The code is based on the CADA framework that taken from https://github.com/mohamedr002/CADA
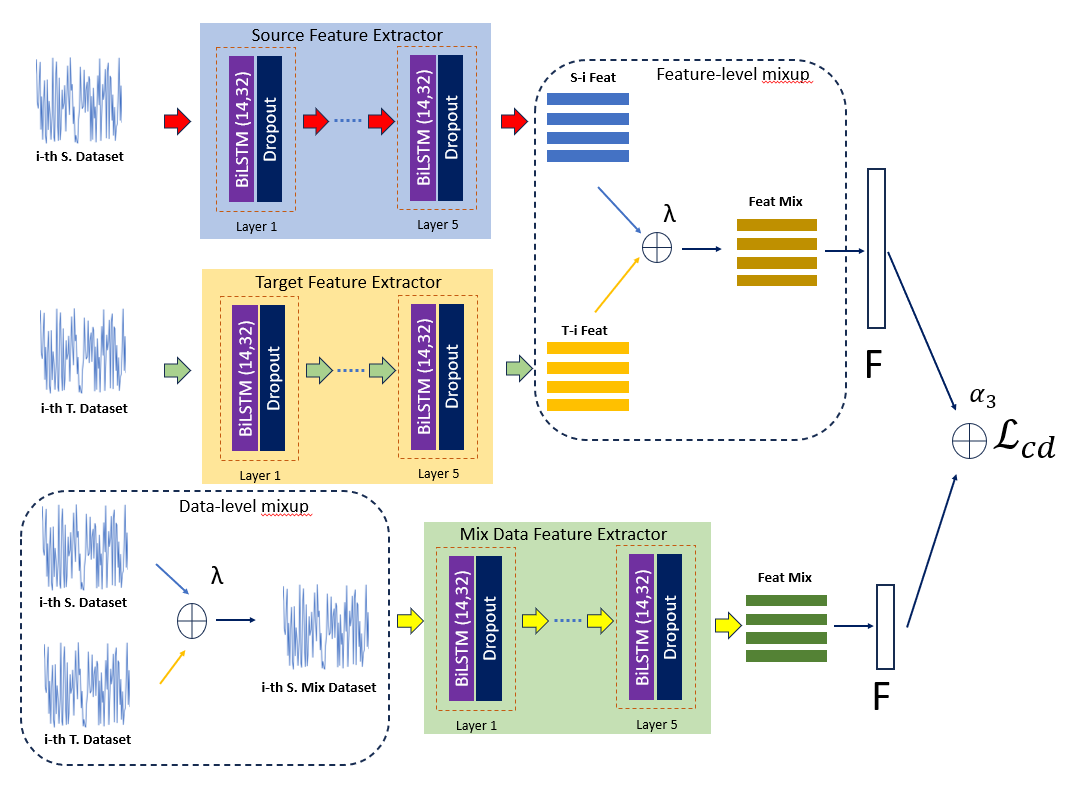
Remaining Useful Life (RUL) predictions play vital role for asset planning and maintenance leading to many benefits to industries such as reduced downtime, low maintenance costs, etc. Although various efforts have been devoted to study this topic, most existing works are restricted for i.i.d conditions assuming the same condition of the training phase and the deployment phase. This paper proposes a solution to this problem where a mix-up domain adaptation (MDAN) is put forward. The mix-up domain adaptation procedure encompasses a three-staged mechanism where the mix-up strategy is not only performed to regularize the source and target domains but also applied to establish an intermediate mix-up domain where the source and target domains are aligned. The self-supervised learning strategy is implemented to prevent the supervision collapse problem. Rigorous evaluations have been performed where MDAN is compared to recently published works for dynamic RUL predictions. MDAN outperforms its counterparts with substantial margins in 12 out of 12 cases.- Python3.8
- Pytorch==1.7
- Numpy
- Sklearn
- Pandas
- mat4py (for Fault diagnosis preprocessing)
We used NASA turbofan engines dataset
- run_the data/data_preprocessing.py to apply the preprocessings.
- Output the data form each domain in tuple format train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y
- Put the data in the data folder
- run python main_pretrain_source.py
- run python main_pretrain_intermediate.py
- run python main_pretrain_target.py