A set of PIO state machine programs and routines for linking the PICO to a Ti-8X graphing calculator
TiLink.py
Exposes a class called TiLink.
-
TiLink.begin() - Starts TiLink machine
-
TiLink.stop() - Stops TiLink machine
-
TiLink.restart() - Restarts state machine
-
TiLink.get() - Returns last received byte, or blocks until data is available.
-
TiLink.put(data) - Writes data to TiLink, Blocks if Tx fifo has more then 4 bytes.
-
TiLink.irq(routine) - Attached Routine to Received byte
-
TiLink.rx_fifo() returns bytes waiting to be recieved
-
TiLink.tx_fifo() returns bytes waiting to be sent.
This example emulates a Ti GreyLink cable. The Grey Link cable presents it self to a computer as a serial port, and directly translates bytes in and out from the computer and calculator. Upload TiLink.py to your Pico, Run GreyLink.py on the Pico. You can rename GreyLink.py to main.py to have it run on Picoboot.
The Pico is connected to a graphing calculator using 2 GPIO pins and ground.
Quoted from the Ti Link Protocol Guide by Tim Singer And Romain Liévin
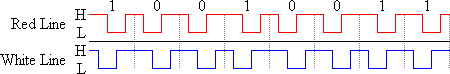
"The link port normally operates in a half-duplex mode where a bit is sent by activating the corresponding line ("ring" or "tip") and the receiver acknowledges by activating the other line. The sender now releases its line and finally the receiver releases the acknowledge. "
Above is an example of sending a 0xC9, Data is shifted out LSB first.
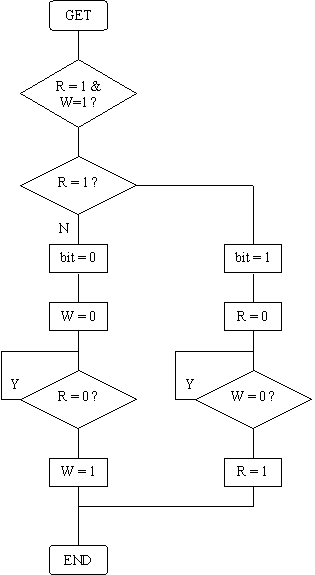
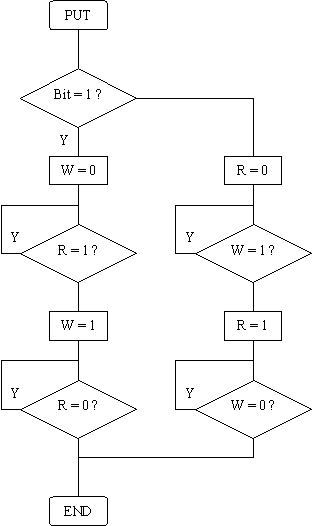
These are a flow chart example of the send/rx logic
Some of the Images used are curtesy of The TI Link Protocol Guide.
Special thanks to
- Iambian
- KermMartian and Articl
- BaldEngineer