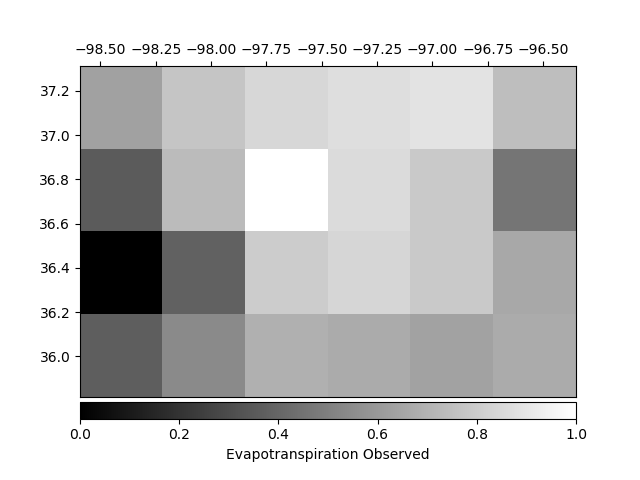
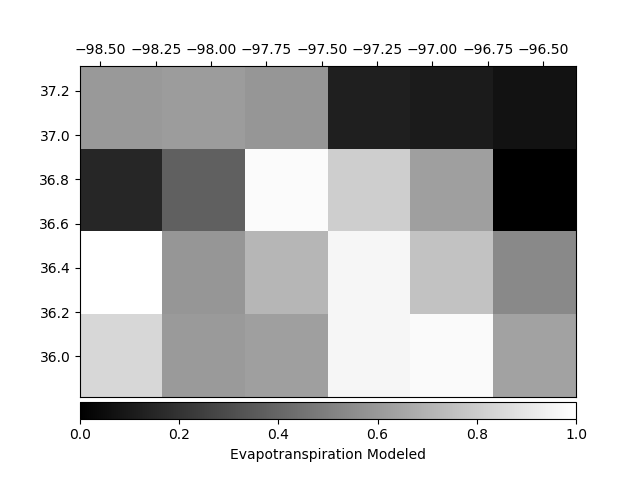
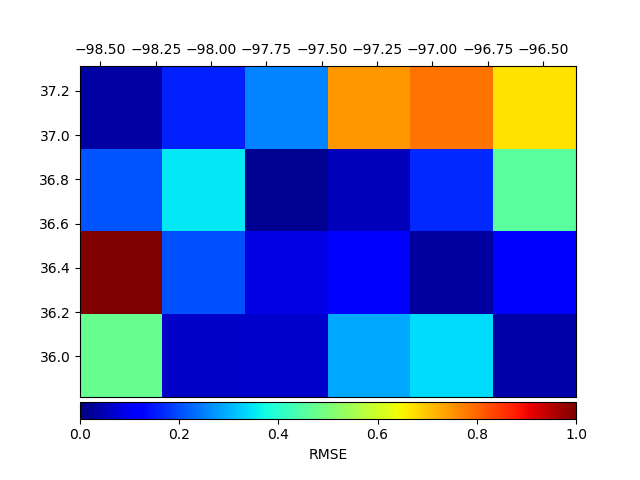
Structural similarity index (SSIM) and mean squared error (MSE)
SSIM is a method that attempts to model the perceived change in the structural information of the image (Wang et al., 2004). The SSIM can be interpreted as a measure of quality of one of the images that are compared, while the other image is considered of perfect quality. The index equation is as follows:
where
SSIM: 0.156
RMSE: 0.389
Dependences:
python - Scikit-image
python - Pandas
python - NumPy
python - Matplolib
python - Gdal
python - Scikit-learn
Page source:
http://scikit-image.org/docs/dev/auto_examples/transform/plot_ssim.html