PACS is a plugin for Pritunl (https://github.com/pritunl/pritunl) with an additional web interface. With PACS you can add a compliance check when a client initiates a Pritunl VPN connection. The web interface gives you the ability to add mac addresses of devices that are allowed to connect with your vpn servers. When a client connects and it has an unknown mac address, the connection will be refused. Optionally you can check the state of your antivirus before connection is allowed. PACS currently supports Cylance antivirus (https://www.cylance.com). PACS can optionally integrate with SCCM to automatically import systems that have been added to
##Prerequisite: Setup Mongo DB Install Mongo DB
apt install mongodb-server
Connect to Mongo
mongo mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
Create a user in MongoDB
use admin
db.createUser(
{
user: "mongoadmin",
pwd: "mongopassword",
roles: ["userAdminAnyDatabase", "dbAdminAnyDatabase", "readWriteAnyDatabase"]
}
)
Under the hood PACS uses the flask-oidc (https://flask-oidc.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) package. This
is the only supported authentication mechanism. Authentication is fully federated, so PACS does
not have a local database with user credentials. PACS has been verified to work with Okta (https://www.okta.com),
but it should support all OIDC compatible identity providers. The below screen shots will show how to
configure PACS in Okta.
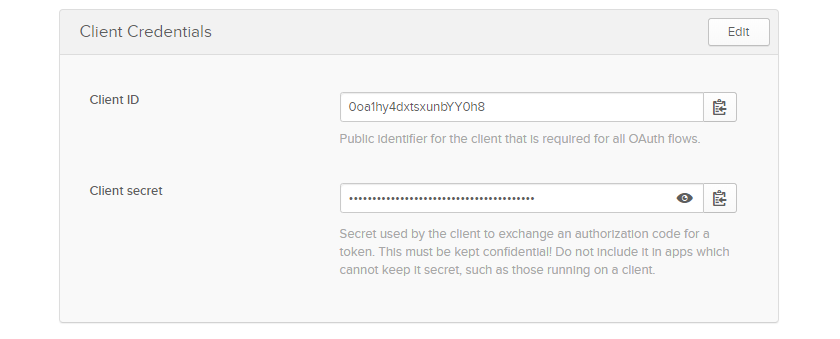
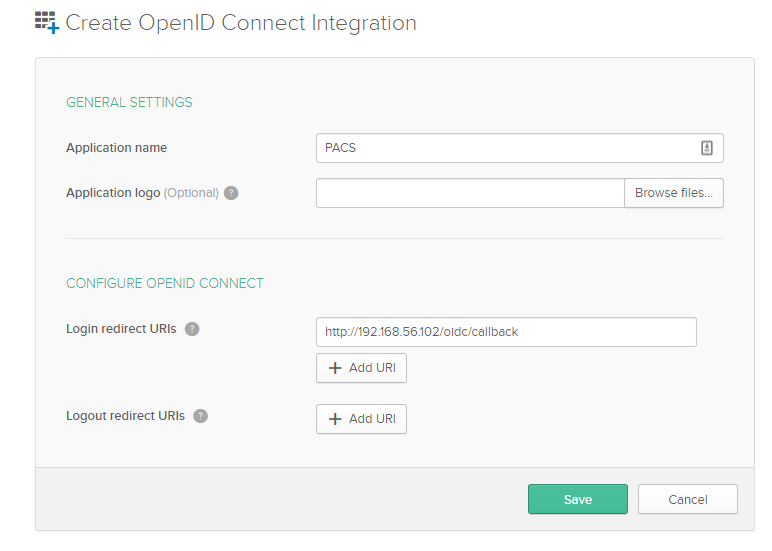 Please note: PACS (i.e. the login redirect url) should be served from HTTPS. The above screenshot
just shows how to configure Okta. The redirect_url should end with /oidc/callback. On the next page
you can copy the client_id and the client_secret. These values are needed when you configure PACS.
Please note: PACS (i.e. the login redirect url) should be served from HTTPS. The above screenshot
just shows how to configure Okta. The redirect_url should end with /oidc/callback. On the next page
you can copy the client_id and the client_secret. These values are needed when you configure PACS.
This has been tested with Debian 10.2 (i.e. Buster)
- Clone this codebase
cd /opt
git clone https://github.com/gerwout/pacs.git
- Install Python and other pre-requisites, also set the default Python to Python 3
apt install python3 python3-pip python3-dev python3-pip python3-venv libldap2-dev libsasl2-dev
pip3 install virtualenv virtualenvwrapper
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python2.7 1
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3.7 2
update-alternatives --config python
- Create pacs user
adduser --shell=/bin/false --disabled-password pacs
- Setup folder structure and switch to this new pacs user
chown -R pacs:pacs /opt/pacs
mkdir /opt/venvs
chown pacs:pacs /opt/venvs/
mkdir /etc/pacs
chown pacs:pacs /etc/pacs/
su -s /bin/bash pacs -
- Create virtual environment edit ~/.bashrc Add the following lines:
export WORKON_HOME=/opt/venvs
source /usr/local/bin/virtualenvwrapper.sh
Log out and log on to reload ~/.bashrc
exit
su -s /bin/bash pacs -
mkvirtualenv -p /usr/bin/python3 pacs-venv
cd /opt/pacs
pip3 install -r requirements_linux.txt
- Activate virtual environment
source /opt/venvs/pacs-venv/bin/activate
- Configure PACS
cp /opt/pacs/config_example.ini /etc/pacs/config.ini
cp /opt/pacs/client_secrets.json.example /etc/pacs/client_secrets.json
chown -R pacs:pacs /etc/pacs
su -s /bin/bash pacs -
PACS has 2 configuration files. The configuration file /etc/pacs/config.ini contains most of the configuration. The configuration file /etc/pacs/client_secrets.json contains settings related to your OIDC SSO provider. PACS has been succesfully integrated with Okta (https://www.okta.com), but it should be possible to use any OIDC compatible provider. Under the hood PACS uses the flask-oidc (https://flask-oidc.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) package. This is the only supported authentication mechanism. Authentication is fully federated, so PACS does not have a local database with user credentials. The below configuration shows the settings from config.ini. Adjust the below to cater for your needs.
[general]
# secret key that is used to sign the CSRF token and some other Flask internals, value should be difficult to predict
# do not use the below!
SECRET_KEY=ce84a559968c8c0f383a02712b5a3e18f10620ce
# secret key that is used for the signed JWT api traffic
# do not use the below!
SECRET_API_KEY=39f0808afea252f7f552152a163683fd
# lifetime in seconds for the CSRF token
WTF_CSRF_TIME_LIMIT=300
# where to store the HTTP sessions
SESSION_TYPE=filesystem
# This file controls if PACS compliance checks are enabled or not
# if it exists, we consider all systems compliant
PACS_STATUS_FILE=C/etc/pacs/pacs.down
[db]
# sqlite database file
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI=sqlite:////etc/pacs/app.db
# mongo db instance, this is used for audit trail and logging
MONGO_DB_URI=mongodb://mongoadmin:mongopassword@127.0.0.1:27017/
MONGO_DB_NAME=pacs
[sso]
# file that contains the OpenID client secrets
OIDC_CLIENT_SECRETS=/etc/pacs/client_secrets.json
# sets secure cookie property, set to True when HTTPS
# when you are using HTTP (which you should not!) and this option is set to True, you will get in
# an endless redirect towards your identity provider
OIDC_COOKIE_SECURE=False
OIDC_CALLBACK_ROUTE=/oidc/callback
OIDC_ID_TOKEN_COOKIE_NAME=oidc_token
# url where to redirect after logout
LOGOUT_REDIRECT=https://makesomethingup.com
# When PACS is behind a reverse proxy like Nginx, you need to set the callback url
OVERWRITE_REDIRECT_URI=https://<pacs domain name>/oidc/callback
/etc/pacs/client_secrets.json contains the details from your identity provider (i.e. client id, client secret, etc.)
{
"web": {
"client_id": "<copy your Okta client id>",
"client_secret": "<copy your Okta client secret>",
"auth_uri": "https://<okta tenant name>.okta.com/oauth2/default/v1/authorize",
"token_uri": "https://<okta tenant name>.okta.com/oauth2/default/v1/token",
"issuer": "https://<okta tenant name>.okta.com/oauth2/default",
"redirect_uris": [
"http://192.168.56.102:5000/oidc/callback"
]
}
}
- Setup database
cd /opt/pacs/
flask db migrate
flask db upgrade
- Start application using gunicorn
pip3 install wheel gunicorn
/opt/venvs/pacs-venv/bin/gunicorn app:app -b 0.0.0.0:5000
Please note: On production systems you most likely don't want to bind to all network interfaces (i.e. 0.0.0.0). Let it run at 127.0.0.1:5000 instead and use a reverse proxy like Nginx to expose it to the outside world.
- Install PACS as a systemd service
cp /opt/pacs/deployment/systemd/pacs.service /etc/systemd/system/pacs.service
chmod 755 /etc/systemd/system/pacs.service
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable pacs
systemctl start pacs
- Install NGINX as a reverse proxy and configure HTTPS using Letsencrypt
apt install nginx
openssl dhparam -out /etc/nginx/dhparams.pem 4096
apt install python-certbot-nginx
# the below command will setup a valid Letsencrypt certificate, that will auto renew every 90 days
# the domain name already needs to resolve to the ip address of the server that is hosting PACS.
certbot --nginx -d <domain name that will be used for PACS>
cp /opt/pacs/deployment/nginx/vhost.conf /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
# edit /etc/nginx/sites-evailable/default (i.e. you need to adjust the servername and the letsencrypt
# private key and certificate location)
systemctl enable nginx
systemctl start nginx
PACS has support to import systems from System Center Configuration Manager. This is a Microsoft product that has all the hardware information from all the computers that are joined to your domain. To be able to configure PACS with SCCM support an active directory service user needs to be created. This user needs to be able to query your active directory using (secure) LDAP and it needs to be able to do WMI queries towards your SCCM server. PACS will read the description that has been set in active directory. It will also detect if a system is still available in SCCM, but no longer in active directory.
- Prerequisites
PACS uses the WMI protocol to communicate with SCCM. When running on a Windows system, PACS will use the Python WMI module to communicate. This module does not function on Linux systems. To be able to use PACS on a Linux system, it uses the wmi-client-wrapper-py3 (https://pypi.org/project/wmi-client-wrapper-py3/) module. This module uses the wmic command that can be found in the Greenbone OpenVAS SMB library (https://github.com/greenbone/openvas-smb/releases). You can compile this binary from source on a Debian system like this.
apt install cmake gcc cmake pkg-config gcc-mingw-w64 libgnutls28-dev perl-base heimdal-dev libpopt-dev libglib2.0-dev libsqlite3-dev
wget https://github.com/greenbone/openvas-smb/archive/v1.0.5.tar.gz
tar -zxvf v1.0.5.tar.gz
cd openvas-smb-1.0.5
mkdir /opt/smb
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
cp wmi/wmic /usr/bin
- Configure SCCM integration
Edit /etc/pacs/config.ini and add the following section:
[ldap]
# LDAP/Active directory endpoint
LDAP_END_POINT=ldaps://name.domain:3269
# LDAP/Active directory username
LDAP_USER=domain\username
# LDAP/Active directory password
LDAP_PASS=difficult_to_guess
# needs to be in "distinguished name" format
LDAP_SEARCH_START=dc=domain,dc=local
# When True, will check the issuer that is set with LDAP_CA_CERT_ISSUER option
LDAP_REQUIRE_VALID_CERT=True
# BASE64 encoded root certificate reference, used when LDAP_REQUIRED_VALID_CERT=True
LDAP_CA_CERT_ISSUER=/etc/pacs/root_ca_server.crt
[sccm]
# Show import button in web interface
SCCM_SHOW_BUTTON=True
# hostname sccm server
SCCM_END_POINT=<ip address sccm server>
# SCCM Namespace (i.e. ROOT\SMS\sitename), you can find it with wmi control mmc snapin
SCCM_NAME_SPACE=ROOT\SMS\site_name
# sccm user
SCCM_USER=domain\username
# sccm passwords
SCCM_PASS=difficult_to_guess
PACS currently supports integration with a single domain controller (please note: a future version will most likely support multiple domain controllers). It is adviced to set LDAP_REQUIRE_VALID_CERT to True. This will check if the domain controller has a valid certificate. The local certificate authority that has issued the certificate needs to be configured in the LDAP_CA_CERT_ISSUER configuration option. If your domain controller is using a self signed certificate (i.e. default behaviour when you don't have installed PKI infrastructure) you need to set this certificate as the certificate issuer. You can obtain the certificate using the following command:
openssl s_client -connect <hostname domain controller>:3269 -showcerts
You need to copy the content starting with -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- and it ends with -----END CERTIFICATE-----. The LDAP_SEARCH_START configuration option determines where it searches for computer objects in active directory.
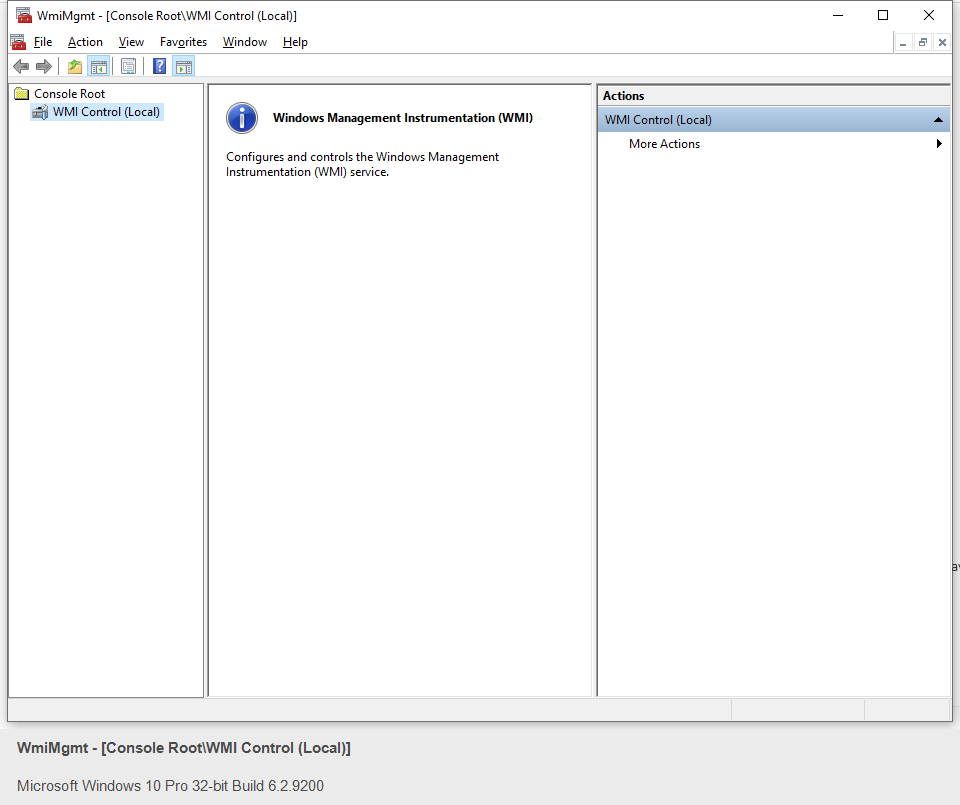
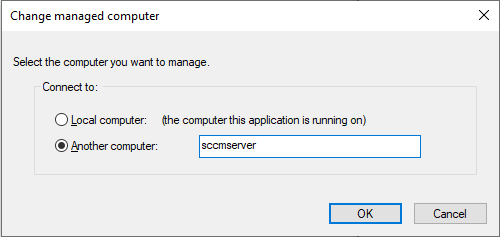
- How to determine the SCCM_NAME_SPACE? You can setup multiple sites in SCCM. There are different ways to determine the namespace that you'll want to use. This documentation describes how to do this with the wmimgmt.msc mmc snap-in. You'll need to start this snap-in as a user that has permissions to query the SCCM server.
Go to Action -> Connect to other computer ...
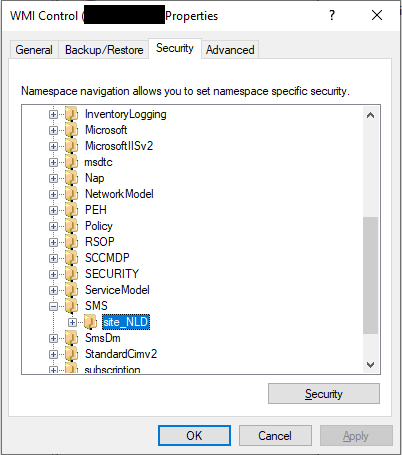
Right click WMI control and select properties, click the security tab.
You can find your site names under ROOT\SMS. In the above example the namespace needs to be configured as ROOT\SMS\site_NLD.
- Automate SCCM/Active directory import using a cron job
crontab -u pacs -e
# add the following entry
export PYTHONPATH=/opt/pacs && cd /opt/pacs/ && /opt/venvs/pacs-venv/bin/python /opt/pacs/app/import_from_sccm.py
This will add a cron job for the pacs user that runs every 4 hours.
Copy all the files from the pritunl_plugin directory to the Pritunl plugin directory (Usually located at /var/lib/pritunl/plugins) on all your Pritunl servers.
- Install the requirements
/usr/lib/pritunl/bin/pip install -r requirements.txt - Rename config.ini.example to config.ini and edit the configuration
The API_SECRET_KEY configuration option needs to have the same value as the SECRET_API_KEY configuration option that is defined in the config.ini from the PACS web interface. This is a shared secret that is used to sign the API traffic. The COMPLIANCE_URL configuration setting needs to point to the API interface from PACS. This is by default the /check-compliance url (i.e. https://pacs.example.com/check-compliance).
- Stop and start Pritunl
systemctl stop pritunl
systemctl start pritunl