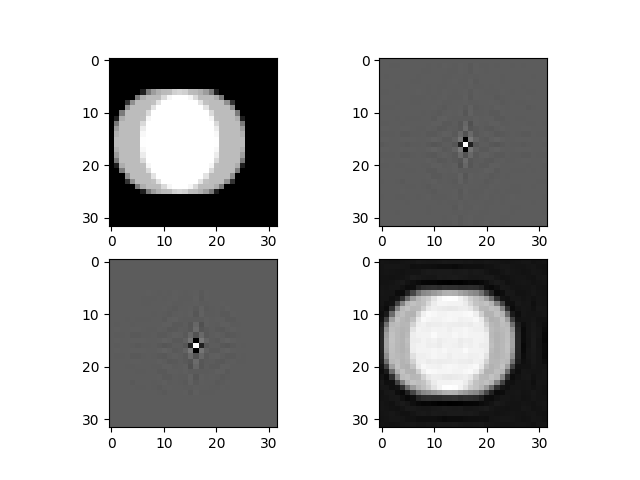
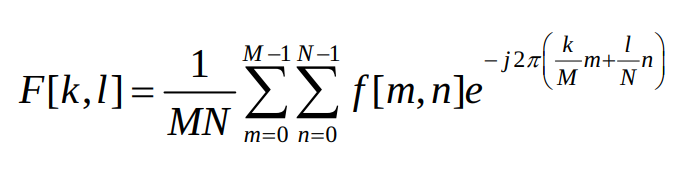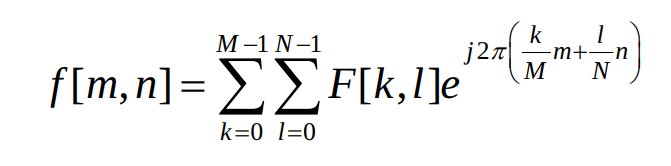A simple demo of Fourier image transformation by from-scratch DFT and iDFT functions.
The discrete two-dimensional Fourier transform of an image array is defined in series form as
I implemented from scratch in Python (without the normalization part) as follow:
def DFT_2d(image):
#data = np.asarray(image)
data = image
M, N = image.shape # (img x, img y)
dft2d = np.zeros((M,N),dtype=complex)
for k in range(M):
for l in range(N):
sum_matrix = 0.0
for m in range(M):
for n in range(N):
e = cmath.exp(- 2j * np.pi * ((k * m) / M + (l * n) / N))
sum_matrix += data[m,n] * e
dft2d[k,l] = sum_matrix
return dft2dinverse transform equation:
the implementation (and again, without the normalization part) is as follow:
def iDFT_2d(image):
#data = np.asarray(image)
data = image
#M, N = image.size # (img x, img y)
M, N = image.shape
dft2d = np.zeros((M,N),dtype=complex)
for k in range(M):
for l in range(N):
sum_matrix = 0.0
for m in range(M):
for n in range(N):
e = cmath.exp(2j * np.pi * ((k * m) / M + (l * n) / N))
sum_matrix += data[m,n] * e
dft2d[k,l] = sum_matrix
return dft2dThese 4 steps are:
- Showing the original spatial domain of the input image.
- Transform it into the Frequency Domain by applying the Fourier Transform, then show the F-image.
- Cutting some frequencies area, this might be more complex process a you desire, then show the filtered F-image.
- Transfrom into the Saptial Domain and show the result.