This is an extension or API plugin for Looker that integrates LLM's hosted on Vertex AI into a natural language experience powered by Looker's modeling layer.
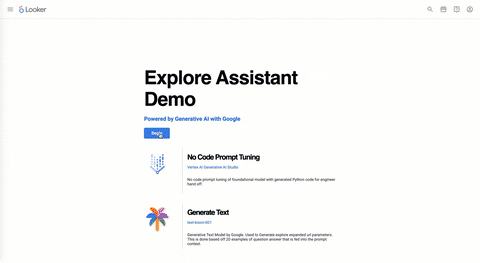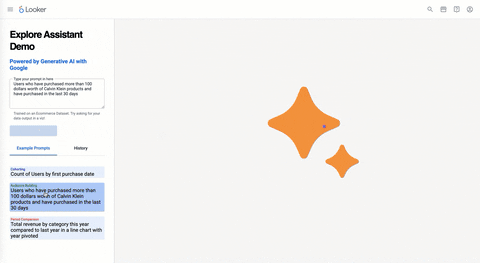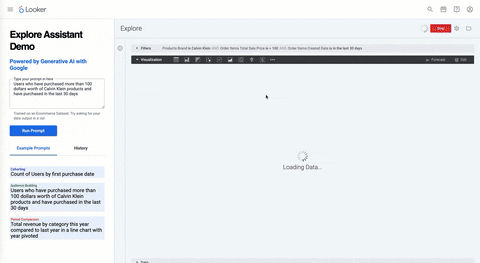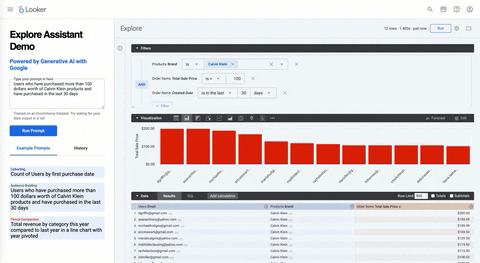
The Explore Assistant allows a user to generate a Looker Explore Query via natural language outputted into a visualization. As opposed to writing the raw SQL itself, the LLM is optimized to translate a text input into a Looker explore query. This is important as the LLM does what it's great at, generative content, and Looker powers it with all the underlying data context, metadata and nuances that come with business data and analytics.
Additionally, the extension provides:
- Question History (this is stored in the browser with IndexDB)
- Categorized Prompts (these can be customized by the use cases of your organization)
- Cached Explore URL's when clicking from History
- Structured Logging with Input & Output Token Counts (enables a workflow of log sink to BQ for cost estimation & tracking)
- Gemini Pro Update in Cloud Function
- NEW BigQuery Deployment Workflow
Upcoming capabilities on the roadmap:
- Historical questions (broken down by user, ranked by popularity/frequency, and categorized by type)
- LLM suggested questions (iterative suggestions for follow up queries)
- Refinement (refining the visualization returned by the LLM through natural language)
There are two options for deployment this repository provides, please choose the deployment model that fits your use case:
- Cloud Function Deployment: This deployment model is great if you are an application developer and plan on either leveraging an LLM deployed on infrastructure outside of the Vertex AI Platform or using the Looker + LLM integration as a standalone API in your own application.
- BigQuery Deployment: This deployment model is great if you want to manage training data and the integration itself through BigQuery and plan on using a model deployed on Vertex AI Platform infrastructure.
The Explore Assistant API is an API only version of the Explore Assistant intended to be integrated with your Backend to surface visualizations from natural language in a custom application. Below the requirements, setup and an example curl request is detailed:
From the root of the directory (ie. looker-explore-assistant/)
cd explore-assistant-api &&
export PROJECT=<your GCP Project> &&
export REGION=<your GCP region>Ensure you have venv installed before running the following:
# Create a new virtualenv named "explore-assistant"
python3 -m venv explore-assistant &&
# Activate the virtualenv (OS X & Linux)
source explore-assistant/bin/activate &&
# Activate the virtualenv (Windows)
explore-assistant\Scripts\activateRun the following cURL command to ensure your the Explore Assistant API server is running and working:
curl --location 'http://localhost:8000/' --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --data '{
"model": "thelook",
"explore": "order_items",
"question": "total sales trending overtime as an area chart"
}'Before deploying, you will want to swap out the example LookML explore metadata text file and jsonl file for files that are customized for your Explore data. Please see this notebook for more details on generating these:
-
From the Explore Assistant root directory (
cd) to the Explore Assistant API folder.cd explore-assistant-api/terraform -
Replace defaults in the
variables.tffile for project, region and endpoint name. -
Ensure that Terraform is installed on your machine. Then Deploy resources.
Initialize Terraform
terraform init
Plan resource provisioning
terraform planProvision Resources
terraform apply -
Save Deployed Cloud Run URL Endpoint and make authenticated cURL request (filling in the placeholders for your environment details):
curl --location '<CLOUD RUN URL>' -h 'Content-Type: application/json' -h 'Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-identity-token)' --data '{
"model": "YOUR LOOKML MODEL",
"explore": "YOUR LOOKML EXPLORE",
"question": "NATURAL LANGUAGE QUESTION"
}'The returned Cloud Run URL will be private, meaning an un-authorized and un-authenticated client won't be able to reach it. In the example above we are generating an identity token and passing it in the Authorization header of the request. Google Cloud provides a few options for authenticating request to a private Cloud Run service and the right one will vary depending on your setup. Please see this doc for more details
This app uses a one shot prompt technique for fine tuning a model, meaning that all the metadata for the model is contained in the prompt. It's a good technique for a small dataset, but for a larger dataset, you may want to use a more traditional fine tuning approach. This is a simple implementation, but you can also use a more sophisticated approach that involves generating embeddings for explore metadata and leveraging a vector database for indexing.
Any jsonl file you see in this repo is used to train the llm with representative Looker Explore Query examples. These examples are used to help the understand how to create different variations of Looker Explore Queries to account for requests that might result in pivots, relative date filters, includes string syntax, etc. For convenience and customization we recommend using Looker System Activity, filtering queries for the model and explore you plan on using the assistant with, and then using the top 20-30 queries as your example input output string with their expanded url syntax. Please see the Explore Assistant Training Notebook for creating query examples for new datasets via an automated process.