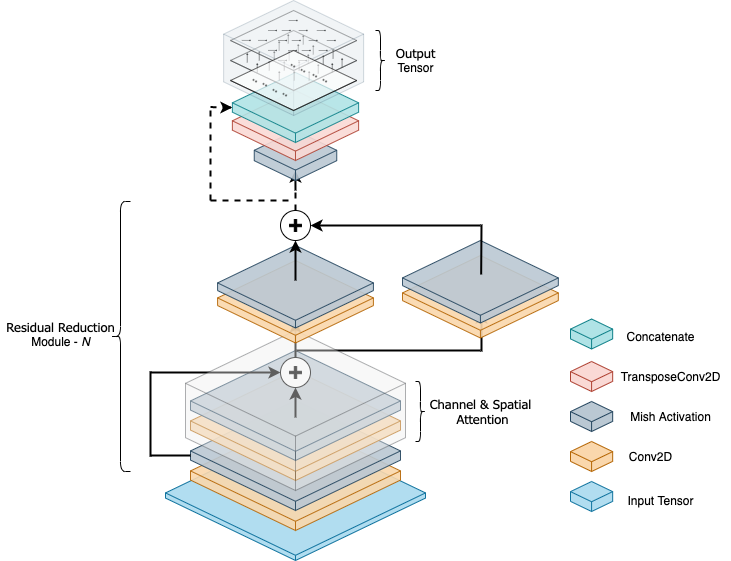
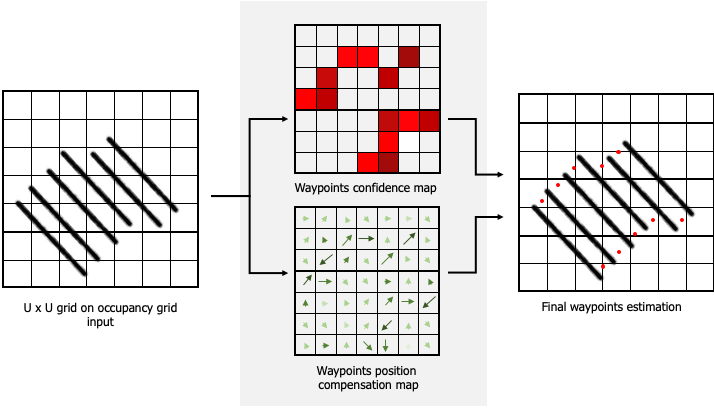
This repository contains all the code related to DeepWay, a deep learning model able to predict the position of waypoints useful for global path planning of autonomous unmanned robots in row-crop fields.
- Clone this repository
git clone https://github.com/fsalv/DeepWay.git
- Install the required packages
cd DeepWay
pip install -r requirements.txt
We recommend to do it in a separate virtual environment with respect to your main one to avoid compatibility issues for packages versions. In this case, remember to create a jupyter kernel linked to the new environment.
Warning If you don't have gpu available or if you have CUDA issues all calculations will be performed by your CPU.
Run the jupyter notebook Artificial Dataset Generator.ipynb to generate the random synthethic dataset. You can modify useful parameters in the first cells of the notebook.
You can re-train DeepWay on the new generated dataset with the notebook DeepWay Train.ipynb. You can modify network parameters inside the configuration file utils/config.json. In particular, by modifying the DATA_N and DATA_N_VAL values you can choose to train/validate with fewer images to see how prediction quality changes with dataset dimension. You can also modify the network architecture changing K, MASK_DIM, the number of FILTERS per layer or the KERNEL_SIZE.
You can test DeepWay on both the satellite and synthethic test datasets with the notebook DeepWay Test.ipynb. This notebooks allows you to compute the AP metric on the selected images. You can change the test set inside the notebook in the section Import the Test Dataset. If you set name_model = 'deep_way_pretrained.h5' in the third cell, you can use the weights pretrained by us.
Warning If you don't have gpu support, comment the third cell ("select a GPU and set memory growth") on both the training and testing notebooks.
To generate the paths with the A* algorithm and compute the coverage metric, you can use the ``` Prediction and Path Planning.ipynb``` notebook. Again, you can change the test set inside the notebook to select satellite or synthethic datasets. Note that the A* execution will require a lot of time, exspecially if it finds some trouble in generating the path for too narrow masks.Warning: If you don't have gpu support, comment the fourth cell ("select a GPU and set memory growth").
If you enjoyed this repository and you want to cite our work, you can find the post-print editorial version of our paper here.
@article{MAZZIA2021106091,
title = {DeepWay: A Deep Learning waypoint estimator for global path generation},
journal = {Computers and Electronics in Agriculture},
volume = {184},
pages = {106091},
year = {2021},
issn = {0168-1699},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2021.106091},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168169921001095},
author = {Vittorio Mazzia and Francesco Salvetti and Diego Aghi and Marcello Chiaberge}
}
Note on the satellite dataset:
The 100 masks of the real-world remote-sensed dataset have been derived by manual labeling of images taken from Google Maps. Google policy for the products of its satellite service can be found [here](https://www.google.com/permissions/geoguidelines/). Images can be used for reasearch purposes by giving the proper attribution to the owner. However, for this repository we chose to release the masks only and not the original satellite images.