a Python tool to enforce dependencies, written in Rust. Inspired by modular monolithic architecture.
Tach lets you define and enforce dependencies between Python modules within your project.
Here's an example:
If a module tries to import from another module that is not listed as a dependency, Tach can prevent it.
Tach is:
- 🌎 Open source
- 🐍 Installable via pip
- 🔧 Able to be adopted incrementally
- ⚡ Implemented with no runtime impact
- ♾️ Interoperable with your existing systems (cli, hooks, ci, etc.)
pip install tachTach allows you to configure where you want to place module boundaries in your project.
You can do this interactively - run:
tach mod
# Up/Down: Navigate Enter: Mark/unmark module Right: Expand Left: Collapse Ctrl + Up: Jump to parent
# Ctrl + s: Exit and save Ctrl + c: Exit without saving Ctrl + a: Mark/unmark allMark each module boundary with 'Enter'. You can mark all of your top-level Python source packages, or just a few which you want to isolate.
If your Python code lives below your project root, mark your Python source root using the 's' key.
This will create the config file for your project, tach.yml.
Once you've marked all the modules you want to enforce dependencies between, run:
tach syncDependencies that exist between each module you've marked will be written to tach.yml.
Check out what Tach has found!
cat tach.yml
Note: Your 'project root' directory (where tach.yml is) will be treated as a module boundary, and can show up as <root>.
Tach comes with a cli command to enforce the boundaries that you just set up! From the root of your Python project, run:
tach checkYou will see:
✅ All module dependencies validated!You can validate that Tach is working by either:
- Commenting out an item in a
depends_onkey intach.yml - By adding an import between modules that didn't previously import from each other.
Give both a try and run tach check again. This will generate an error:
❌ tach/check.py[L8]: Cannot import 'tach.filesystem'. Tag 'tach' cannot depend on 'tach.filesystem'. Each error indicates an import which violates your dependencies. If your terminal supports hyperlinks, click on the file path to go directly to the error.
tach check will also raise an error code. It can be easily integrated with CI/CD, Pre-commit hooks, and VS Code, and more!
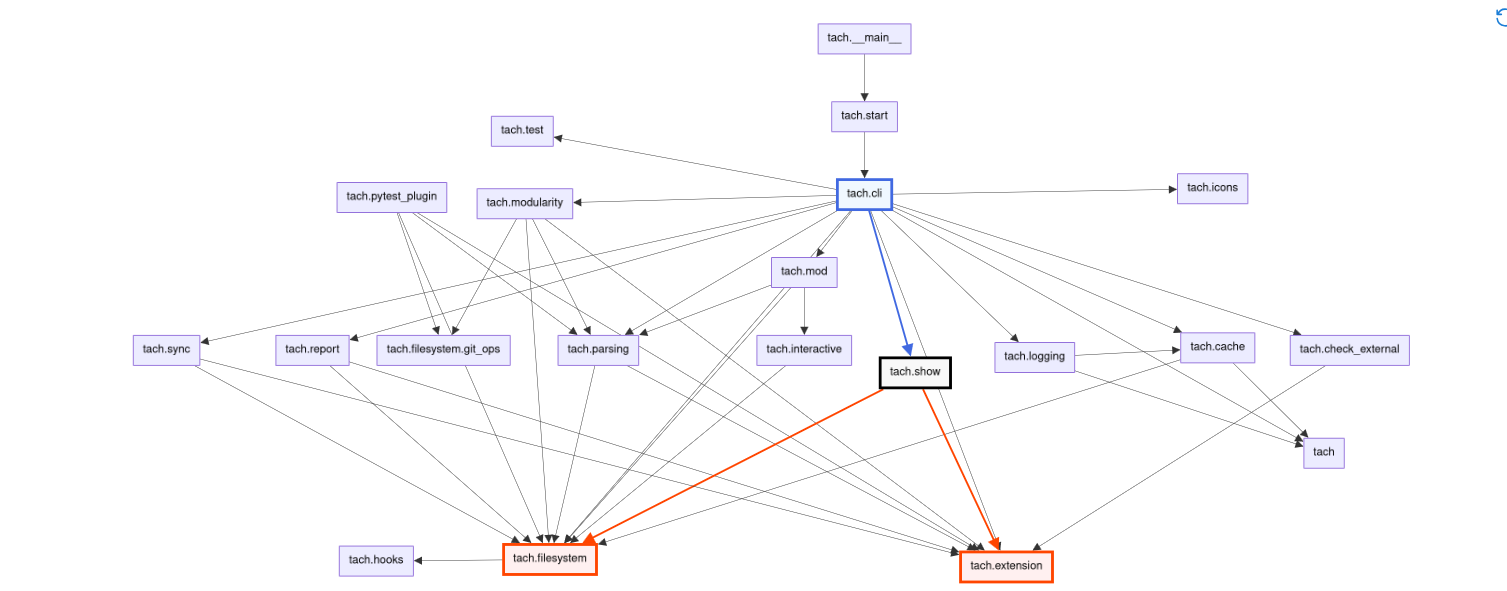
Visualize your dependency graph.
tach showTach will generate a graph of your dependencies. Here's what this looks like for Tach:
Note that this graph is generated remotely the contents of your tach.yml.
You can view the dependencies and usages for a given path:
tach report my_package/
# OR
tach report my_module.pye.g.:
> tach report python/tach/filesystem
[Dependencies of 'python/tach/filesystem']
python/tach/filesystem/install.py[L6]: Import 'tach.hooks.build_pre_commit_hook_content'
python/tach/filesystem/project.py[L5]: Import 'tach.constants.CONFIG_FILE_NAME'
...
-------------------------------
[Usages of 'python/tach/filesystem']
python/tach/cache/access.py[L8]: Import 'tach.filesystem.find_project_config_root'
python/tach/cache/setup.py[L7]: Import 'tach.filesystem.find_project_config_root'
...Tach also supports:
More info in the docs. Tach logs anonymized usage statistics which are can be opted out of. If you have any feedback, we'd love to talk!
If you have any questions or run into any issues, let us know by either reaching out on Discord or submitting a Github Issue!