该项目是从
React官方的脚手架 Create React App 开始的, 相关信息与配置请移步. 目的: react 全家桶, 快速进入业务开发,同时对开发规范作一个约定。
技术栈
- react
- react-dom
- react-router-dom
- prop-types
- redux
- react-redux
- react-router-redux
- redux-saga
- immutable
- redux-immutable
- styled-components
开发流程
为了规范流程和统一编码风格,以及以后更好维护。我们遵从以下原则:
-
immutable的使用
除了request请求后端, 以及组件内部(不需要跟redux或者其他组件交互)可以使用JS原生数据格式(JSD),其他在原则上统一使用immutable数据格式。
解释:
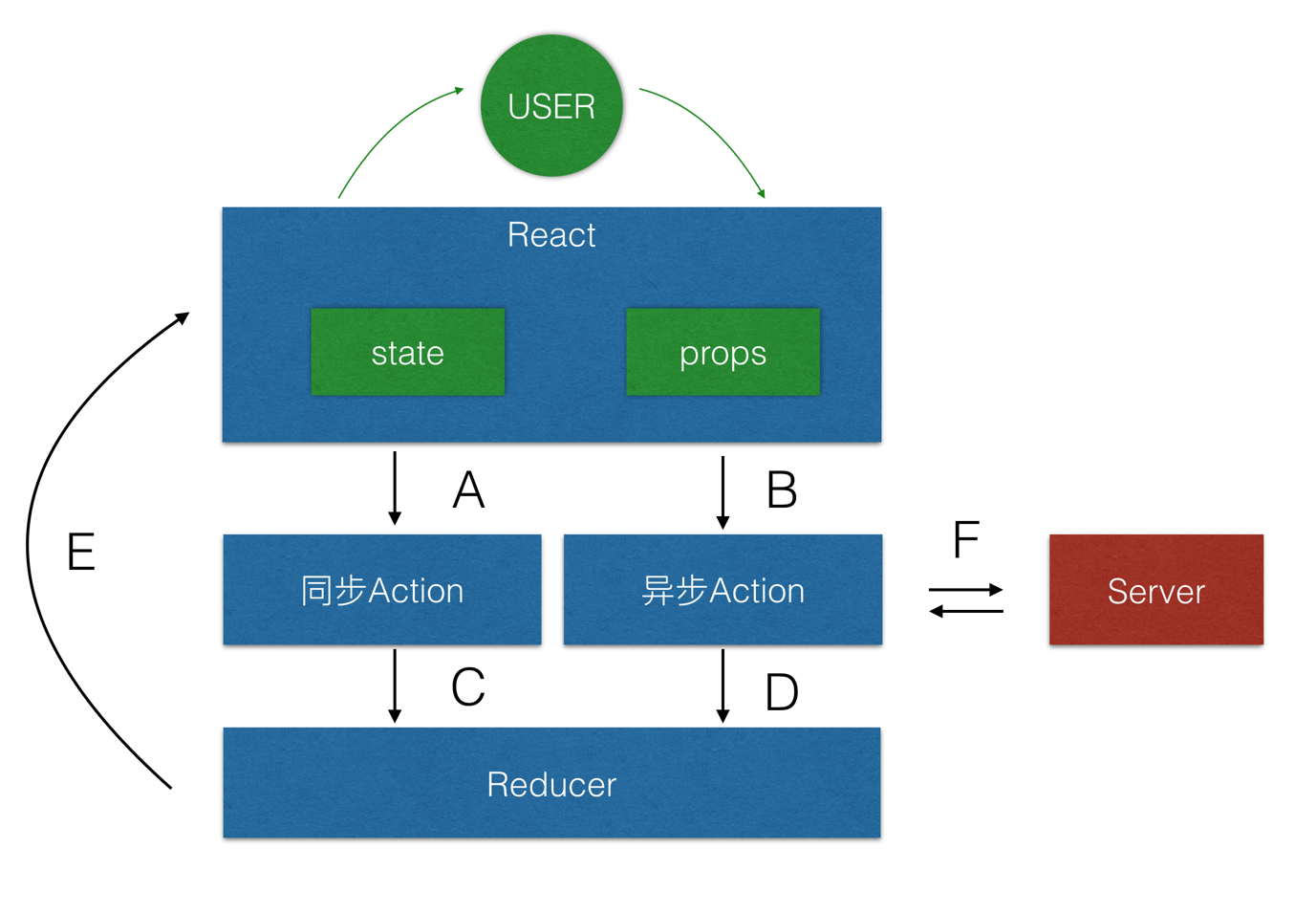
- 在 React 视图里,props 其实就来自于 Redux 维护的全局的 state 的,所以 props 中的每一项一定是 immutable 的。
- 在 React 视图里,组件自己维护的局部 state 如果是用来提交到 store 的, 必须为 immutable 的,否则不强制。
- 从视图层向同步和异步 action 发送的数据(A/B),必须是 immutable 的。
- Action 提交给 reducer 的数据(C/D),必须是 immutable 的。
- reducer 处理后所得 state (E)当然一定是 immutable 的。 这样似乎看起来,所有地方都是 immutable 的,但是其实异步 action 和服务器的交互当然是 JSD (F)。换句话说,我们要求,除了向服务端发送数据请求的时候,其他位置,不允许出现toJS的代码。而接收到服务端的数据后,在流转入全局 state 之前,统一转化为 immutable 数据。
为什么要做这种统一呢?是因为:
- 避免 JSD 和 immutable 的混用导致出错;
- 统一 JSD 和 immutable 的转化路径。比如你在局部 state 里不使用 immutable,但是这些局部的 state 很可能被用来通过异步 action 提交的服务端,这样在数据流里就会同时存在 JSD 和 immutable,这对于代码的维护性是一种灾难。
更多react、redux、immutable 配合使用的方式与解释可参考(仅作参考,因为库一直在升级,如 prop-types 的验证等):
-
代码按照业务进行划分,而不是按功能。业务中再按功能分。 init 中的文件划分想法来自于之前使用 angular 中的实践。
也可以参考下面文章
剩余问题
- 数据模拟问题
- style的组织。sass,less or cssModule or styleComponent ?
- code split (按需加载的必要性?实现?)
- 单元测试与集成测试
Folder Structure
react-init/
README.md
config # 构建
node_modules/
package.json
public/
index.html
favicon.ico
src/
common # 公共的 组件等
modules # 模块
Dashboard # 模块名 ( pascal-case ? )
actions # Dashboard 模块下的 action
reducers # Dashboard 模块下的 reducer
sagas # Dashboard 模块下的 saga
index.js
redux # 数据 状态管理
reducers # root reducer
index.js
sagas # root saga
index.js
store # rootStore
index.js
index.css
index.js
logo.svg
For the project to build, these files must exist with exact filenames:
public/index.htmlis the page template;src/index.jsis the JavaScript entry point.
You can delete or rename the other files.
You may create subdirectories inside src. For faster rebuilds, only files inside src are processed by Webpack.
You need to put any JS and CSS files inside src, otherwise Webpack won’t see them.
Only files inside public can be used from public/index.html.
Read instructions below for using assets from JavaScript and HTML.
You can, however, create more top-level directories.
They will not be included in the production build so you can use them for things like documentation.
Scripts
In the project directory, you can run:
npm start
Runs the app in the development mode.
Open http://localhost:3000 to view it in the browser.
The page will reload if you make edits.
You will also see any lint errors in the console.
npm test
Launches the test runner in the interactive watch mode.
See the section about running tests for more information.
npm run build
Builds the app for production to the build folder.
It correctly bundles React in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.
Your app is ready to be deployed!
See the section about deployment for more information.
npm run eject
Note: this is a one-way operation. Once you eject, you can’t go back!
If you aren’t satisfied with the build tool and configuration choices, you can eject at any time. This command will remove the single build dependency from your project.
Instead, it will copy all the configuration files and the transitive dependencies (Webpack, Babel, ESLint, etc) right into your project so you have full control over them. All of the commands except eject will still work, but they will point to the copied scripts so you can tweak them. At this point you’re on your own.
You don’t have to ever use eject. The curated feature set is suitable for small and middle deployments, and you shouldn’t feel obligated to use this feature. However we understand that this tool wouldn’t be useful if you couldn’t customize it when you are ready for it.
Getting Started with Styleguidist
Styleguidist combines a style guide, where all your components are presented on a single page with their props documentation and usage examples, with an environment for developing components in isolation, similar to Storybook. In Styleguidist you write examples in Markdown, where each code snippet is rendered as a live editable playground.
First, install Styleguidist:
npm install --save react-styleguidistAlternatively you may use yarn:
yarn add react-styleguidistThen, add these scripts to your package.json:
"scripts": {
+ "styleguide": "styleguidist server",
+ "styleguide:build": "styleguidist build",
"start": "react-scripts start",Then, run the following command inside your app’s directory:
npm run styleguideAfter that, follow the instructions on the screen.
Learn more about React Styleguidist:
Analyzing the Bundle Size
Source map explorer analyzes JavaScript bundles using the source maps. This helps you understand where code bloat is coming from.
To add Source map explorer to a Create React App project, follow these steps:
npm install --save source-map-explorerAlternatively you may use yarn:
yarn add source-map-explorerThen in package.json, add the following line to scripts:
"scripts": {
+ "analyze": "source-map-explorer build/static/js/main.*",
"start": "react-scripts start",
"build": "react-scripts build",
"test": "react-scripts test --env=jsdom",Note:
This doesn't quite work on Windows because it doesn't automatically expand
*in the filepath. For now, the workaround is to look at the full hashed filename inbuild/static/js(e.g.main.89b7e95a.js) and copy it intopackage.jsonwhen you're running the analyzer. For example:+ "analyze": "source-map-explorer build/static/js/main.89b7e95a.js",Unfortunately it will be different after every build. You can express support for fixing this on Windows in this issue.
Then to analyze the bundle run the production build then run the analyze script.
npm run build
npm run analyze
Deployment
npm run build creates a build directory with a production build of your app. Set up your favourite HTTP server so that a visitor to your site is served index.html, and requests to static paths like /static/js/main.<hash>.js are served with the contents of the /static/js/main.<hash>.js file.
Static Server
For environments using Node, the easiest way to handle this would be to install serve and let it handle the rest:
npm install -g serve
serve -s buildThe last command shown above will serve your static site on the port 5000. Like many of serve’s internal settings, the port can be adjusted using the -p or --port flags.
Run this command to get a full list of the options available:
serve -hOther Solutions
You don’t necessarily need a static server in order to run a Create React App project in production. It works just as fine integrated into an existing dynamic one.
Here’s a programmatic example using Node and Express:
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'build')));
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, 'build', 'index.html'));
});
app.listen(9000);The choice of your server software isn’t important either. Since Create React App is completely platform-agnostic, there’s no need to explicitly use Node.
The build folder with static assets is the only output produced by Create React App.
However this is not quite enough if you use client-side routing. Read the next section if you want to support URLs like /todos/42 in your single-page app.
Serving Apps with Client-Side Routing
If you use routers that use the HTML5 pushState history API under the hood (for example, React Router with browserHistory), many static file servers will fail. For example, if you used React Router with a route for /todos/42, the development server will respond to localhost:3000/todos/42 properly, but an Express serving a production build as above will not.
This is because when there is a fresh page load for a /todos/42, the server looks for the file build/todos/42 and does not find it. The server needs to be configured to respond to a request to /todos/42 by serving index.html. For example, we can amend our Express example above to serve index.html for any unknown paths:
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'build')));
-app.get('/', function (req, res) {
+app.get('/*', function (req, res) {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, 'build', 'index.html'));
});If you’re using Apache HTTP Server, you need to create a .htaccess file in the public folder that looks like this:
Options -MultiViews
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteRule ^ index.html [QSA,L]
It will get copied to the build folder when you run npm run build.
If you’re using Apache Tomcat, you need to follow this Stack Overflow answer.
Now requests to /todos/42 will be handled correctly both in development and in production.
On a production build, and in a browser that supports service workers,
the service worker will automatically handle all navigation requests, like for
/todos/42, by serving the cached copy of your index.html. This
service worker navigation routing can be configured or disabled by
ejecting and then modifying the
navigateFallback
and navigateFallbackWhitelist
options of the SWPreachePlugin configuration.
Building for Relative Paths
By default, Create React App produces a build assuming your app is hosted at the server root.
To override this, specify the homepage in your package.json, for example:
"homepage": "http://mywebsite.com/relativepath",This will let Create React App correctly infer the root path to use in the generated HTML file.
Serving the Same Build from Different Paths
Note: this feature is available with
react-scripts@0.9.0and higher.
If you are not using the HTML5 pushState history API or not using client-side routing at all, it is unnecessary to specify the URL from which your app will be served. Instead, you can put this in your package.json:
"homepage": ".",This will make sure that all the asset paths are relative to index.html. You will then be able to move your app from http://mywebsite.com to http://mywebsite.com/relativepath or even http://mywebsite.com/relative/path without having to rebuild it.
Azure
See this blog post on how to deploy your React app to Microsoft Azure.
Firebase
Install the Firebase CLI if you haven’t already by running npm install -g firebase-tools. Sign up for a Firebase account and create a new project. Run firebase login and login with your previous created Firebase account.
Then run the firebase init command from your project’s root. You need to choose the Hosting: Configure and deploy Firebase Hosting sites and choose the Firebase project you created in the previous step. You will need to agree with database.rules.json being created, choose build as the public directory, and also agree to Configure as a single-page app by replying with y.
=== Project Setup
First, let's associate this project directory with a Firebase project.
You can create multiple project aliases by running firebase use --add,
but for now we'll just set up a default project.
? What Firebase project do you want to associate as default? Example app (example-app-fd690)
=== Database Setup
Firebase Realtime Database Rules allow you to define how your data should be
structured and when your data can be read from and written to.
? What file should be used for Database Rules? database.rules.json
✔ Database Rules for example-app-fd690 have been downloaded to database.rules.json.
Future modifications to database.rules.json will update Database Rules when you run
firebase deploy.
=== Hosting Setup
Your public directory is the folder (relative to your project directory) that
will contain Hosting assets to uploaded with firebase deploy. If you
have a build process for your assets, use your build's output directory.
? What do you want to use as your public directory? build
? Configure as a single-page app (rewrite all urls to /index.html)? Yes
✔ Wrote build/index.html
i Writing configuration info to firebase.json...
i Writing project information to .firebaserc...
✔ Firebase initialization complete!Now, after you create a production build with npm run build, you can deploy it by running firebase deploy.
=== Deploying to 'example-app-fd690'...
i deploying database, hosting
✔ database: rules ready to deploy.
i hosting: preparing build directory for upload...
Uploading: [============================== ] 75%✔ hosting: build folder uploaded successfully
✔ hosting: 8 files uploaded successfully
i starting release process (may take several minutes)...
✔ Deploy complete!
Project Console: https://console.firebase.google.com/project/example-app-fd690/overview
Hosting URL: https://example-app-fd690.firebaseapp.comFor more information see Add Firebase to your JavaScript Project.
GitHub Pages
Note: this feature is available with
react-scripts@0.2.0and higher.
Step 1: Add homepage to package.json
The step below is important!
If you skip it, your app will not deploy correctly.
Open your package.json and add a homepage field:
"homepage": "https://myusername.github.io/my-app",Create React App uses the homepage field to determine the root URL in the built HTML file.
Step 2: Install gh-pages and add deploy to scripts in package.json
Now, whenever you run npm run build, you will see a cheat sheet with instructions on how to deploy to GitHub Pages.
To publish it at https://myusername.github.io/my-app, run:
npm install --save gh-pagesAlternatively you may use yarn:
yarn add gh-pagesAdd the following scripts in your package.json:
"scripts": {
+ "predeploy": "npm run build",
+ "deploy": "gh-pages -d build",
"start": "react-scripts start",
"build": "react-scripts build",The predeploy script will run automatically before deploy is run.
Step 3: Deploy the site by running npm run deploy
Then run:
npm run deployStep 4: Ensure your project’s settings use gh-pages
Finally, make sure GitHub Pages option in your GitHub project settings is set to use the gh-pages branch:
Step 5: Optionally, configure the domain
You can configure a custom domain with GitHub Pages by adding a CNAME file to the public/ folder.
Notes on client-side routing
GitHub Pages doesn’t support routers that use the HTML5 pushState history API under the hood (for example, React Router using browserHistory). This is because when there is a fresh page load for a url like http://user.github.io/todomvc/todos/42, where /todos/42 is a frontend route, the GitHub Pages server returns 404 because it knows nothing of /todos/42. If you want to add a router to a project hosted on GitHub Pages, here are a couple of solutions:
- You could switch from using HTML5 history API to routing with hashes. If you use React Router, you can switch to
hashHistoryfor this effect, but the URL will be longer and more verbose (for example,http://user.github.io/todomvc/#/todos/42?_k=yknaj). Read more about different history implementations in React Router. - Alternatively, you can use a trick to teach GitHub Pages to handle 404 by redirecting to your
index.htmlpage with a special redirect parameter. You would need to add a404.htmlfile with the redirection code to thebuildfolder before deploying your project, and you’ll need to add code handling the redirect parameter toindex.html. You can find a detailed explanation of this technique in this guide.
Heroku
Use the Heroku Buildpack for Create React App.
You can find instructions in Deploying React with Zero Configuration.
Resolving Heroku Deployment Errors
Sometimes npm run build works locally but fails during deploy via Heroku. Following are the most common cases.
"Module not found: Error: Cannot resolve 'file' or 'directory'"
If you get something like this:
remote: Failed to create a production build. Reason:
remote: Module not found: Error: Cannot resolve 'file' or 'directory'
MyDirectory in /tmp/build_1234/src
It means you need to ensure that the lettercase of the file or directory you import matches the one you see on your filesystem or on GitHub.
This is important because Linux (the operating system used by Heroku) is case sensitive. So MyDirectory and mydirectory are two distinct directories and thus, even though the project builds locally, the difference in case breaks the import statements on Heroku remotes.
"Could not find a required file."
If you exclude or ignore necessary files from the package you will see a error similar this one:
remote: Could not find a required file.
remote: Name: `index.html`
remote: Searched in: /tmp/build_a2875fc163b209225122d68916f1d4df/public
remote:
remote: npm ERR! Linux 3.13.0-105-generic
remote: npm ERR! argv "/tmp/build_a2875fc163b209225122d68916f1d4df/.heroku/node/bin/node" "/tmp/build_a2875fc163b209225122d68916f1d4df/.heroku/node/bin/npm" "run" "build"
In this case, ensure that the file is there with the proper lettercase and that’s not ignored on your local .gitignore or ~/.gitignore_global.
Modulus
See the Modulus blog post on how to deploy your react app to Modulus.
Netlify
To do a manual deploy to Netlify’s CDN:
npm install netlify-cli
netlify deployChoose build as the path to deploy.
To setup continuous delivery:
With this setup Netlify will build and deploy when you push to git or open a pull request:
- Start a new netlify project
- Pick your Git hosting service and select your repository
- Click
Build your site
Support for client-side routing:
To support pushState, make sure to create a public/_redirects file with the following rewrite rules:
/* /index.html 200
When you build the project, Create React App will place the public folder contents into the build output.
Now
now offers a zero-configuration single-command deployment. You can use now to deploy your app for free.
-
Install the
nowcommand-line tool either via the recommended desktop tool or via node withnpm install -g now. -
Build your app by running
npm run build. -
Move into the build directory by running
cd build. -
Run
now --name your-project-namefrom within the build directory. You will see a now.sh URL in your output like this:> Ready! https://your-project-name-tpspyhtdtk.now.sh (copied to clipboard)Paste that URL into your browser when the build is complete, and you will see your deployed app.
Details are available in this article.
S3 and CloudFront
See this blog post on how to deploy your React app to Amazon Web Services S3 and CloudFront.
Surge
Install the Surge CLI if you haven’t already by running npm install -g surge. Run the surge command and log in you or create a new account.
When asked about the project path, make sure to specify the build folder, for example:
project path: /path/to/project/buildNote that in order to support routers that use HTML5 pushState API, you may want to rename the index.html in your build folder to 200.html before deploying to Surge. This ensures that every URL falls back to that file.
Advanced Configuration
You can adjust various development and production settings by setting environment variables in your shell or with .env.
| Variable | Development | Production | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| BROWSER | ✅ | ❌ | By default, Create React App will open the default system browser, favoring Chrome on macOS. Specify a browser to override this behavior, or set it to none to disable it completely. If you need to customize the way the browser is launched, you can specify a node script instead. Any arguments passed to npm start will also be passed to this script, and the url where your app is served will be the last argument. Your script's file name must have the .js extension. |
| HOST | ✅ | ❌ | By default, the development web server binds to localhost. You may use this variable to specify a different host. |
| PORT | ✅ | ❌ | By default, the development web server will attempt to listen on port 3000 or prompt you to attempt the next available port. You may use this variable to specify a different port. |
| HTTPS | ✅ | ❌ | When set to true, Create React App will run the development server in https mode. |
| PUBLIC_URL | ❌ | ✅ | Create React App assumes your application is hosted at the serving web server's root or a subpath as specified in package.json (homepage). Normally, Create React App ignores the hostname. You may use this variable to force assets to be referenced verbatim to the url you provide (hostname included). This may be particularly useful when using a CDN to host your application. |
| CI | 🔶 | ✅ | When set to true, Create React App treats warnings as failures in the build. It also makes the test runner non-watching. Most CIs set this flag by default. |
| REACT_EDITOR | ✅ | ❌ | When an app crashes in development, you will see an error overlay with clickable stack trace. When you click on it, Create React App will try to determine the editor you are using based on currently running processes, and open the relevant source file. You can send a pull request to detect your editor of choice. Setting this environment variable overrides the automatic detection. If you do it, make sure your systems PATH environment variable points to your editor’s bin folder. |
Troubleshooting
npm start doesn’t detect changes
When you save a file while npm start is running, the browser should refresh with the updated code.
If this doesn’t happen, try one of the following workarounds:
- If your project is in a Dropbox folder, try moving it out.
- If the watcher doesn’t see a file called
index.jsand you’re referencing it by the folder name, you need to restart the watcher due to a Webpack bug. - Some editors like Vim and IntelliJ have a “safe write” feature that currently breaks the watcher. You will need to disable it. Follow the instructions in “Adjusting Your Text Editor”.
- If your project path contains parentheses, try moving the project to a path without them. This is caused by a Webpack watcher bug.
- On Linux and macOS, you might need to tweak system settings to allow more watchers.
- If the project runs inside a virtual machine such as (a Vagrant provisioned) VirtualBox, create an
.envfile in your project directory if it doesn’t exist, and addCHOKIDAR_USEPOLLING=trueto it. This ensures that the next time you runnpm start, the watcher uses the polling mode, as necessary inside a VM.
If none of these solutions help please leave a comment in this thread.
npm test hangs on macOS Sierra
If you run npm test and the console gets stuck after printing react-scripts test --env=jsdom to the console there might be a problem with your Watchman installation as described in facebookincubator/create-react-app#713.
We recommend deleting node_modules in your project and running npm install (or yarn if you use it) first. If it doesn't help, you can try one of the numerous workarounds mentioned in these issues:
It is reported that installing Watchman 4.7.0 or newer fixes the issue. If you use Homebrew, you can run these commands to update it:
watchman shutdown-server
brew update
brew reinstall watchman
You can find other installation methods on the Watchman documentation page.
If this still doesn’t help, try running launchctl unload -F ~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.github.facebook.watchman.plist.
There are also reports that uninstalling Watchman fixes the issue. So if nothing else helps, remove it from your system and try again.
npm run build exits too early
It is reported that npm run build can fail on machines with limited memory and no swap space, which is common in cloud environments. Even with small projects this command can increase RAM usage in your system by hundreds of megabytes, so if you have less than 1 GB of available memory your build is likely to fail with the following message:
The build failed because the process exited too early. This probably means the system ran out of memory or someone called
kill -9on the process.
If you are completely sure that you didn't terminate the process, consider adding some swap space to the machine you’re building on, or build the project locally.
npm run build fails on Heroku
This may be a problem with case sensitive filenames. Please refer to this section.
Moment.js locales are missing
If you use a Moment.js, you might notice that only the English locale is available by default. This is because the locale files are large, and you probably only need a subset of all the locales provided by Moment.js.
To add a specific Moment.js locale to your bundle, you need to import it explicitly.
For example:
import moment from 'moment';
import 'moment/locale/fr';If import multiple locales this way, you can later switch between them by calling moment.locale() with the locale name:
import moment from 'moment';
import 'moment/locale/fr';
import 'moment/locale/es';
// ...
moment.locale('fr');This will only work for locales that have been explicitly imported before.
Something Missing?
If you have ideas for more “How To” recipes that should be on this page, let us know or contribute some!