Bioinformatics
Molecular biology examples using Python
dna_validation
DNA is made up of molecules called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar group and a nitrogen base. The four types of nitrogen bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C).
DNA sequence is valid if it contains only these bases, and it starts and ends with the appropriate nucleotide triplets.
rna_validation
RNA also contains four different bases and starts and ends with specific triplets. Three of these bases the same as in DNA: adenine, guanine, and cytosine. RNA contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
complementary_dna_strand
Two chains that make up a double helix of DNA, with corresponding positions on the two chains being composed of a pair of complementary bases, are complementary DNA strands.
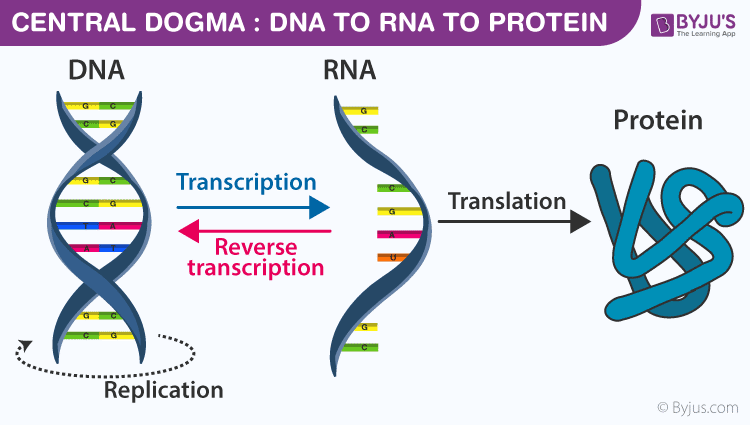
transcription
The central dogma of molecular biology describes the two-step process, transcription and translation, by which the information in genes flows into proteins: DNA → RNA → protein.
Transcription is the synthesis of an RNA copy of a segment of DNA.
translation
The process by which RNA is used to produce proteins is called translation.
The input used, BRCA1 is a human tumor suppressor gene (also known as a caretaker gene) and is responsible for repairing DNA
gene_mutation
A gene mutation is a permanent alteration in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene, such that the sequence differs from what is found in most people.
The example shows random mutation in the nucleotide sequence, which will be translated in a protein.