Below you'll find the instructions to release a knative.dev repository.
Schedule has the roster for each Knative release.
We release the components of Knative every 6 weeks. All of these components must be moved to the latest "release" of all shared dependencies prior to each release.
Check to make sure you already are in the "Knative Release Leads" team in
https://github.com/knative/community/blob/main/peribolos/knative.yaml and
https://github.com/knative/community/blob/main/peribolos/knative-sandbox.yaml
. If not, send a PR like
this one to grant yourself some
super power. Ensure to run /hack/update-codegen.sh to add yourself to the owner
files as well, as part of the PR.
Ask someone from the TOC to create a release-# Slack channel that will be
used to help manage this release.
Update the defaults in knative-releasability.yaml to this release by creating a PR. Example PR.
These changes will be propagated to the rest of Knative in the next round of workflow syncs. Check to ensure that it has indeed propagated and if not the sync will have to manually triggered.
Announce on #general that pkg will be cut in a week.
The supporting repos are the base repos where we have common code and common scripts. For these repos (except hack), we follow the same release process as explained in release a repository, but no prow job is executed, hence no git tag and Github release are produced.
NOTE: The supporting repos must be released in the correct order, so you need to check if the dependencies should be updated after each repo release.
First repo that needs to be released is hack. As mentioned, hack is special because it has no dependencies and hence there's no releasability checks, just ensure there are no outstanding PRs and create a release branch.
After hack release branch has been cut, follow the release a repository guide for the following repos skipping the prow job part:
| Repo | Releasability |
|---|---|
| knative.dev/pkg |
After pkg repo has their release branch cut, follow the release a repository guide for the following repos skipping the prow job part:
| Repo | Releasability |
|---|---|
| knative.dev/networking | |
| knative.dev/caching | |
| knative.dev/reconciler-test |
After reconciler-test repo has been cut, follow the release a repository guide for the following repos skipping the prow job part:
| Repo | Releasability |
|---|---|
| knative.dev/control-protocol |
Automation will propagate these updates to all the downstream repos in the next
few cycles. The goal is to have the first wave of repo releases (serving,
eventing, etc) to become "releasable" by the end of the week.
This is signaled via the Slack report of releasability posted to the release-#
channel every morning (5am PST, M-F).
Announce on #general that the release will be cut in a week and that additional caution should be used when merging big changes.
Check the status of the nightly builds for each repo. If they are failing, reach out the respective WG leads to investigate.
Make a new HackMD release notes document. last release notes document, empty it out and send it to the WG leads of the respective project (serving or eventing) to fill in. Coordinate with both serving and eventing leads.
Each repo has a Release Notes GitHub Action workflow. This can be used to
generate the starting point for the release notes. See an example in
Eventing.
The default starting and ending SHAs will work if running out of the main
branch, or you can determine the correct starting and ending SHAs for the script
to run.
Confirm with the respective WG leads that the release is imminent and obtain green light.
Check the status of the nightly builds for each repo. If they are failing, reach out the respective WG leads to investigate.
Follow the release a repository instructions for each repo. Wait for release automation to kick in (runs on a 2 hour interval). Once the release automation passed, it will create a release tag in the repository. Enhance the respective tags with the collected release-notes using the GitHub UI.
NOTE: The release day does not mean one has to release everything. The pipeline outlined below will take time to complete and it is ok for the release to take days. The day of the release marks the beginning of this process.
In general the release dependency order is something like the following (as of
v0.20). Note: buoy check will fail if the dependencies are not yet ready.
First:
After eventing:
| Repo | Release | Releasability | Nightly |
|---|---|---|---|
| knative.dev/eventing-ceph |  |
||
| knative.dev/eventing-kogito |  |
||
| knative.dev/eventing-natss |  |
||
| knative.dev/eventing-rabbitmq |  |
||
| knative.dev/sample-source |  |
After both eventing and serving:
| Repo | Release | Releasability | Nightly |
|---|---|---|---|
| knative.dev/client |  |
||
| knative.dev/eventing-kafka |  |
||
| knative.dev/eventing-redis |  |
||
| knative.dev/eventing-github |  |
||
| knative.dev/eventing-gitlab |  |
Lastly:
We have a few repos inside of Knative that are not handled in the standard process at the moment. They might have additional dependencies or depend on the releases existing. Skip these. Special cases are:
| Repo | Release | Releasability | Nightly |
|---|---|---|---|
| knative.dev/operator |  |
||
| knative.dev/docs | N/A | N/A | N/A |
After the client release, the Homebrew tap needs to be updated with the new release:
- Copy
kn.rbto thekn@${PREV_RELEASE}.rbwith$PREV_RELEASEto be replace with the latest release (e.g.0.19). - In
kn@${PREV_RELEASE}.rbreplaceclass Knwithclass KnAT${PREV_RELEASE_DIGITS}, e.gclass KnAT019for an previous release0.19. - In
kn.rb- Replace the old version number in
vwith the released version (e.g.v = "v0.20.0") - Replace the
sha256checksums with the values from the client release page. The checksums have been released, too (e.g. checksums.txt)
- Replace the old version number in
Create a PR and merge the changes. Prow is not enabled for the homebrew repo, so the merge needs to be performed manually.
Similar to the client repo, the client plugin's Homebrew repo needs to be updated for the the plugins supported after their repos have successfully created a release.
Currently the following plugins are available with their own formulas:
- kn-plugin-admin is managed via the
admin.rbformula - kn-plugin-source-kafka is managed via
source-kafka.rbformula - kn-plugin-source-kamelet is managed via
source-kamelet.rbformula - kn-plugin-quickstart is managed via
quickstart.rbformula - kn-plugin-event is managed via
event.rbformula
Releasing a repository includes:
- Aligning the
knative.devdependencies to the other release versions on main (except hack, which has no dependencies) - For some repositories some additional validation need to be performed before a release can be cut. Check special repository checks for which repository extra steps needs to be performed.
- Creating a new branch starting from main for the release (e.g.
release-0.20) - Execute the job on Prow that builds the code from the release branch, tags the revision, publishes the images, publishes the yaml artifacts and generates the Github release.
Most of the above steps are automated, although in some situations it might be necessary to perform some of them manually.
Before beginning, check if the repository is in a good shape and the builds pass consistently. This is required because the Prow job that builds the release artifacts will execute all the various tests (build, unit, e2e) and, if something goes wrong, you will probably need to restart this process from the beginning.
For any problems in a specific repo, get in touch with the relevant WG leads to fix them.
In order to align the knative.dev dependencies, knobots will perform PRs like
this for each repo, executing
the command ./hack/update-deps.sh --upgrade --release 0.20 and committing all
the content.
- If no dependency bump PR is available, manually trigger the generation of these PRs starting the
Knobots Auto Update Deps
and wait for the PR to pop in the repo you need. Note you have to change the
field
If true, send update PRs even for deps changes that don't change vendor. Use this only for releases.to true, because in some cases there no code changes in the vendor. - Check the
go.modto ensure hashes point to commit hash at the head of the release branch of the dependency repo- For the support repos (
hack,pkg, etc) you should see the dependency version pointing at a revision which should match theHEADof the release branch. E.g.knative.dev/pkg v0.0.0-20210112143930-acbf2af596cfpoints at the revisionacbf2af596cf, which is theHEADof therelease-0.20branch inpkgrepo. - For the release repos, you should see the dependency version pointing at the
version tag. E.g.
knative.dev/eventing v0.20.0points at the tagv0.20.0in theeventingrepo.
- For the support repos (
For some repositories some extra manual validation and updates need to be performed before the release branch is cut:
- Update the version numbers of Serving and Eventing in test/presubmit-integration-tests-latest-release.sh so that the integration test is already running against the just released serving and eventing versions.
- (optional) Check that CHANGELOG.adoc contains a section about the release, i.e. the top-level "(Unreleased)" section should be changed to point to the upcoming release version and number. It's not critical if the changelog is aligned after the release in retrospective.
If the validation fails, the fix should be trivial and could be either performed by the release leads or the client team.
- Update the version numbers of Serving / Kourier / Eventing in pkg/install/install.go so that the plugin will use the just-released versions.
At this point, you can proceed with the releasability check. A releasability check is executed periodically and posts the result on the Slack release channel and it fails if the dependencies are not properly aligned. If you don't want to wait, you can manually execute the Releasability workflow.
If the releasability reports NO-GO, probably there is some deps misalignment, hence you need to go back to the previous step and check the dependencies, otherwise, you're ready to proceed.
If there are changes, then it's NO-GO, otherwise it's GO.
NOTE: The releasability check will not work on dot releases and there is a potential for false positives.
Now you're ready to create the release-x.y branch. This can be done by using
the GitHub UI:
-
Click on the branch selection box at the top level page of the repository.
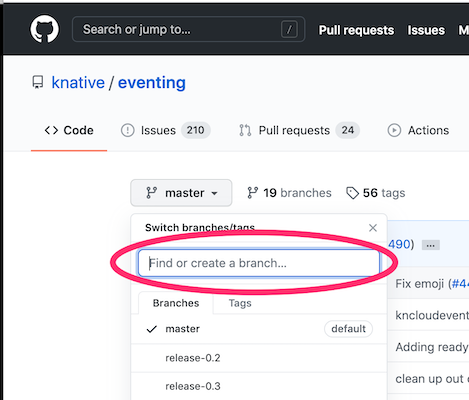
-
Search for the correct
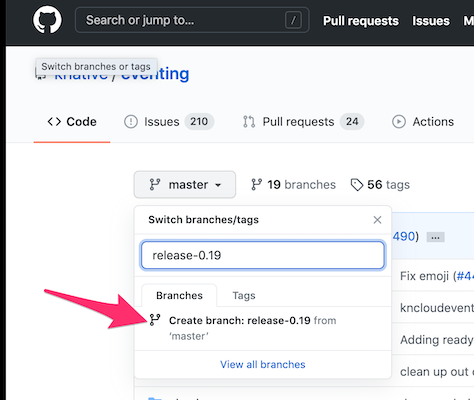
release-x.ybranch name for the release. -
Click "Create branch: release-x.y".
Otherwise, you can do it by hand on your local machine.
After a release-x.y branch exists, a 4 hourly prow job will build the code
from the release branch, tag the revision, publish the images, publish the yaml
artifacts and generate the Github release. Update the description of the release
with the release notes collected.
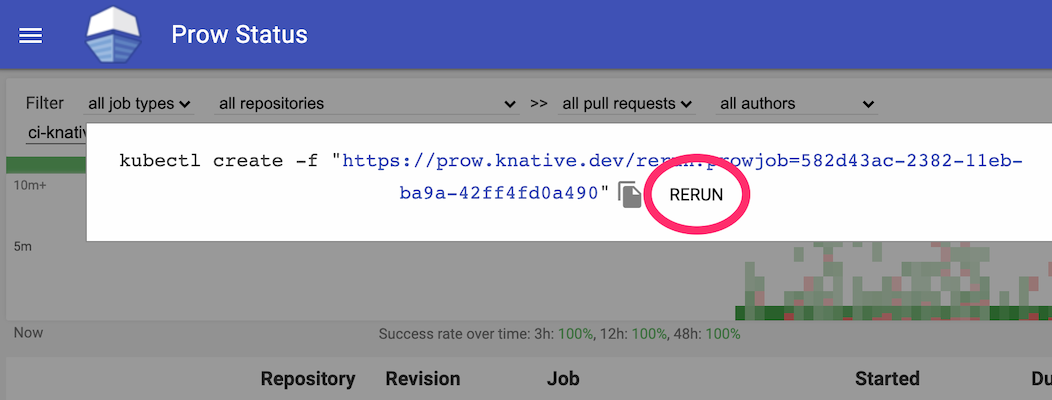
You can manually trigger the release:
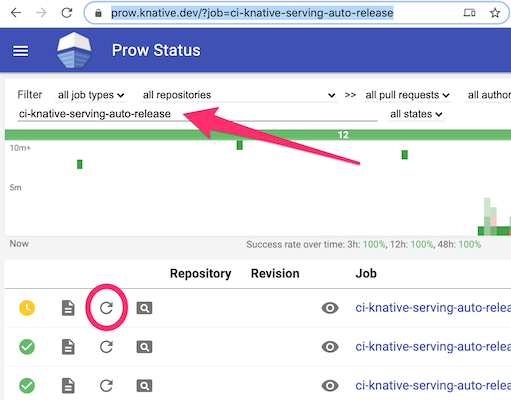
-
Navigate to https://prow.knative.dev/
-
Search for the
*-auto-releasejob for the repository. -
Rerun the auto-release job.
The automation used to cut the actual releases is the very same as the automation used to cut nightly releases. Verify via testgrid that all relevant nightly releases are passing. If they are not coordinate with the relevant WG leads to fix them.
In case you cut a branch before it was ready (e.g. some deps misalignment, a failing test, etc), then follow the steps below:
- Mark the broken release as a
pre-release - Create a dot release
- Repeat the steps for a release for the new dot release