DISCLAIMER: PYQT IS AVAILABLE THROUGH THE GPL LICENSE. THE MIT LICENSE ONLY APPLIES TO NON-PYQT CODE
Python implementation of the programming assignment from the chapter "Multimedia Networking" (chapter 7 in the 6th edition) of the book "Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach" by Jim Kurose.
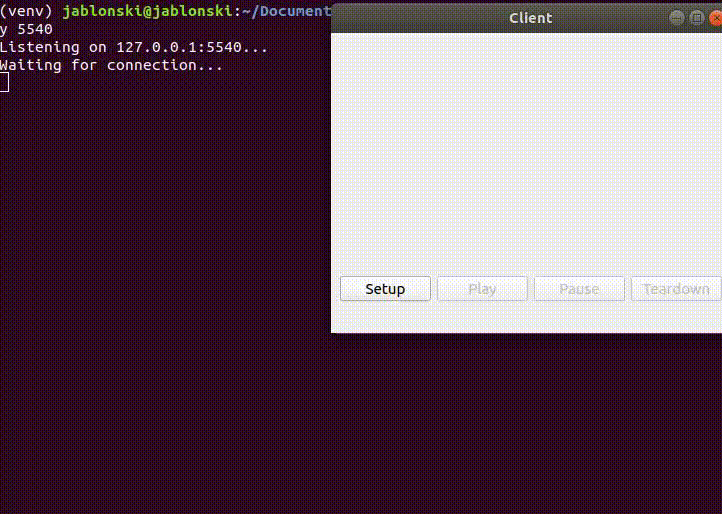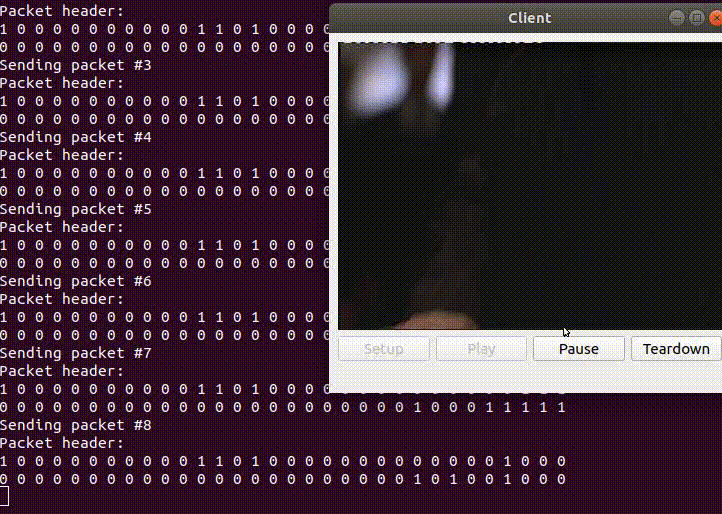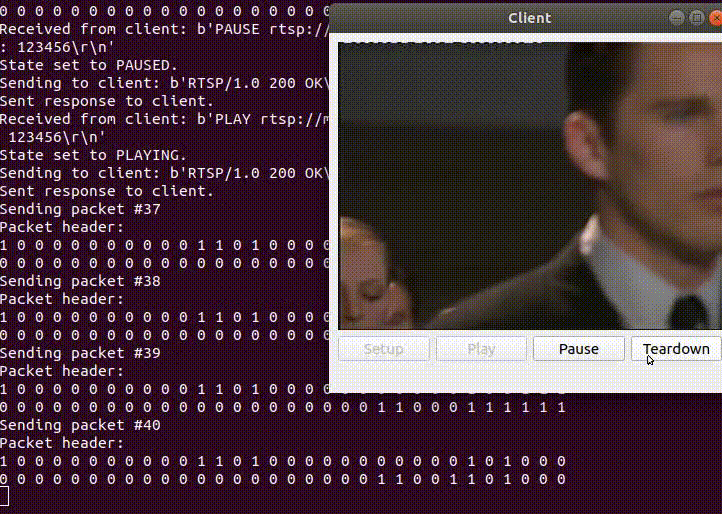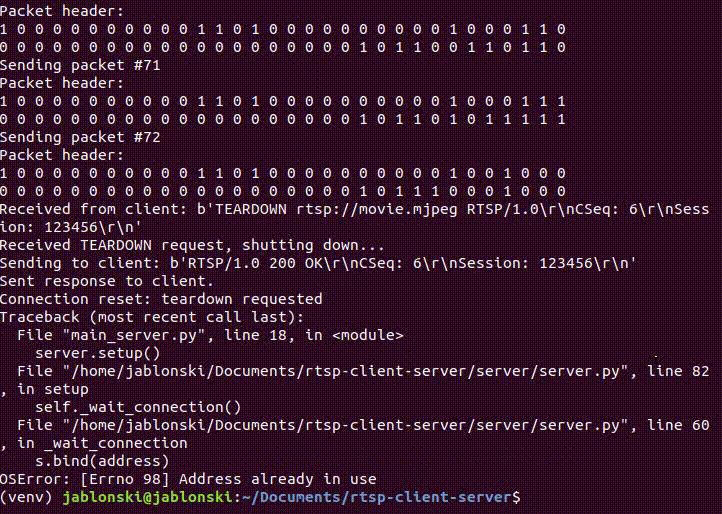
Implements basic RTSP and RTP streaming functionality using the standard Python 3 library, plus PyQt5 and Pillow for stuff related to GUI. Further info available in the assignment guide (from the 3rd edition, newer versions of the book might change the assignment slightly). Error handling is very minimal, reopening the server and client is required to run another session.
Clone the repository with git clone https://github.com/gabrieljablonski/rtsp-rtp-stream.
Having python>=3.6 installed, create a virtual environment by running python -m venv venv inside the cloned folder.
Activate the virtual environment (source venv/bin/activate on Linux, .\venv\Scripts\activate on Windows).
Install the requirements with python -m pip install -r requirements.txt.
Go to the sources folder with cd src/ (video stream class assumes mjpeg file is in working directory).
Server should be run first with
python main_server.py <port>
In which port is the port number for the RTSP socket to listen on.
Client can then be run with
python main_client.py <file name> <host address> <host port> <RTP port>
in which file name is the name for the file to be sent via RTP (movie.mjpeg is the available sample), host address is the server address (localhost if running on same machine), host port is the port selected when running the server, RTP port is the port for receiving the video via RTP.
Since you're probably running each instance on separate terminals, remember to activate the venv on both.
Suggested configs are:
python main_server.py 5540
python main_client.py movie.mjpeg localhost 5540 5541