Automate the retraining of cascade classifiers with OpenCV by providing:
- a simple annotation tool for image/video capture and save
- generation of additional positive images from existing positives and negatives
- retraining of OpenCV Cascade classifiers using HAAR, LBP features

.
├── annotate.py -> image/video annotation tool
├── clean.sh -> clean all files directory for a new training
├── data -> cascade classifier output directory
├── genpos -> directory will contain the additional positives generated from the existing ones
├── genpos.sh -> generate additional positives from the existing ones
├── info -> images displayed in the readme file
├── LICENSE
├── neg -> holds the negative images for training
├── pos -> holds the positive images for training
├── prepare_data.py -> generate the dat files needed for OpenCV cascade tool
├── raw -> directory to store annotated images
├── README.md
├── test_cascade.py -> simple tools to test cascade classifier
└── train.sh -> start the training process
The scrips are relying on the built-in tools of OpenCV, therefore, to work OpenCV must be installed first installed.
sudo apt-get install python-opencv
Test existence of the OpenCV cascade trainer tools, type in the terminal window:
opencv_[TAB]
The following list should appear:
opencv_annotation opencv_traincascade opencv_visualisation
opencv_createsamples opencv_version
If we have the screen above, we are settled.
Cascade is very sensitive to the training data, therefore by collecting the negative samples, makes sure that no object which follows to be detected is contained. Negatives can be collected from the internet, the format shall be *.jpg, size does not matter.
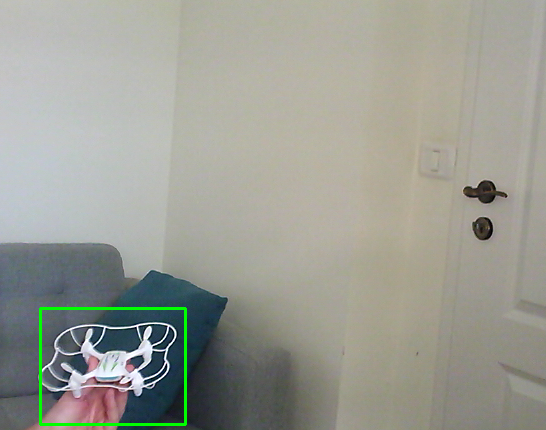
Collecting positive samples can happen using the annotation tool. Captures will be saved in the "raw" directory
python3 annotate.py --help
usage: annotate.py [-h] [-cam CAM] [-vid VID]
Simple annotation tool Use "a" to start to annotate, ENTER to return
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cam CAM Camera index
-vid VID Video file
Usually, there are needed about ~300 positive images and 1000-1200 negatives for reasonable training with less false positives.
The train.sh script does the 'dirty work'. There are many hyperparameters to set, which can influence the classification accuracy but training time too.
# Number of training stages
nrStages=20
# detection types [HAAR,LBP]
fn=HAAR
# object size, width, height
imgw=30
imgh=21
Usually, a well-trained cascade will reach 20 stages of the training. HAAR is slower than LBP, but more accurate. The image size by default is (24,24), here is settled for rectangle objects. Changing these parameters will have a high impact on training time.
In case everything went well, the training will start...
===== TRAINING 0-stage =====
<BEGIN
POS count : consumed 13 : 13
NEG count : acceptanceRatio 13 : 1
Precalculation time: 0
+----+---------+---------+
| N | HR | FA |
+----+---------+---------+
| 1| 1| 1|
+----+---------+---------+
| 2| 1| 0|
+----+---------+---------+
END>
Training until now has taken 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 0 seconds.
After the training has finished (i.e. max number of stages reached), a 'cascade.xml' fill will be created automatically in the 'data' folder.
After the 'cascade.xml' file was created, testing follows. Use the below provided utility for fast feedback.
python3 test_cascade.py --help
usage: test_cascade.py [-h] [-cam CAM] [-n N] [-s S]
Cascade tester. Defaults: -cam 0 -n 0 -s 1.1
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-cam CAM Camera ID
-n N Number of neighbors for detections
-s S Scale factor
If there appears a lot of random detections (false positives):
- try to adjust the classifier hyperparameters in 'test_cascade.py' file
python3 test_cascade.py -n 2 -s 1.2
- increase the number of positive/negative samples, use 'clean.sh' to clear the intermediate files and retrain the cascade classifier till the results are acceptable.
https://docs.opencv.org/2.4/doc/user_guide/ug_traincascade.html
/Enjoy.