This is a step-by-step guide on how to set up a GitOps workflow for OpenFaaS with Weave Flux.
GitOps is a way to do Continuous Delivery, it works by using Git as a source of truth for
declarative infrastructure and workloads. In practice this means using git push instead of kubectl create/apply or helm install/upgrade.
OpenFaaS (Functions as a Service) is Serverless Functions Made Simple for Docker and Kubernetes. With OpenFaaS you can package any container or binary as a serverless function - from Node.js to Golang to C# on Linux or Windows.
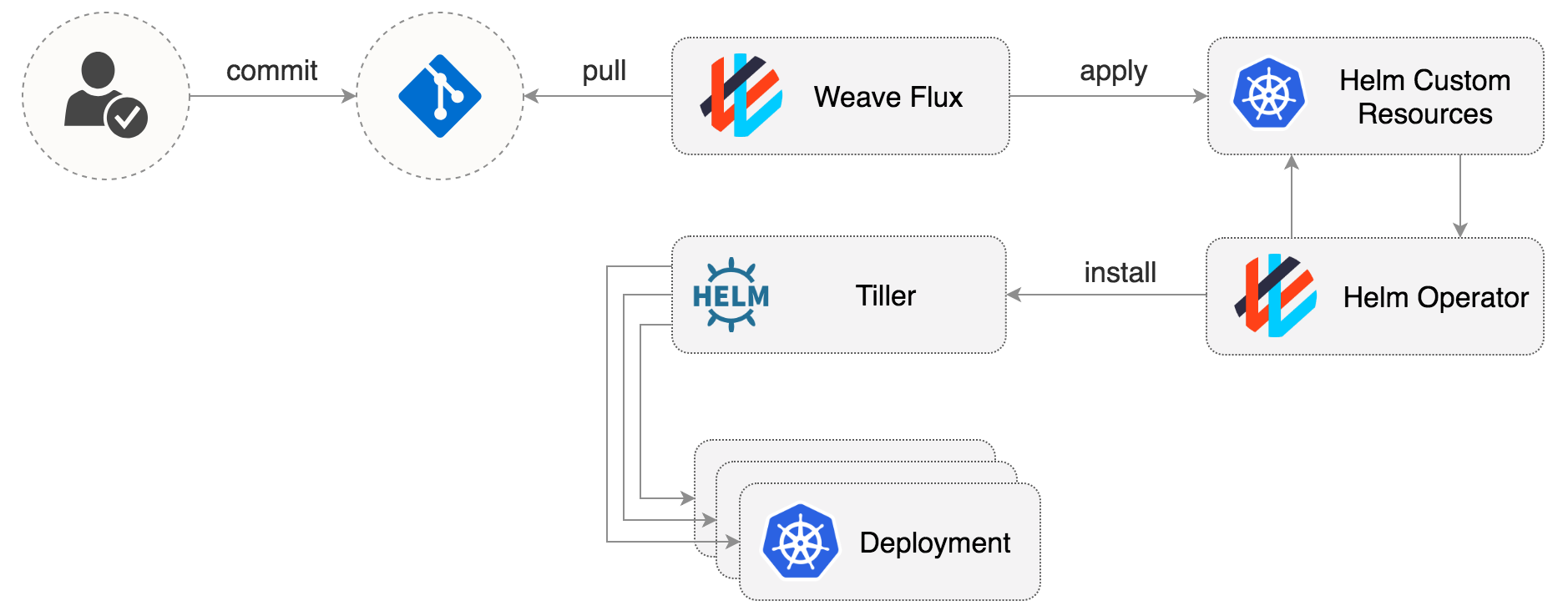
Weave Flux is a GitOps Operator for Kubernetes that keeps your cluster state is sync with a Git repository. Because Flux is pull based and also runs inside Kubernetes, you don't have to expose the cluster credentials outside your production environment. Once you enable Flux on your cluster any changes in your production environment are done via pull request with rollback and audit logs provided by Git.
You can define the desired state of your cluster with Helm charts, Kubernetes deployments, network policies and even custom resources like OpenFaaS functions or sealed secrets. Weave Flux implements a control loop that continuously applies the desired state to your cluster, offering protection against harmful actions like deployments deletion or network policies altering.
Add the Weave Flux chart repo:
helm repo add weaveworks https://weaveworks.github.io/fluxInstall Weave Flux and its Helm Operator by specifying your fork URL
(replace stefanprodan with your GitHub username):
helm install --name flux \
--set helmOperator.create=true \
--set git.url=git@github.com:stefanprodan/openfaas-flux \
--set git.chartsPath=charts \
--namespace flux \
weaveworks/fluxConnect Weave Flux to Weave Cloud using a service token:
helm install --name flux \
--set token=YOUR_WEAVE_CLOUD_SERVICE_TOKEN \
--set helmOperator.create=true \
--set git.url=git@github.com:stefanprodan/openfaas-flux \
--set git.chartsPath=charts \
--namespace flux \
weaveworks/fluxNote: The Flux Helm Operator only works with Kubernetes 1.9 or newer.
At startup, Flux generates a SSH key and logs the public key. Find the SSH public key with:
kubectl -n flux logs deployment/flux | grep identity.pub In order to sync your cluster state with git you need to copy the public key and create a deploy key with write access on your GitHub repository.
Open GitHub and fork this repo, navigate to your fork, go to Settings > Deploy keys click on Add deploy key, check Allow write access, paste the Flux public key and click Add key.
After a couple of seconds Flux:
- creates the
openfaasandopenfaas-fnnamespaces - installs OpenFaaS Helm release
- creates the OpenFaaS functions
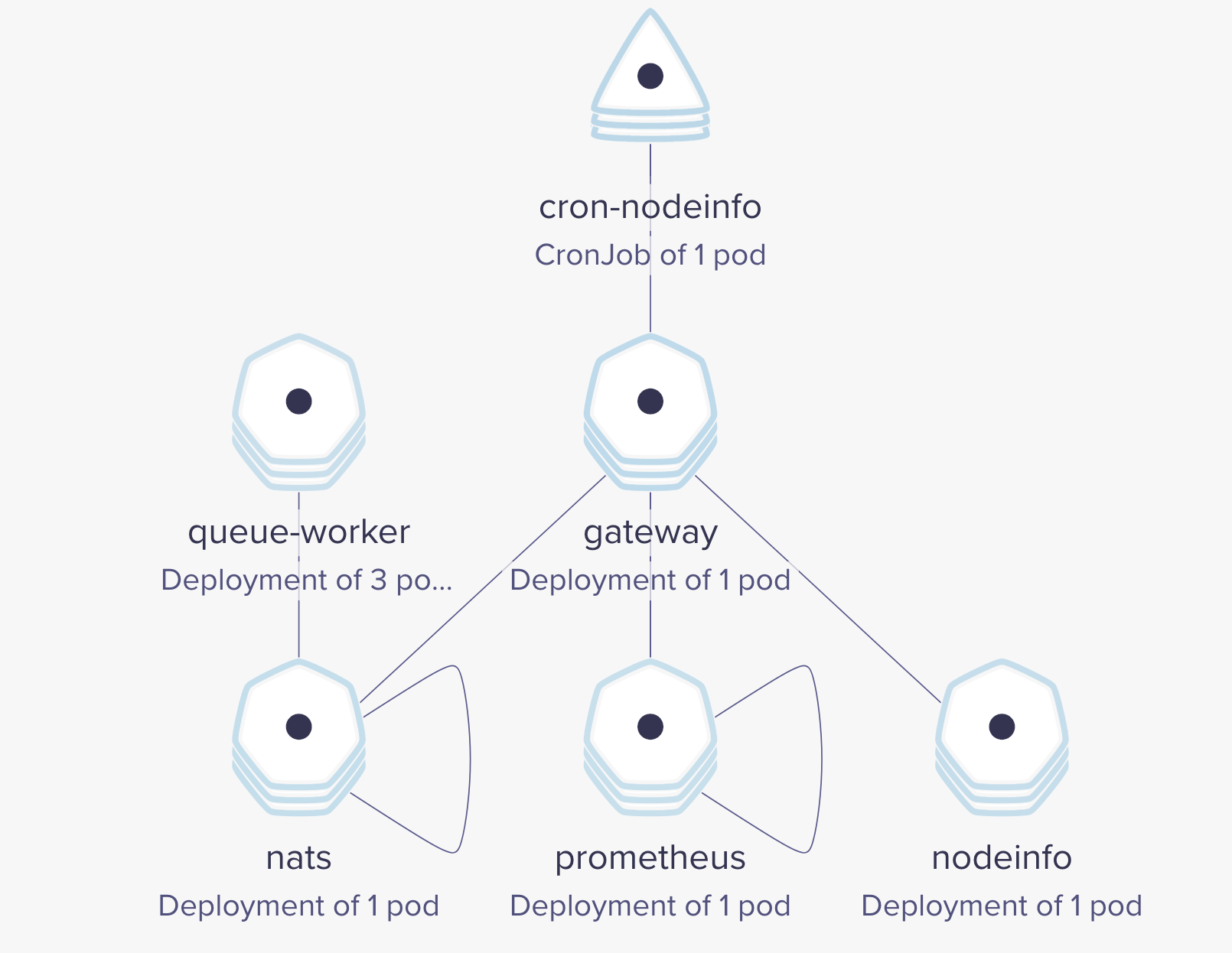
Check the OpenFaaS services deployment status:
kubectl -n openfaas get deployments
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
gateway 1 0 0 0 49s
nats 1 1 1 1 49s
prometheus 1 1 1 1 49s
queue-worker 3 3 3 3 49s
At this stage the gateway is not exposed outside the cluster and will enter a crash loop because it tries to mount the basic auth credentials from a secret that's not yet present on the cluster.
The Flux Helm operator provides an extension to Weave Flux that automates Helm Chart releases for it.
A Chart release is described through a Kubernetes custom resource named FluxHelmRelease.
The Flux daemon synchronizes these resources from git to the cluster,
and the Flux Helm operator makes sure Helm charts are released as specified in the resources.
OpenFaaS release definition:
apiVersion: helm.integrations.flux.weave.works/v1alpha2
kind: FluxHelmRelease
metadata:
name: openfaas
namespace: openfaas
labels:
chart: openfaas
spec:
chartGitPath: openfaas
releaseName: openfaas
values:
basic_auth:
enabled: true
gateway:
image: openfaas/gateway:0.8.5
replicas: 2
operator:
image: functions/openfaas-operator:0.8.0
queueWorker:
image: functions/queue-worker:0.4.4
replicas: 3
nats:
image: nats-streaming:0.6.0
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:v2.3.1Flux Helm release fields:
metadata.nameis mandatory and needs to follow k8s naming conventionsmetadata.namespaceis optional and determines where the release is createdmetadata.labels.chartis mandatory and should match the directory containing the chartspec.releaseNameis optional and if not provided the release name will be$namespace-$namespec.chartGitPathis the directory containing the chart, given relative to the charts pathspec.valuesare user customizations of default parameter values from the chart itself
The following Helm releases are part of this setup:
- openfaas (OpenFaaS Gateway, OpenFaaS K8s Operator, Prometheus, NATS, OpenFaaS Queue Worker)
- sealed-secrets (Bitnami SealedSecrets K8s Controller)
- contour (Heptio Contour Envoy based K8s Ingress Controller)
- cert-manager (Jetstack CertManager K8s Controller with Let's Encrypt support)
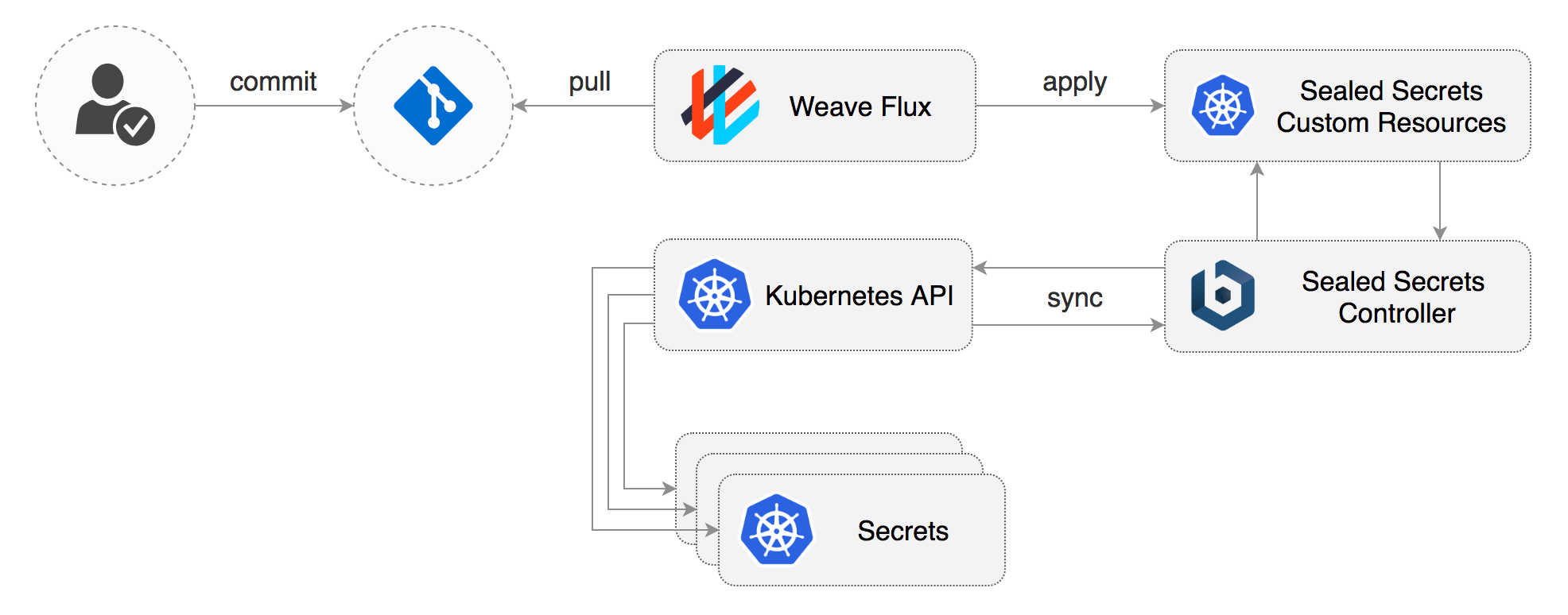
On the first Git sync, Flux deploys the Bitnami Sealed Secrets Controller. Sealed-secrets is a Kubernetes Custom Resource Definition Controller that allows you to store sensitive information in Git.
In order to encrypt secrets, install the kubeseal CLI:
release=$(curl --silent "https://api.github.com/repos/bitnami-labs/sealed-secrets/releases/latest" | sed -n 's/.*"tag_name": *"\([^"]*\)".*/\1/p')
GOOS=$(go env GOOS)
GOARCH=$(go env GOARCH)
wget https://github.com/bitnami/sealed-secrets/releases/download/$release/kubeseal-$GOOS-$GOARCH
sudo install -m 755 kubeseal-$GOOS-$GOARCH /usr/local/bin/kubesealNavigate to ./secrets dir and delete all files inside.
rm -rf secrets && mkdir secretsAt startup, the Sealed Secrets Controller generates a RSA key and logs the public key.
Using kubeseal you can save your public key as pub-cert.pem,
the public key can be safely stored in Git, and can be used to encrypt secrets offline:
kubeseal --fetch-cert \
--controller-namespace=flux \
--controller-name=sealed-secrets \
> secrets/pub-cert.pemNext let's create a secret with the basic auth credentials for the OpenFaaS Gateway.
Use kubectl to locally generate the basic-auth secret:
password=$(head -c 12 /dev/random | shasum| cut -d' ' -f1)
echo $password
kubectl -n openfaas create secret generic basic-auth \
--from-literal=basic-auth-user=admin \
--from-literal=basic-auth-password=$password \
--dry-run \
-o json > basic-auth.jsonEncrypt the secret with kubeseal and save it in the secrets dir:
kubeseal --format=yaml --cert=secrets/pub-cert.pem < basic-auth.json > secrets/basic-auth.yamlThis generates a custom resource of type SealedSecret that contains the encrypted credentials:
apiVersion: bitnami.com/v1alpha1
kind: SealedSecret
metadata:
name: basic-auth
namespace: openfaas
spec:
encryptedData:
basic-auth-password: AgAR5nzhX2TkJ.......
basic-auth-user: AgAQDO58WniIV3gTk.......Finally delete the basic-auth.json file and commit your changes:
rm basic-auth.json
git add . && git commit -m "Add OpenFaaS basic auth credentials" && git pushThe Flux daemon applies the sealed secret on your cluster. The Sealed Secrets Controller will then decrypt it into a Kubernetes secret.
Now that the OpenFaaS credentials are stored in the cluster you can access the Gateway UI
on your local machine at http://localhost:8080 with port forwarding:
kubectl -n openfaas port-forward deployment/gateway 8080:8080Inside the releases dir you can find a Helm release definition for Heptio Contour. Contour is a Kubernetes ingress controller powered by the Envoy proxy.
Find the Contour LoadBalancer pubic IP (depending on your cloud provider this can take several minutes):
public-ip=$(kubectl -n contour describe service contour | grep Ingress | awk '{ print $NF }')If you run Kubernetes on-prem or on bare-metal, you should change the Contour service type from LoadBalancer to NodePort to expose OpenFaaS on the internet.
In order to setup TLS with Let's Encrypt point your DNS to the Contour LoadBalancer IP.
Once the DNS is set, use Jetstack's cert-manager to request a TLS certificate for your domain from LE.
Create a cluster issuer definition in the certs dir,
replace EMAIL@DOMAIN.NAME with a valid email address:
apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: openfaas
namespace: cert-manager
spec:
acme:
email: EMAIL@DOMAIN.NAME
http01: {}
privateKeySecretRef:
name: openfaas-cert
server: https://acme-v01.api.letsencrypt.org/directoryAdd the ingress definition to releases/openfaas.yaml,
replace DOMAIN.NAME with your own domain:
apiVersion: helm.integrations.flux.weave.works/v1alpha2
kind: FluxHelmRelease
metadata:
name: openfaas
namespace: openfaas
labels:
chart: openfaas
spec:
chartGitPath: openfaas
releaseName: openfaas
values:
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "contour"
certmanager.k8s.io/cluster-issuer: "openfaas"
hosts:
- host: DOMAIN.NAME
serviceName: gateway
servicePort: 8080
path: /
tls:
- secretName: openfaas-cert
hosts:
- DOMAIN.NAMECommit and push your changes to Git:
git add . && git commit -m "Add OpenFaaS TLS ingress" && git pushAfter Flux applies the changes, you can check cert-manager logs and see if your certificate has been issued by letsencrypt.org:
kubectl -n cert-manager logs deployment/cert-manager cert-manager
sync.go:238] Preparing certificate with issuer
controller.go:152] clusterissuers controller: Finished processing work item "openfaas"
sync.go:248] Issuing certificate...
sync.go:269] Certificated issued successfully
controller.go:187] certificates controller: syncing item 'openfaas/openfaas-cert'
sync.go:200] Certificate scheduled for renewal in 1438 hoursVerify the LE cert using certinfo function:
curl -d "your-domain.name" https://your-domain.name/function/certinfo
Host 35.189.75.57
Port 443
Issuer Let's Encrypt Authority X3
CommonName openfaas.your-domain.name
NotBefore 2018-05-23 07:15:20 +0000 UTC
NotAfter 2018-08-21 07:15:20 +0000 UTC
SANs [openfaas.your-domain.name]
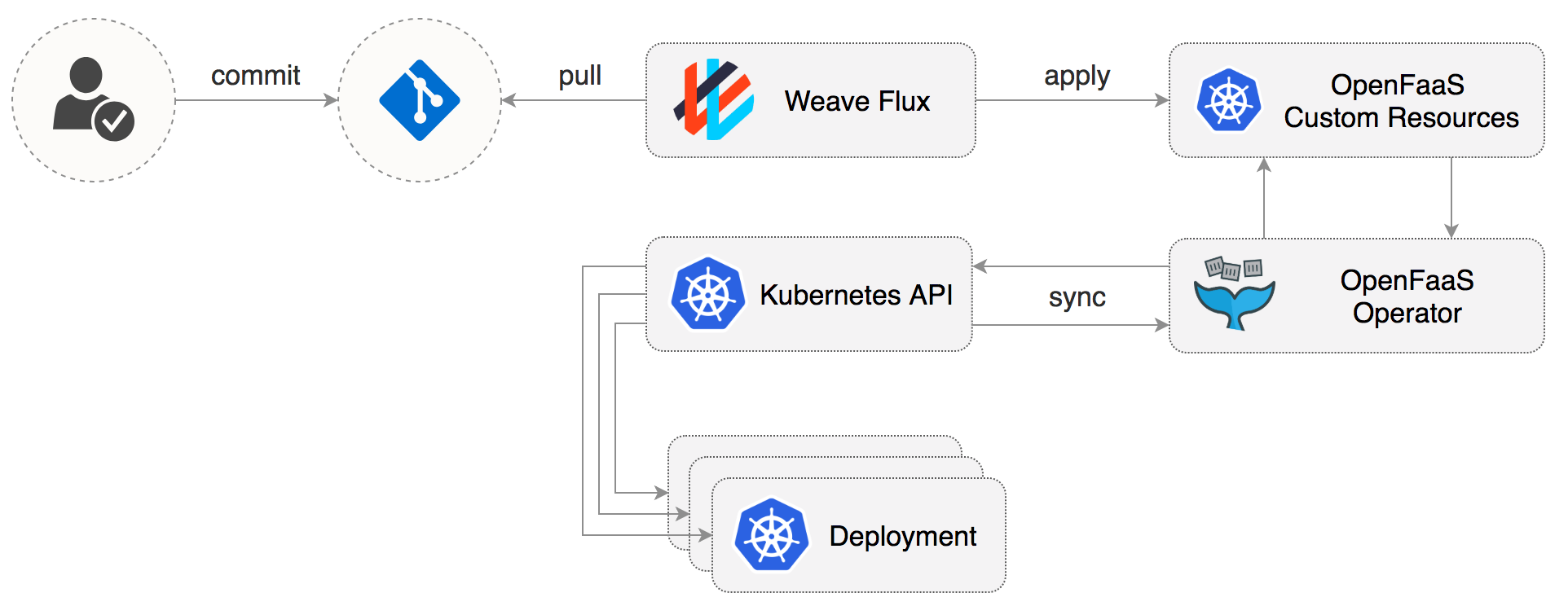
TimeRemaining 2 months from nowAn OpenFaaS function is described through a Kubernetes custom resource named function.
The Flux daemon synchronizes these resources from git to the cluster,
and the OpenFaaS Operator creates for each function a Kubernetes deployment and a ClusterIP service as
specified in the resources.
OpenFaaS function definition:
apiVersion: openfaas.com/v1alpha2
kind: Function
metadata:
name: sentimentanalysis
namespace: openfaas-fn
spec:
name: sentimentanalysis
image: functions/sentimentanalysis
environment:
output: "verbose"
limits:
cpu: "2000m"
memory: "512Mi"
requests:
cpu: "10m"
memory: "64Mi"Since sentiment analysis is a ML function you will probably want to auto-scale it based on resource usage. You can use the Kubernetes horizontal pod autoscaler to automatically scale a function based on the average CPU usage and memory consumption.
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: sentimentanalysis
namespace: openfaas-fn
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
kind: Deployment
name: sentimentanalysis
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
targetAverageUtilization: 50
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
targetAverageValue: 400MiLet's run a load test to validate that HPA works as expected:
go get -u github.com/rakyll/hey
hey -n 100000 -c 10 -q 1 -d "$(cat README.md)" http://localhost:8080/function/sentimentanalysisMonitor the autoscaler with:
kubectl -n openfaas-fn describe hpa
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal SuccessfulRescale 12m horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 1; reason: All metrics below target
Normal SuccessfulRescale 4m horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 4; reason: cpu resource utilization (percentage of request) above target
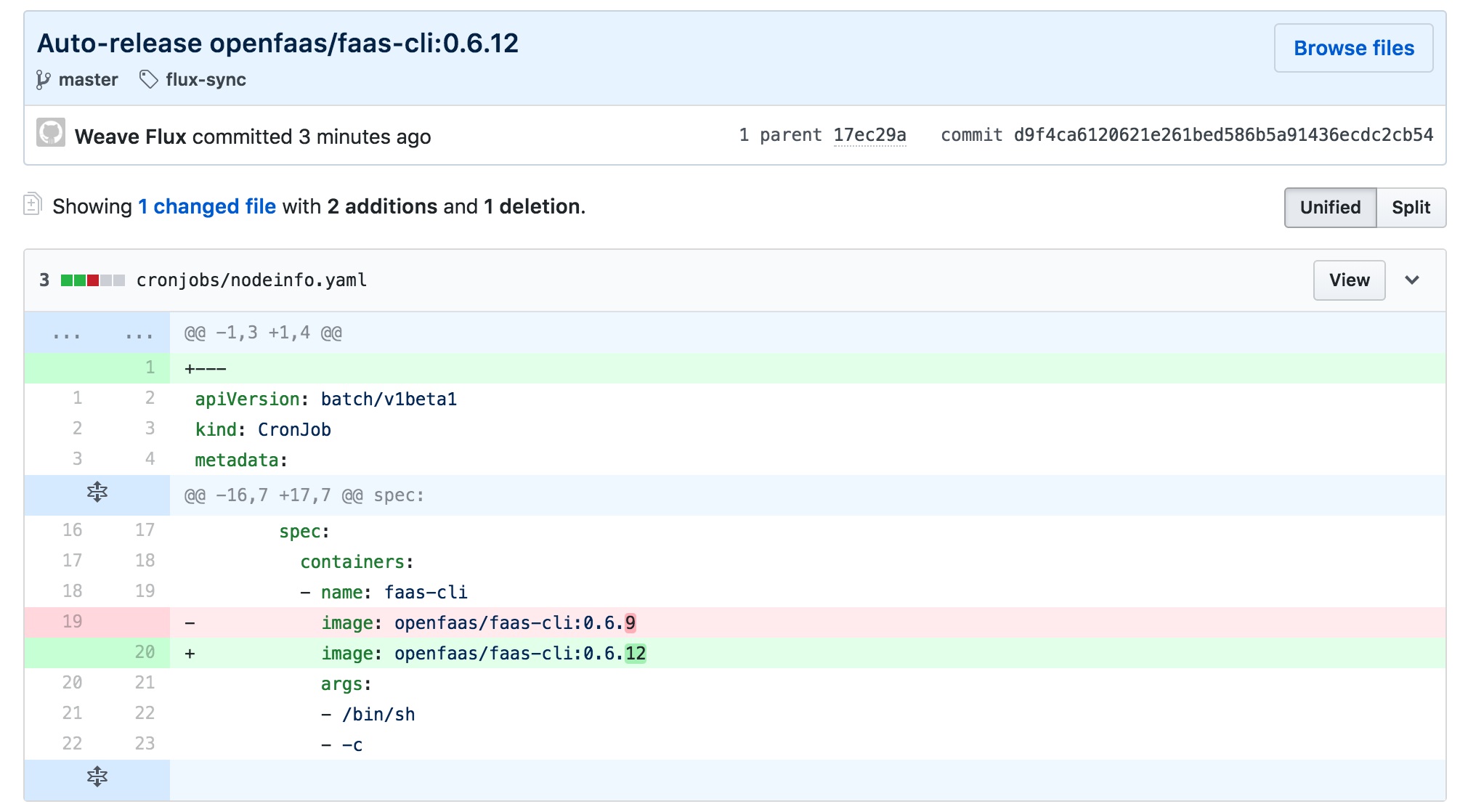
Normal SuccessfulRescale 1m horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 8; reason: cpu resource utilization (percentage of request) above targetRunning functions on a schedule can be done with Kubernetes ConJobs and the OpenFaaS CLI:
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: cron-nodeinfo
namespace: openfaas
annotations:
flux.weave.works/automated: "true"
spec:
schedule: "*/1 * * * *"
concurrencyPolicy: Forbid
successfulJobsHistoryLimit: 1
failedJobsHistoryLimit: 3
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: faas-cli
image: openfaas/faas-cli:0.6.9
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- echo "verbose" | ./faas-cli invoke nodeinfo -g http://gateway:8080
restartPolicy: OnFailureThe above cron job calls the nodeinfo function every minute using verbose as payload.
You can instruct Flux to update the cron job container image by adding the
flux.weave.works/automated annotation.
When a new tag is pushed to Docker Hub, Flux will change the cron job definition in the yaml file, will commit and push the change to your git repo and finally will apply the change on your cluster.
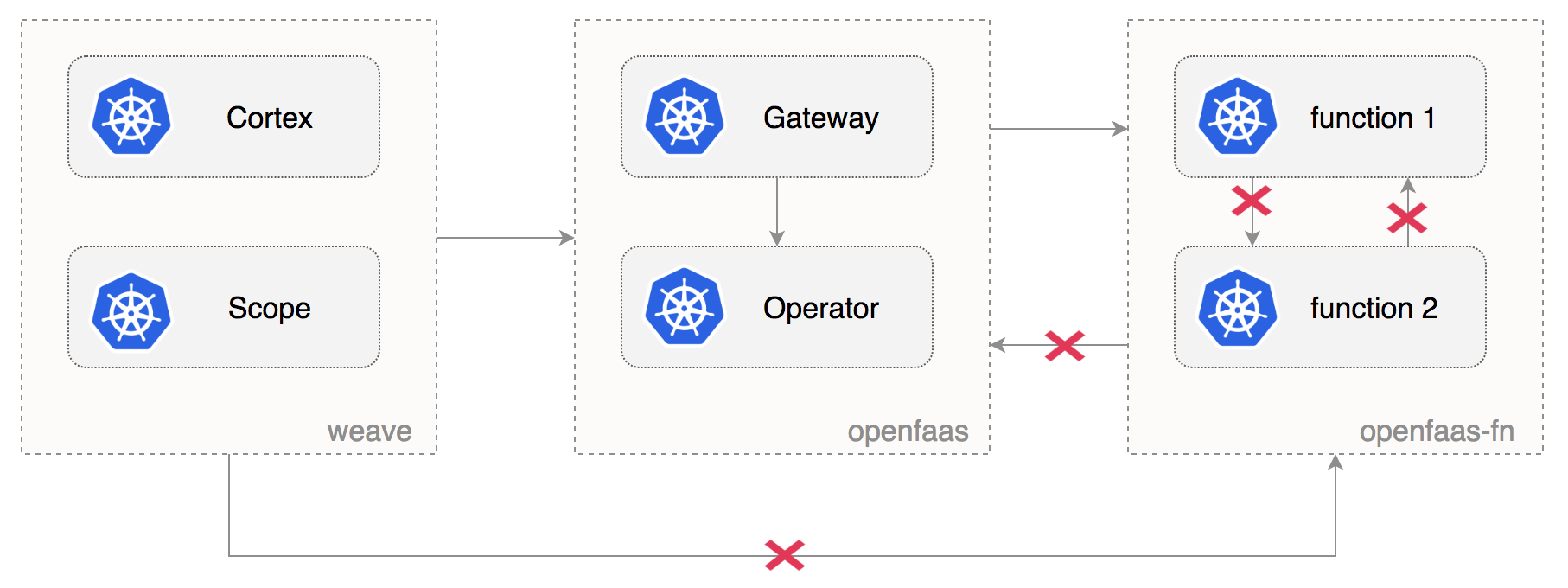
If you use a CNI like Weave Net or Calico that supports network policies you can enforce traffic rules for OpenFaaS
by placing the NetworkPolicy definitions inside the network-policies dir.
The Flux daemon will apply the policies on your cluster along with the namespaces labels.
Deny ingress access to functions except from namespaces with role: openfaas-system label:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: openfaas-fn
namespace: openfaas-fn
spec:
policyTypes:
- Ingress
podSelector: {}
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
role: openfaas-systemAllow OpenFaaS core services to reach the openfaas-fn namespace by applying the role: openfaas-system label:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: openfaas
labels:
role: openfaas-system
access: openfaas-systemDeny ingress access to OpenFaaS core services except from namespaces with access: openfaas-system label:
kind: NetworkPolicy
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: openfaas
namespace: openfaas
spec:
policyTypes:
- Ingress
podSelector: {}
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
access: openfaas-systemAllow Weave Cloud to scrape the OpenFaaS Gateway by applying the access: openfaas-system label to weave namespace:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: weave
labels:
access: openfaas-systemIn order to recover from a major disaster like a cluster melt down, all you need to to is create a new Kubernetes cluster, deploy Flux with Helm and update the SSH public key in the GitHub repo. Weave Flux will restore all workloads on the new cluster, the only manifests that will fail to apply are the sealed secrets since the private key used for decryption will have changed.
To prepare for disaster recovery you should backup the SealedSecrets private key with:
kubectl get secret -n flux sealed-secrets-key -o yaml --export > sealed-secrets-key.yamlTo restore from backup after a disaster, replace the newly-created secret and restart the sealed-secrets controller:
kubectl replace secret -n flux sealed-secrets-key -f sealed-secrets-key.yaml
kubectl delete pod -n flux -l app=sealed-secretsOnce the correct private key is in place, the sealed-secrets controller will create the Kubernetes secrets and your OpenFaaS cluster will be fully restored.