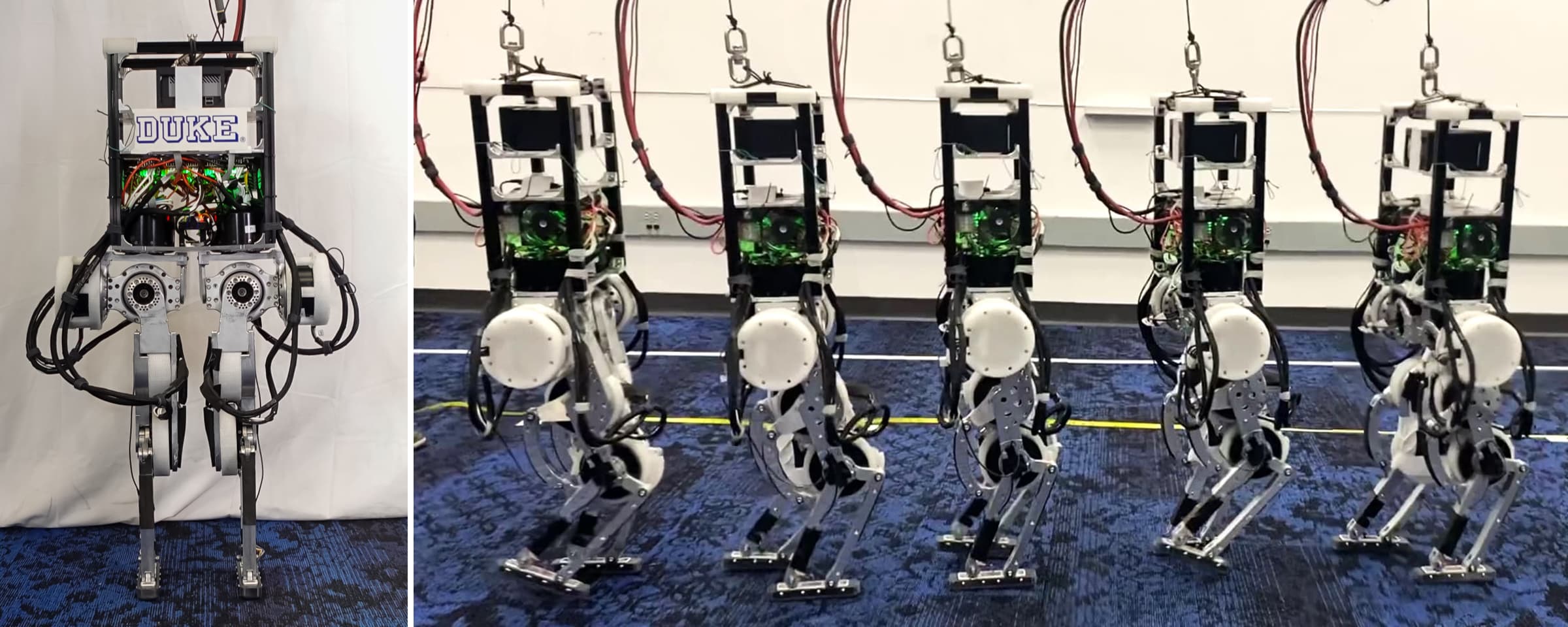
The Duke Humanoid: Design and Control For Energy Efficient Bipedal Locomotion Using Passive Dynamics
Boxi Xia,
Bokuan Li,
Jacob Lee,
Michael Scutari,
Boyuan Chen
Duke University
We present the Duke Humanoid, an open-source 10-degrees-of-freedom humanoid, as an extensible platform for locomotion research. The design mimics human physiology, with minimized leg distances and symmetrical body alignment in the frontal plane to maintain static balance with straight knees. We develop a reinforcement learning policy that can be deployed zero-shot on the hardware for velocity-tracking walking tasks. Additionally, to enhance energy efficiency in locomotion, we propose an end-to-end reinforcement learning algorithm that encourages the robot to leverage passive dynamics. Our experiment results show that our passive policy reduces the cost of transport by up to
🌐 Project website | 🎥 Video | 📄 Paper | 🔧 Hardware wiki
If you find our paper or codebase helpful, please consider citing:
@misc{xia2024dukehumanoiddesigncontrol,
title={The Duke Humanoid: Design and Control For Energy Efficient Bipedal Locomotion Using Passive Dynamics},
author={Boxi Xia and Bokuan Li and Jacob Lee and Michael Scutari and Boyuan Chen},
year={2024},
eprint={2409.19795},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.RO},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.19795},
}
.
├── control # contains the hardware control code
├── doc
├── legged_env # contains the simulation and RL code
├── LICENSE
└── README.md
Clone with submodules and follow the instructions in the respective submodules.
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/generalroboticslab/DukeHumanoidv1.git