Git is a version control software designed by Linus Torvalds, thinking about the efficiency and reliability of maintaining application versions when they have a large number of code files.
- ✔️ Better teamwork
- ✔️ Control of changes in the project
- ✔️ Audit and reliability
- ✔️ Return to previous versions
- ✔️ Local & Remotes Repositories
- ▪️▪️▪️ And much more
Download
Linux Debian:$ sudo apt-get install git
Linux Fedora:$ sudo yum install git
Mac
Windows
You can write the commands in your CMD or in the git bash terminal
- 🔈 Everything in bold means that the value is relative, it changes according to each one.
- 🔈 Is not a finished version.
The easiest way you can contribute is by "starring" this project on GitHub! This will help you to "bookmark" the content so you can return to it. But it will also help the people who "follow" you on GitHub to discover that you find it interesting or useful.
The more people star and share the project, the more possible contributors are able to understand the value of contributing and open sourcing their knowledge!
![]() I will be grateful that you follow me
I will be grateful that you follow me ![]()
git --version
git config --global user.name "germancutraro"
git config —-global user.email “germancutraro@hotmail.com”
git config --global advice.detachedHead false
git config —-list
git config --list --global
git help
git help commit
git init
rm -rf .git
git add index.html
git add index.html index.js
git add .
git add *.txt
git add css/
git add -u
git add pdfs/*.pdf
git status
git status -s
git status -sb
git reset index.js
git reset *.xml
git commit -m 'navbar created'
git log
git log --oneline --decorate --all --graph
git config --global alias.lg "log --oneline --decorate --all --graph"
So now we can do: git lg for the pretty log command 👆
$ git init-> Initialize a local Git Repository$ git add <file>-> Add file to the Staging Area$ git status-> Check status of files in the working branch$ git commit-> Commit Changes$ git push-> Push to Remote Repository
git diff
git diff --staged
git checkout .
git checkout -- README.md
git commit -am 'README actualizado'
git commit --amend -m 'We edited the message!'
git reset --soft HEAD^
git reset --soft 39ae8e6
git reset --hard 39ae8e6
git reflog
git reset --hard 43809d4
git mv index.js app.js
git rm app.js
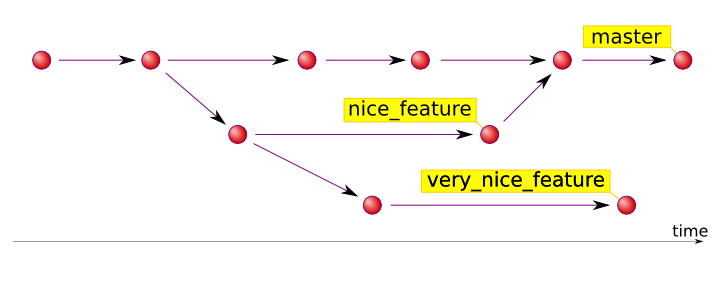
A branch is basically a new timeline that stores commits. They are used to develop functionalities independent of each other. The master branch is the default branch when you create a repository. Create new branches during development and merge them to the main branch when you finish.
git branch myBranch
git branch
git checkout myBranch
git checkout -b myBranch
git checkout master
git merge myBranch
git branch -d myBranch
git tag -a v1.0.0 -m "Version 1.0.0"
git tag -a v0.1.0 43809d4 -m 'Alpha Version'
git tag
git show v1.0.0
git tag -d v0.1.0
git stash
git stash list
git remote add origin yourRepo.git
git remove -v
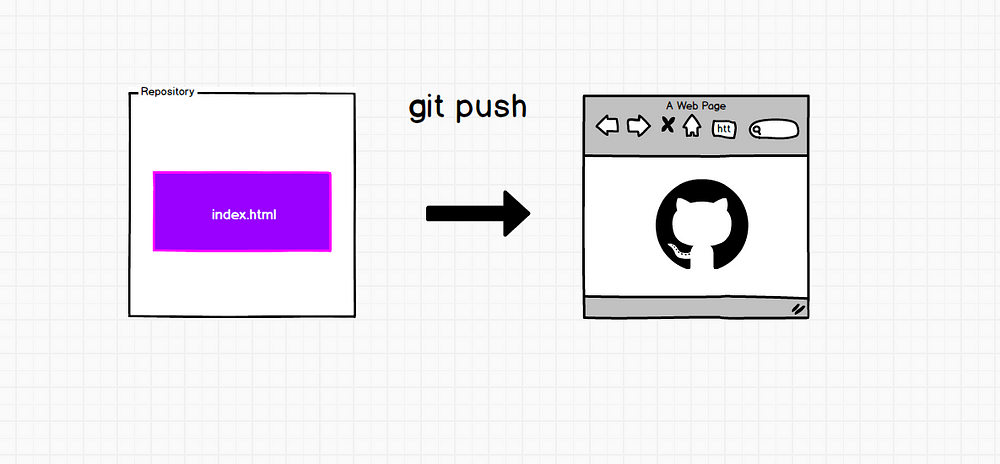
Once we have all our commits done and we have added the remote repository we can upload our files to Github:
git push -u origin master
But, as you can see, the tags are not uploaded with the git push command:
git push --tags
For this, you must create a .gitignore files, and there you can write the files and foulders that you dont want to upload to the github repository like:
node_modules package-lock.json
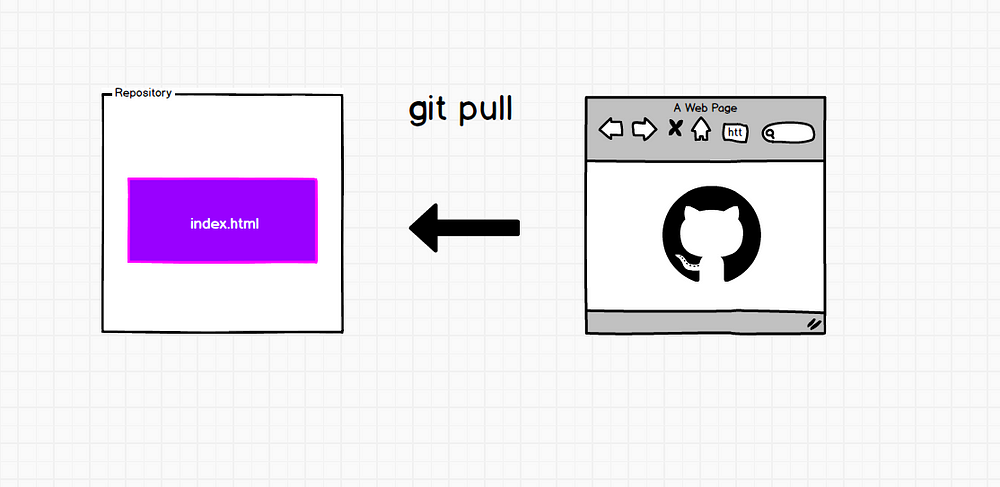
git pull
git clone repoUrl.git
git clone repoUrl.git my-folder