The eXtra-fast Essential Video Encoder (XEVE) is an opensource and fast MPEG-5 EVC encoder.
MPEG-5 Essential Video Coding (EVC) is a video compression standard of ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Grop (MPEG). The main goal of the EVC is to provide a significantly improved compression capability over existing video coding standards with timely publication of terms. The EVC defines two profiles, including "Baseline Profile" and "Main Profile". The "Baseline profile" contains only technologies that are older than 20 years or otherwise freely available for use in the standard. In addition, the "Main profile" adds a small number of additional tools, each of which can be either cleanly disabled or switched to the corresponding baseline tool on an individual basis.
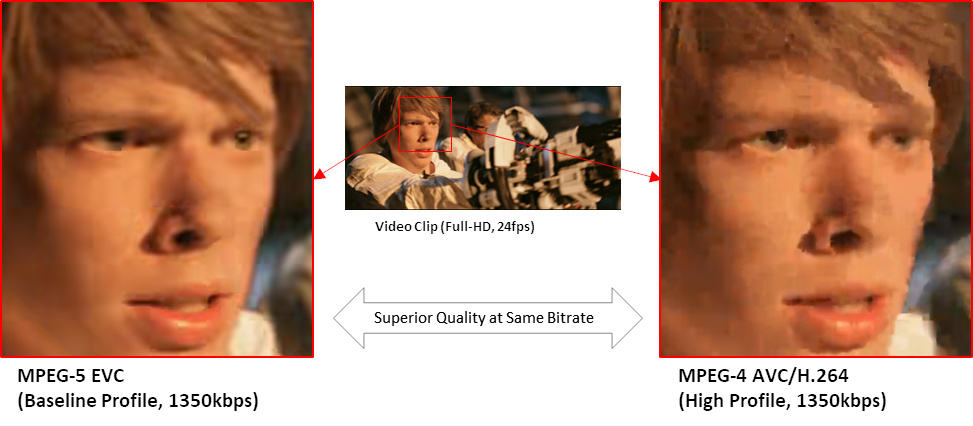
MPEG-5 EVC Baseline Profile can show 2-times better coding gain over MPEG-4 AVC/H.264 codec and superior quality on the same bitrate
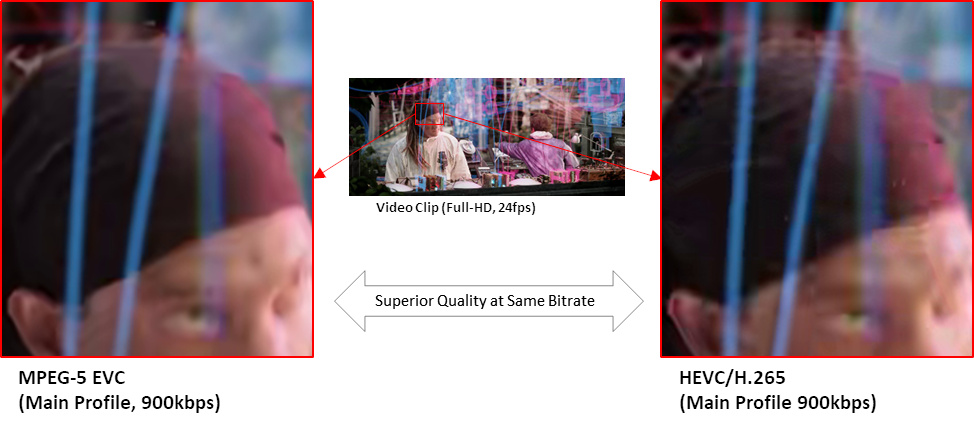
MPEG-5 EVC Main Profile can show 2-times better coding gain over HEVC/H.265 codec and superior quality on the same bitrate
-
Build Requirements
- CMake 3.12 or later (download from https://cmake.org/)
- GCC 5.4.0 or later
-
Build Instructions for Baseline Profile
$mkdir build $cd build $cmake .. -DSET_PROF=BASE $make $sudo make install- Output Location
- Executable application (xeveb_app) can be found under build/bin/.
- Library files (libxeveb.so and libxexeb.a) can be found under build/lib/.
- Output Location
-
Build Instructions for Main Profile
$mkdir build $cd build $cmake .. $make $sudo make install- Output Location
- Executable application (xeve_app) can be found under build/bin/.
- Library files (libxeve.so and libxexe.a) can be found under build/lib/.
- Application and libraries built with Main Profile can also support Baseline Profile operation.
- Output Location
-
Build Requirements
- CMake 3.5 or later (download from https://cmake.org/)
- MinGW-64 or Microsoft Visual Studio
-
Build Instructions for Baseline Profile
- MinGW-64
$mkdir build $cd build $cmake .. -G "MinGW Makefiles" -DSET_PROF=BASE $make $sudo make install - Microsoft Visual Studio
You can change '-G' option with proper version of Visual Studio.
$mkdir build $cd build $cmake .. -G "Visual Studio 15 2017 Win64" -DSET_PROF=BASE $make
- MinGW-64
-
Build Instructions for Main Profile
- MinGW-64
$mkdir build $cd build $cmake .. -G "MinGW Makefiles" $make $sudo make install - Microsoft Visual Studio
You can change '-G' option with proper version of Visual Studio.
$mkdir build $cd build $cmake .. -G "Visual Studio 15 2017 Win64" $make - Application and libraries built with Main Profile can also support Baseline Profile operation.
- MinGW-64
Full help message will be presented if xeve application is executed with '--help' option.
Syntax:
xeve_app -i 'input-file' [ options ]
Options:
--help
: list options
-v, --verbose [INTEGER] (optional) [1]
: verbose (log) level
- 0: no message
- 1: simple messages
- 2: frame-level messages
-i, --input [STRING]
: file name of input video
-o, --output [STRING] (optional) [None]
: file name of output bitstream
-r, --recon [STRING] (optional) [None]
: file name of reconstructed video
-w, --width [INTEGER]
: pixel width of input video
-h, --height [INTEGER]
: pixel height of input video
-q, --qp [INTEGER] (optional) [32]
: QP value (0~51)
-z, --fps [INTEGER]
: frame rate (frame per second)
-I, --keyint [INTEGER] (optional) [0]
: I-picture period
-b, --bframes [INTEGER] (optional) [15]
: maximum number of B frames (1,3,7,15)
-m, --threads [INTEGER] (optional) [1]
: force to use a specific number of threads
-d, --input-depth [INTEGER] (optional) [8]
: input bit depth (8, 10)
--codec-bit-depth [INTEGER] (optional) [10]
: codec internal bit depth (10, 12)
--input-csp [INTEGER] (optional) [1]
: input color space (chroma format)
- 0: YUV400
- 1: YUV420
--profile [STRING] (optional) [baseline]
: profile setting flag (main, baseline)
--level-idc [INTEGER] (optional) [0]
: level setting
--preset [STRING] (optional) [medium]
: Encoder PRESET [fast, medium, slow, placebo]
--tune [STRING] (optional) [None]
: Encoder TUNE [psnr, zerolatency]
AND MORE...
$xeve_app -i RaceHorses_416x240_30.yuv -w 416 -h 240 -z 30 -o xeve.evc
$xeve_app -i RaceHorses_416x240_30.y4m -o xeve.evc
The following code is a pseudo code for understanding how to use the library
#include <xeve.h>
#define MAX_BITSTREAM_SIZE (10*1000*1000) /* 10Mbyte, need to be set properly */
/* prepare coding parameters ***************************/
XEVE_CDSC cdsc;
cdsc.max_bs_buf_size = MAX_BITSTREAM_SIZE;
/* get default parameters */
xeve_param_default(&cdsc.param);
/* set specific profile, preset, tune, if needs */
xeve_param_ppt(&cdsc.param, XEVE_PROFILE_BASELINE, XEVE_PRESET_SLOW, XEVE_TUNE_NONE);
/* create new instance *********************************/
XEVE id = xeve_create(&cdsc, NULL);
/* encode pictures *************************************/
XEVE_BITB bitb; /* bitstream buffer */
memset(&bitb, 0, sizeof(XEVE_BITB));
bitb.addr = malloc(MAX_BITSTREAM_SIZE); /* assign buffer */
bitb.bsize = MAX_BITSTREAM_SIZE;
XEVE_STAT stat; /* encoding status */
XEVE_IMGB image; /* input picture */
while (!end_of_sequence)
{
end_of_seqeunce = read_image(&image); /* read new image */
xeve_push(id, &image); /* input new image to encoder */
ret = xeve_encode(id, &bitb, &stat); /* actual encode image to bitstream */
if (ret == XEVE_OK && stat.write > 0)
{
write_bitstream(bitb.addr, stat.write); /* write encoded bitstream */
}
}
/* clean-up ********************************************/
xeve_delete(id);See COPYING file for details.