Cultural Algorithms optimization framework for mixed integer, dynamic optimization problems. This method uses an ensmble of search strategies. The dynamic balance between the strategies is maintained by a game-theoretic heuristic.
-
Install Visual Studio (VS) 2019 (or later)
-
You can get the free community edition from here: https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/vs/community/
-
During setup, select support for F# language and .Net Core. The Visual Studio setup utility has 'Workloads' that bundle commonly used features. Select appropriate boxes as shown below to get F# and .Net core installed:
-
After VS is installed, open the 'solution' file CALib.sln with Visual Studio
-
In the 'Solution Explorer' window right click on the root of the tree and select "Restore NuGet Packages" as shown below:
- After the package load is complete, compile solution to check configuration validity
A sample for Rastrigin function is given Sample.fsx.
#load "SetupEnv.fsx"
open CA
let n = 5.
let A = 10.
let twoPi = 2. * System.Math.PI
let An = n * A
//objective function to be minimized
let rastrigin (xs:float[]) =
let sum = xs |> Array.map(fun x -> x*x - A*cos(twoPi * x)) |> Array.sum
An + sum
//define parameters (and associated ranges) that will be searched for optimality
let parms = [|for _ in 1 .. int n -> F(4.,-5.12,5.12) |]
//Note: 'F' is for float parameters and 'I' (not shown) for integer parameters
//initialize
let mutable step = CALib.API.initCA(parms, rastrigin, Minimize)
//step through till termination criteria is met
//here it is the number of generations (steps)
//you can define your own
for i in 0 .. 15000 do
step <- CALib.API.Step step
step.Best.[0].MParms //best solution parameter values
step.Best.[0].MFitness //best solution fitness value
//rastrigin [|for _ in 1 .. int n -> 0.0|] //true solution
//Note: A globally optimum solution is not guaranteed in evolutionary optimization methods. Usually such methods find good approximate solutionsOpen "ConesWorldVisualization.fsx" script in editor and select all text and hit Alt-Enter to run script
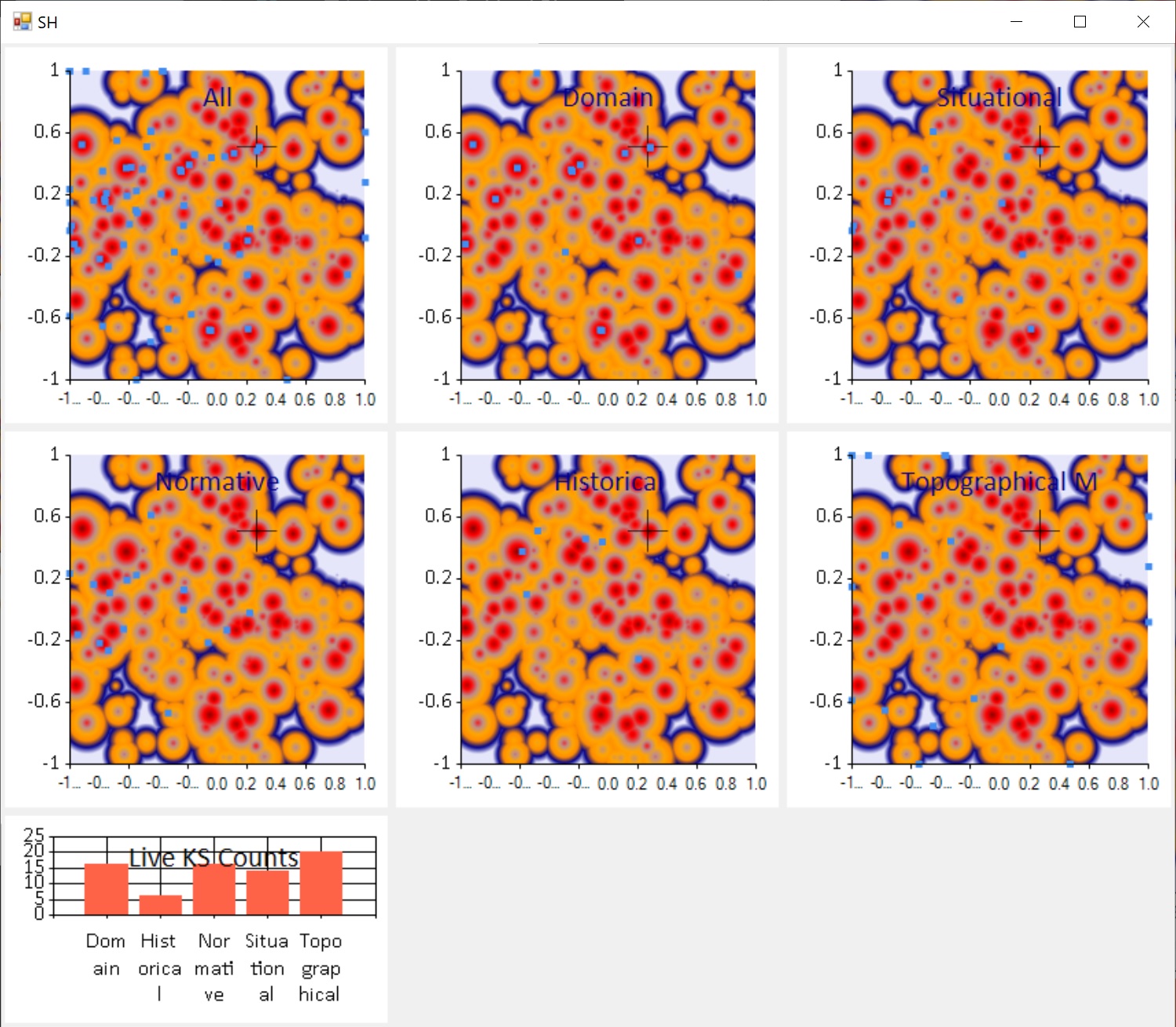
The script should open with animated windows that look like the image below. There are 1000 cones (i.e. 1000 local optima) in each 'landscape'. Periodically the landscape changes, i.e. this is a dynamic optimization problem where the solution is not static over time.
Start with https://fsharp.org/ to access the learning resources available for the F# language
The solution has three projects:
-
CALib - this can be used in two ways:
-
Compiled to a DLL and linked with a .Net application to solve optimization problems
-
Interactively with F# interactive (.fsx) script files, for research and experimentation purposes
-
-
CaLibCore - a version of CALib that runs on Linux (with .Net Core). Its main purpose is to conduct experiments on the Wayne State grid computing environment
-
CAOpt - is intended for runtime use. It has minimal dependencies and is intended to be deployed as a NuGet package