Compile time validation for queries written in HQL, JPQL, and Panache.
This project now requires at least JDK 11, but JDK 15 or above is preferred.
Type ./gradlew from this project directory.
This produces an artifact with the Maven coordinates
org.hibernate:query-validator:2.0-SNAPSHOT in your local
Maven repository.
It also creates a far jar query-validator-2.0-SNAPSHOT-all.jar
in the build/libs directory of this project.
The persistent entity classes must be annotated with the
basic JPA metadata annotations like @Entity, @ManyToOne,
@Embeddable, @MappedSuperclass, @ElementCollection, and
@Access. You may use XML-based mappings to specify database
mapping information like table and column names if that's what
you prefer.
- Put
query-validator-2.0-SNAPSHOT-all.jarin the compile-time classpath of your project. (Or depend onorg.hibernate:query-validator:2.0-SNAPSHOT.) - Annotate a package or toplevel class with
@CheckHQL.
The validator will check any static string argument of
- the
createQuery()method or - the
@NamedQuery()annotation
which occurs in the annotated package or class.
Inside a Panache entity or repository, the following queries will be checked:
list/find/streamcountdeleteupdate
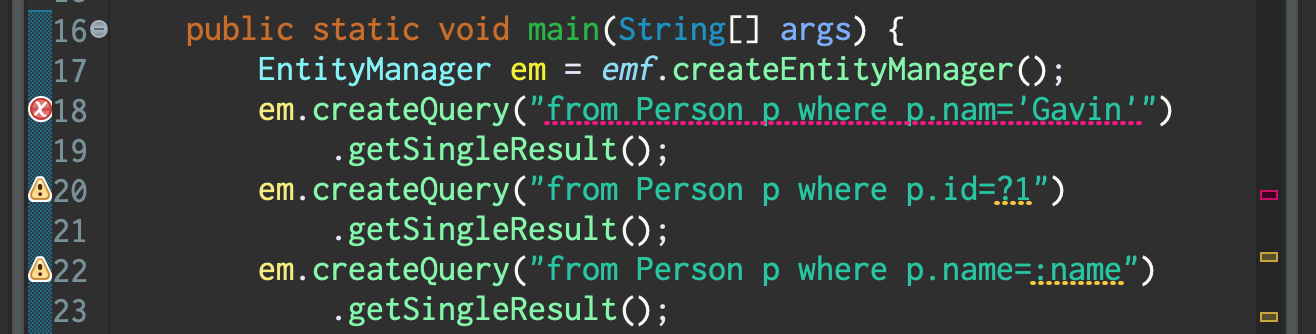
The purpose of the query validator is to detect erroneous query strings and query parameter bindings when the Java code is compiled, instead of at runtime when the query is executed.
A compile-time error is produced if
- the query has syntax errors,
- an entity name in the query doesn't reference a persistent entity class, or
- a member name in the query doesn't reference a mapped field or property of the entity.
A compile-time warning is produced if
- the query calls a function which isn't defined by the JPA specification or by HQL.
The warning may be suppressed by adding the function name to
the whitelist:
@CheckHQL(whitelist={"stddev", "variance", "md5"})
It's even possible to whitelist all the SQL functions known
to a certain Hibernate Dialect:
@CheckHQL(dialect=HSQLDialect.class)
Additionally, any JPA Query instance that is created and
immediately invoked in a single expression will have its
parameter bindings validated. A warning is produced if
- the query string has a parameter with no argument specified
using
setParameter(), or - an argument is specified using
setParameter(), but there is no matching parameter in the query string.
All Panache queries have their parameters validated.
When using a command line compiler, gradle, or mvn, errors
from the query validator are displayed in the compiler output
alongside other compilation errors.
Just compile your code with javac, or even with ECJ
(java -jar ecj-4.6.1.jar), with the query validator jar in
the classpath:
-classpath query-validator-2.0-SNAPSHOT-all.jar
Annoyingly, Gradle requires that the dependency on the query validator be declared twice:
dependencies {
implementation 'org.hibernate:query-validator:2.0-SNAPSHOT'
annotationProcessor 'org.hibernate:query-validator:2.0-SNAPSHOT'
}
Maven handles annotation processors correctly. Just declare the dependency to the query validator.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>query-validator</artifactId>
<version>2.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependencies>
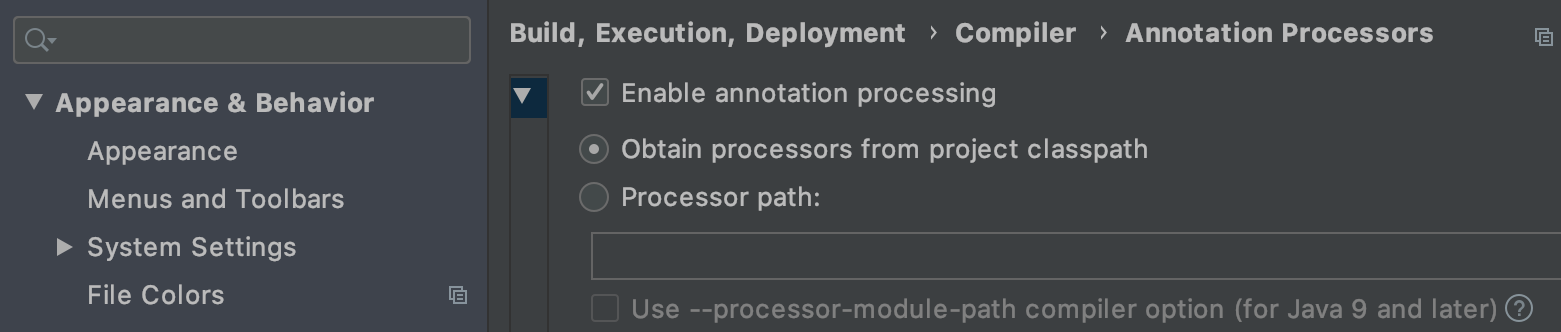
Both IntelliJ and Eclipse require that annotation processing be explicitly enabled.
Select Enable annotation processing in IntelliJ IDEA preferences under Build, Execution, Deployment > Compiler > AnnotationProcessors.
IntelliJ only runs annotation processors during a build (that
is, when you Run your code or explicitly Build Project).
So you won't see errors in your Java editor as you're typing.
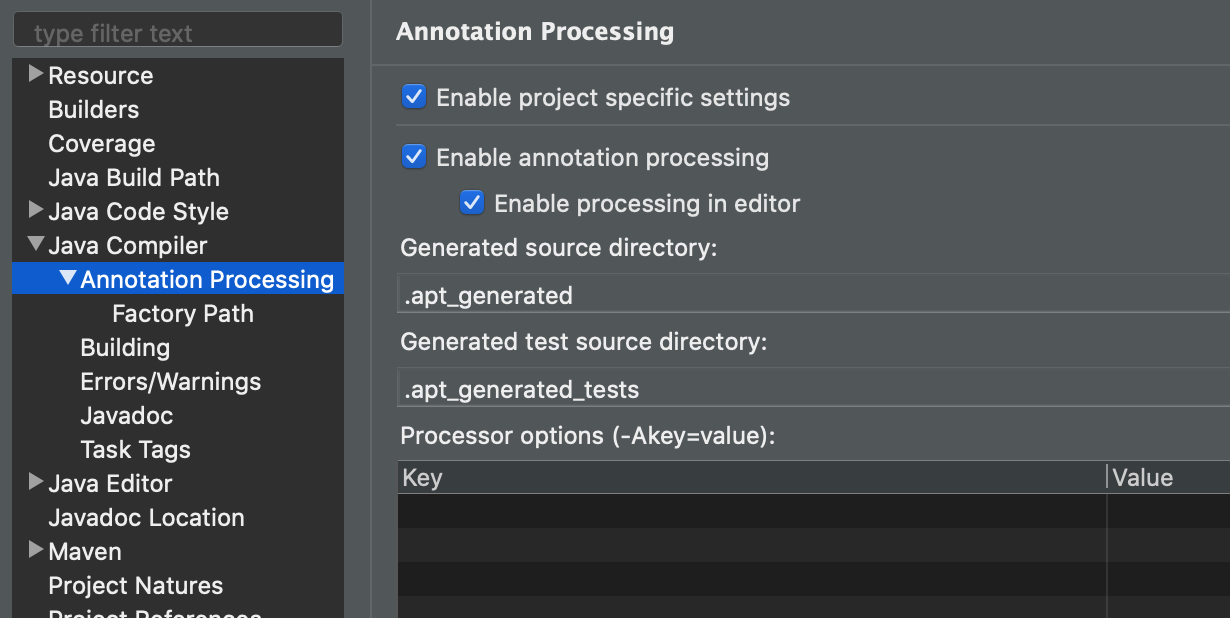
Eclipse IDE doesn't load annotation processors from the project classpath. So you'll need to add the query validator manually.
- In Project > Properties go to Java Compiler > Annotation Processing and select Enable annotation processing.
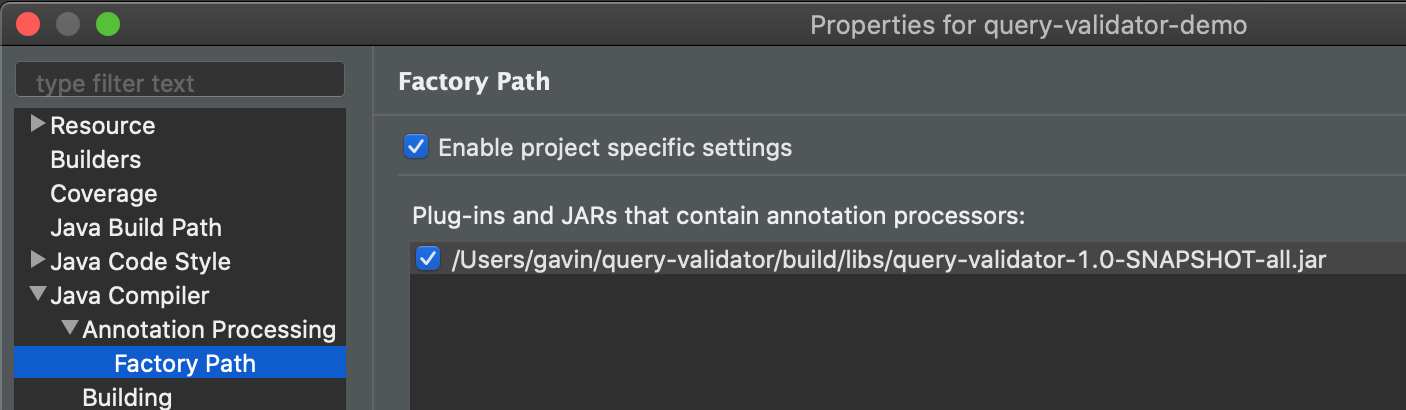
- Then go to Java Compiler > Annotation Processing >
Factory Path and click Add External JARs... and
add
build/libs/query-validator-2.0-SNAPSHOT-all.jarfrom this project directory.
Your project properties should look like this:
Eclipse runs annotation processors during every incremental
build (that is, every time you Save), so you'll see errors
displayed inline in your Java editor.
If the query validator doesn't run, please ensure that:
- Eclipse itself is running on JDK 8.
- Your project is set up to compile with a JDK 8-compatible compiler, and the compiler compliance level is set to 1.8.
The query validator was developed and tested with:
- JDK 15, JDK 17, JDK 20
- Hibernate 5.6.15.Final
- ECJ 3.33.0
- Eclipse IDE with JDT Core 3.33.0
Other versions of javac, ECJ, and Hibernate may or may not
work. The query validator depends on internal compiler APIs in
javac and ECJ, and is therefore sensitive to changes in the
compilers.
Please be aware of the following issues.
Queries are interpreted according to Hibernate's flavor of JPQL (i.e. HQL), which is a superset of the query language defined by the JPA specification.
Hibernate's query translator never typechecks function arguments and instead simply passes anything which looks like it might be a function call straight through to the database.
Fixing this will require a nontrivial enhancement to Hibernate's HQL translator.
In ECJ, don't use @Entity(name="Whatever"), since during an
incremental build, the processor won't be able to discover the
entity named Whatever. (Just let the entity name default to
the name of the class.)
Sometimes Hibernate's HQL parser produces ugly error messages, which are passed on by the query validator.
Fixing this requires a new release of Hibernate.