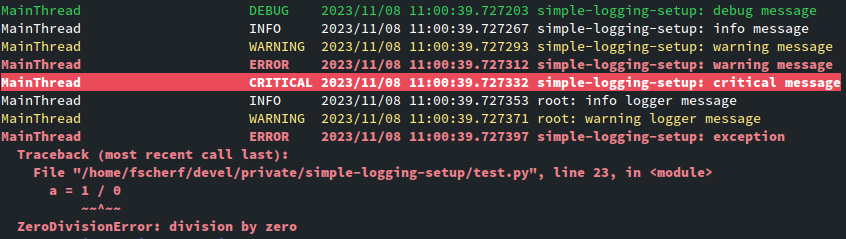
simple-logging-setup is a simple yet highly configurable library that provides sane configuration defaults for the logging system in the Python standard library.
Features:
- No external dependencies
- Simple coloring and detection if the terminal supports colored output
- Formatting for exceptions
- Support for syslog severity levels
- Log filtering
- Easy to integrate into command line options
simple-logging-setup can be installed using pip
pip install simple-logging-setup
import logging
from simple_logging_setup import setup
logger = logging.getLogger('my-logger')
setup(
level='info',
# put your configuration here
)
logger.info('Hi mom!')import argparse
from simple_logging_setup import setup
# parse command line
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
'-l',
'--log-level',
choices=['debug', 'info', 'warn', 'error', 'critical'],
default='info',
)
parser.add_argument(
'--loggers',
type=str,
nargs='+',
)
parser.add_argument(
'--show-timestamps',
action='store_true',
)
args = parser.parse_args()
# setup logging
setup(
level=args.log_level,
loggers=args.loggers,
show_timestamp=args.show_timestamps,
)$ my-tool -l debug --loggers my-logger -disabled-logger
$ my-tool --show-timestamps
All configuration is done by adding keyword arguments to
simple_logging_setup.setup.
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
level |
str |
info |
Log level. Choices (case insensitive): ['debug', 'info', 'warn', 'warning', 'error', 'critical'] |
colors |
switch |
True |
Enables or disables colors. Gets disabled by default if the terminal does not support colored output |
syslog_priorities |
switch |
False |
Enables or disables syslog severity levels. Gets enabled by default if running in journald |
show_thread_name |
switch |
True |
Show thread name in log output |
show_level_name |
switch |
True |
Show log level name in log output. Gets enabled by default if colors are disabled or not available |
show_timestamp |
switch |
True |
Show timestamp in log output |
show_logger_name |
switch |
True |
Show logger name in log output |
switch is a special type that does best-effort parsing of incoming values.
Examples: True, 1, 'True', 'TRUE', 'yes', 'on', [...]
Especially when the log level is set to debug, logging output can become hard
to read. simple-logging-setup allows you to filter loggers by including or
excluding specific logger names.
from simple_logging_setup import setup
setup(
loggers=[
# include loggers to the output (the `+` is optional)
'my-project.logger-1',
'+my-project.logger-1',
# exclude loggers from the output (both `-` and `_` can be used)
'-my-project.logger-1',
'_my-project.logger-1',
],
)Why two prefixes to choose for excludes? The - notation makes more sense in
code but may not be suitable for command line options. This optional extra
notation allows for command line options like
--loggers +included-logger _excluded-logger.
In some cases, it is not useful to always print all logger names. For example,
when creating a command line tool, a logger name like my-project.my-sub-system
is worth printing, but root is not. simple-logging-setup allows you to filter
out logger names, without excluding the logger entirely.
from simple_logging_setup import setup
setup(
filter_logger_names=['root'],
)simple-logging-setup comes with a list of useful presets which can be enabled
via the preset keyword argument.
from simple_logging_setup import setup
setup(preset='service') # 'service' is the default| Name | Description |
|---|---|
service |
Enables all switches and features available |
cli |
Disables all switches but show_logger_name and filters the logger name root |