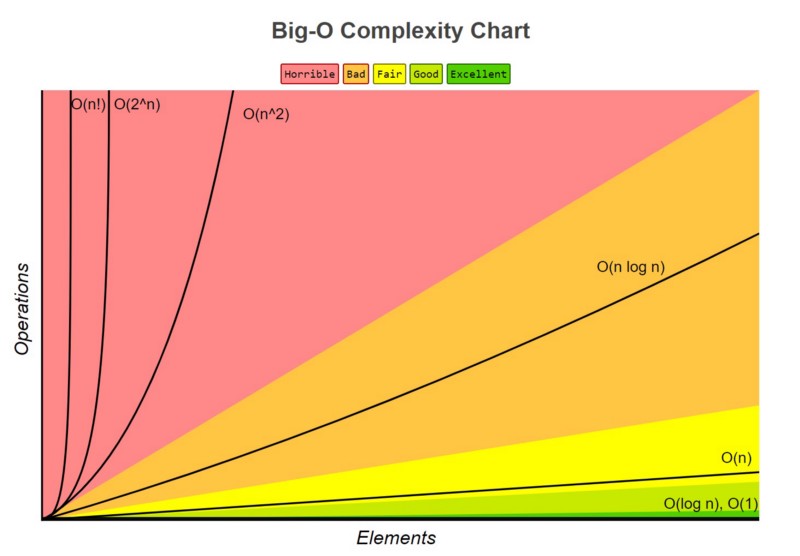
| Algorithm | Time Complexity (Best) | Time Complexity (Average) | Time Complexity (Worst) | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bubble Sort | O(n) | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(1) |
| Selection Sort | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(1) |
| Insertion Sort | O(n) | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(1) |
| Merge Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n) |
| Quick Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n²) | O(log n) |
The way that Bubble Sort works is that as we loop through each item we compare it to the next item in the array.
If the value is larger than next value, we swap. Basicaly we swap if something is larger.
The way that Selection Sort works is that as we loop through each item we compare it to the next item in the array.
We compare the value to the next item until we find a smaller number.
If the "minimum" is not the value (index), we swap the two values.
Then repeat this with the next element until the array is sorted.
The way that Insertion Sort works is building up the sort by gradually creating a larger left half which is alwais sorted.
We compare the second element with the one before it and swap if necessary.
Merge Sort it's a combination of three things - splitting up, merging and sorting!
The way that Merge Sort works is by decomposing an array into smaller arrays of 0 or 1 elements, then building up a newly sorted array.
Like Merge Sort, exploits the fact that array of 0 or 1 element are always sorted. The way that Quick Sort works is by selecting one element (called the pivot) and finding the index where the pivot should end up in the sorted array.