This repo contains some example assets to evaluate how to use Google Cloud Code, Cloud Build, Cloud Deploy and Skaffold to automate software delivery and promote releases through multiple stages on GCP.
Using these assets and following the instructions in this blog article you can experiment an example flow where:
- A developer forks the application repo in his Github account
- The developer makes a change to the code using Cloud Shell Editor and Cloud Code, the change is immediately deployed in his dev cluster running in minikube in the Cloud Shell
- When he is happy with the change he opens a pull request to the main repo
- QA team makes a specific comment to the PR and this automatically executes a Cloud Build trigger that builds a container with Skaffold, creates a release on Cloud Deploy and rolls it out in a QA GKE cluster where usability tests can be run
- After the QA team is happy, the PR is merged and this runs another trigger that promotes the release to a Prod GKE Cluster. The Cloud Deploy prod target requires approval so an approval request is triggered, the App Release team checks the rollout and approves it so the app is released in production with a canary release at 50%
- After checking the canary release the App Release team advances the rollout to 100%
- A GCP project with GKE, Cloud Build, Cloud Deploy, Artifact Registry APIs enabled
- A main Google user account with project owner role on the project that will be used as someone from Platform Team / QA / App Release team
- A Github account
- An additional Google user account that will be used as the 'developer', this account should also have a separate Github account to fork the repo in
- Create 2 GKE Clusters with Anthos Service Mesh enabled: one for the QA environment and the other for the prod environment, both in the same location (zone or region).
- Apply K8s Gateway API CRDs to both clusters:
kubectl get crd gateways.gateway.networking.k8s.io &> /dev/null || \
{ kubectl kustomize "github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/config/crd?ref=v0.6.1" | kubectl apply -f -; }
- Create an Artifact Registry Repository to store your images
- Fork this repo to your Github account and clone locally, this will be used as the application repo for the tutorial
- Run setup.sh from the local repo clone and follow prompt to insert your GCP project, cluster names and location, Artifact Registry repository, Cloud Deploy delivery pipeline region. Then commit and push to your fork.
- Apply gateway.yaml to both clusters to create a Gateway resource using the Istio Ingress Class
- Create a Cloud Deploy delivery pipeline using the manifest provided. It will create a pipeline that has qa and prod as stages each using a profile with the same name and 2 targets mapping the above clusters to the pipeline stages.
- Run createrelease.sh to build your image and create your 1st Cloud Deploy release
- Promote your first release to stable phase in prod stage in Cloud Deploy from GCP Console, approve the promotion if needed
- Create 2 Cloud Build triggers linked to your fork of the Github repo:
- The 1st trigger must be invoked by a pull request with Comment control enabled and use the build-qa.yaml build config
- The 2nd trigger must be invoked by a push to the main branch and should use the release-prod.yaml build config
- Create 1 additional Chrome profile (or use Chrome Incognito window), this will be used for the developer tasks, from this Chrome profile or window:
- Log in to the additional Github account
- Create another fork of the repo (this will be the developer fork in the flow) from the one forked by the main account
- Log in to Google Cloud Shell
- Configure personal access token for Github account
- Clone the fork of the repo locally
- Move in the local repo folder and launch Cloud Shell Editor with the repo folder added to his workspace with the command
cloudshell workspace .
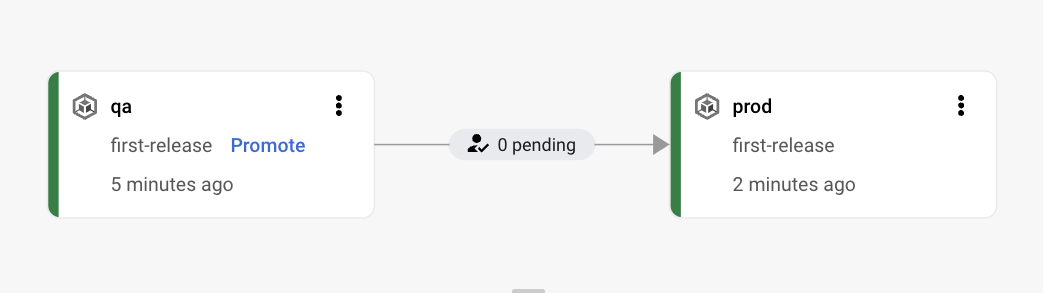
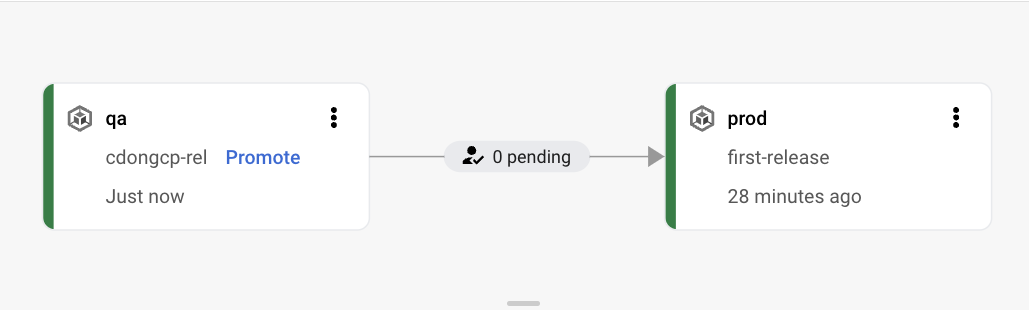
- Open Cloud Deploy in GCP console and explore/show the cd-on-gcp-pipeline delivery pipeline: a release named first-release has been rolled out to qa and prod stages
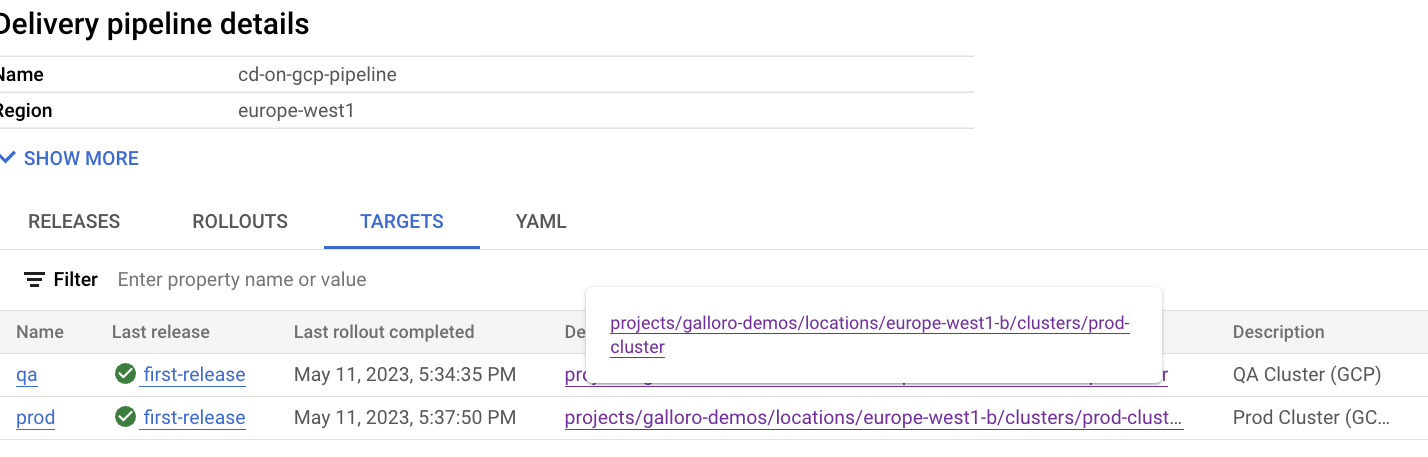
- Explore the targets, click on the prod-cluster link under 'Deployment Targets', the production GKE cluster GCP console page will open
- Get the Gateway resource IP of your prod cluster with
kubectl get gtw, put it into a browser, you will see that your application is deployed in production:
- From the developer Cloud shell editor in the developer Chrome window launch minikube (in the lower blue Cloud Code bar click minikube and choose minikube in the upper window that should be the only option, and then Start)
- If asked, click AUTHORIZE on the Authorize Cloud Shell prompt
- Click on the Cloud Code status bar (in the lower left corner) and then select Run on Kubernetes
- When asked for the Skaffold profile choose [default]
- In the Output pane you see that the build start for the cdongcp-app application image
- When deployment is complete Skaffold/Cloud Code will print the exposed url where the services have been forwarded, click the link and then Open web preview
- You see the app frontpage displaying this message:
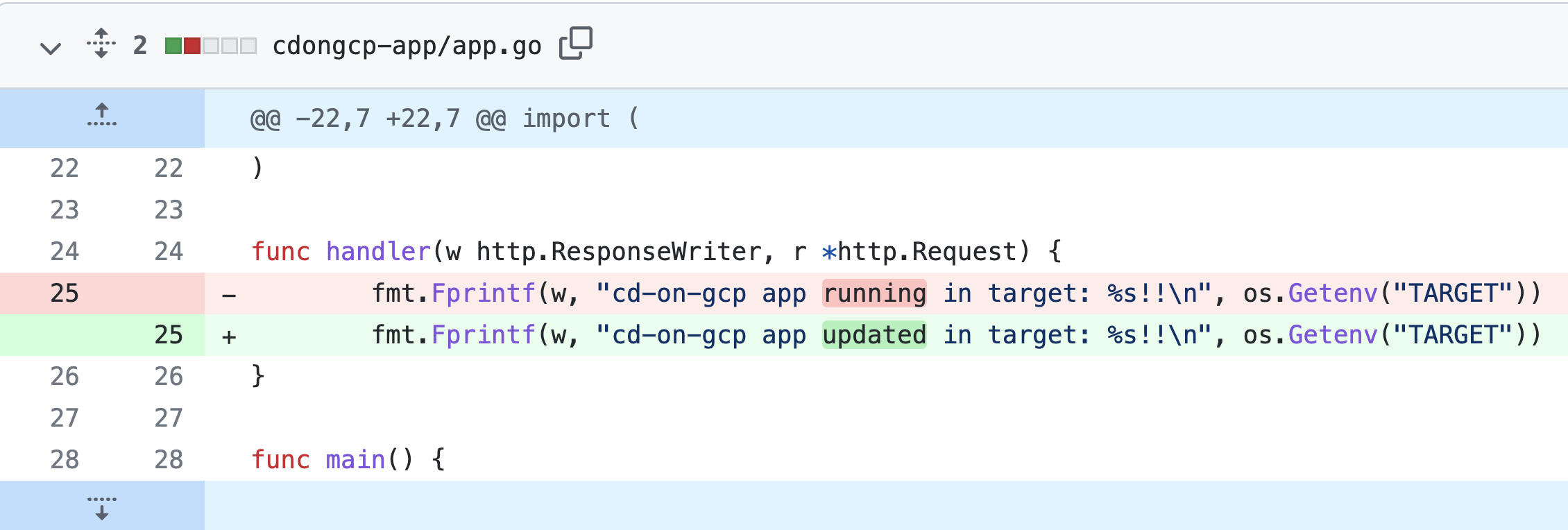
- Now, let’s try to update the application to see the change implemented immediately in the deployment on the cluster, open the app.go file in cdongcp-app folder in Cloud Shell Editor
- Change the message in row 25 to “
cd-on-gcp app updated in target: …”, you should see the build and deployment process starting immediately - At the end of the deploy click again on the forwarded url or refresh the browser window with the application to see your change deployed
-
After the developer is happy with the change he wants to commit so, execute:
git add cdongcp-app/app.go git commit -m "new feature" git push -
Go on the developer github page containing the repository and create a pull request
-
You will see that some check fails because the Cloud Build Trigger require a comment from the central repo owner (QA team)
-
From the main browser window (the one with your main account logged), go to the repository on Github, click on the new-feature PR, examine code changes, you ar acting as the QA team at the moment
- In the conversation, write
/gcbrunin a new comment, this will make the Cloud Build Trigger configured in build-qa.yaml run, you will see checks running on Github. As you can see from the build config file, this build will:- Build a container image with your updated code using
skaffold build - Store the image in your Artifact Registry repository
- Create a Cloud Deploy Release (this will automatically roll out the release in the 1st stage of the pipeline that is the QA Cluster)
- Build a container image with your updated code using
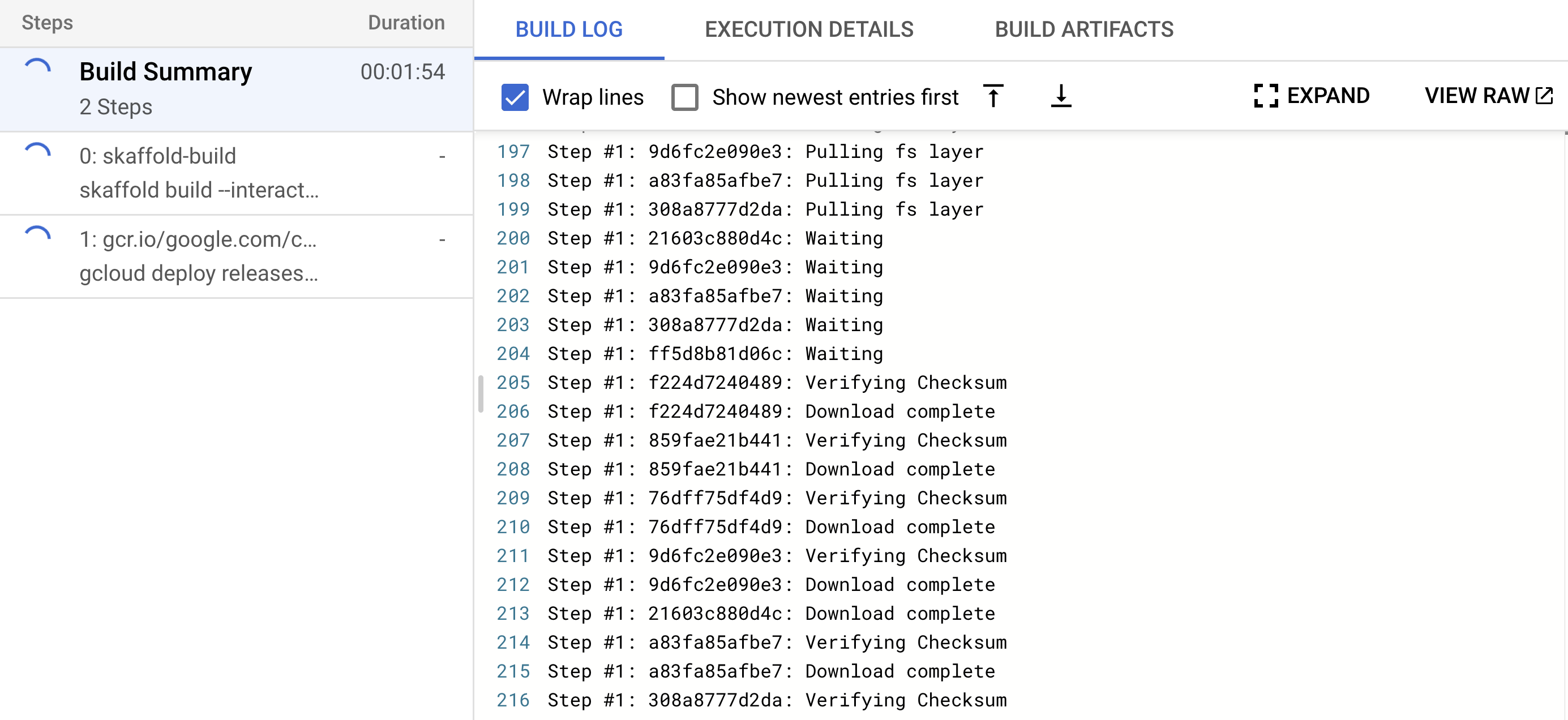
- Go to Cloud Build History, you will see a build running, click on it, you will see the logs
- After the build completes you should be able to see your container image uploaded to your Artifact Registry repository, the image tag will be the repository commit id
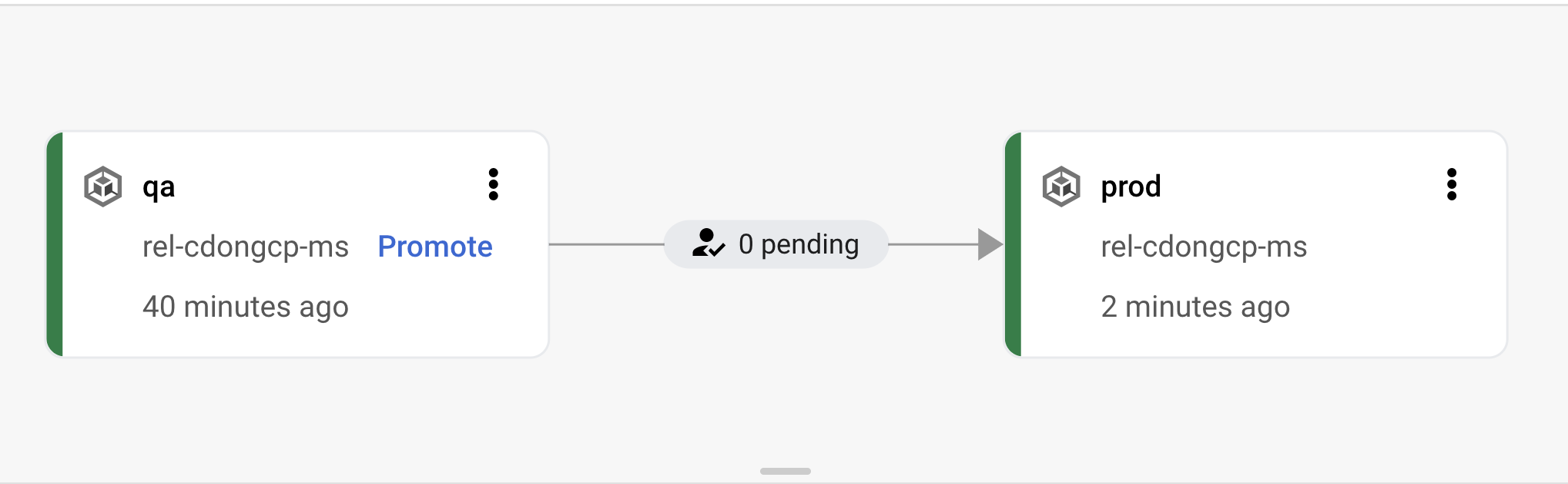
- From the GCP Console, go to Cloud Deploy, you should see your rollout completed (or in progress) to the QA stage of the pipeline
- Get the Gateway resource IP of your QA cluster with
kubectl get gtw, put it into a browser, you will see the updated version of your application deployed in QA environemnt:
- Let’s pretend that the QA team performs some usability test now, when they are happy, go back to the Github page from your main account and merge the PR
- This will cause the execution of the trigger linked to the release-prod.yaml build, promoting the previously created release to the prod environment. If you go back to Cloud Build history you should see a new build running
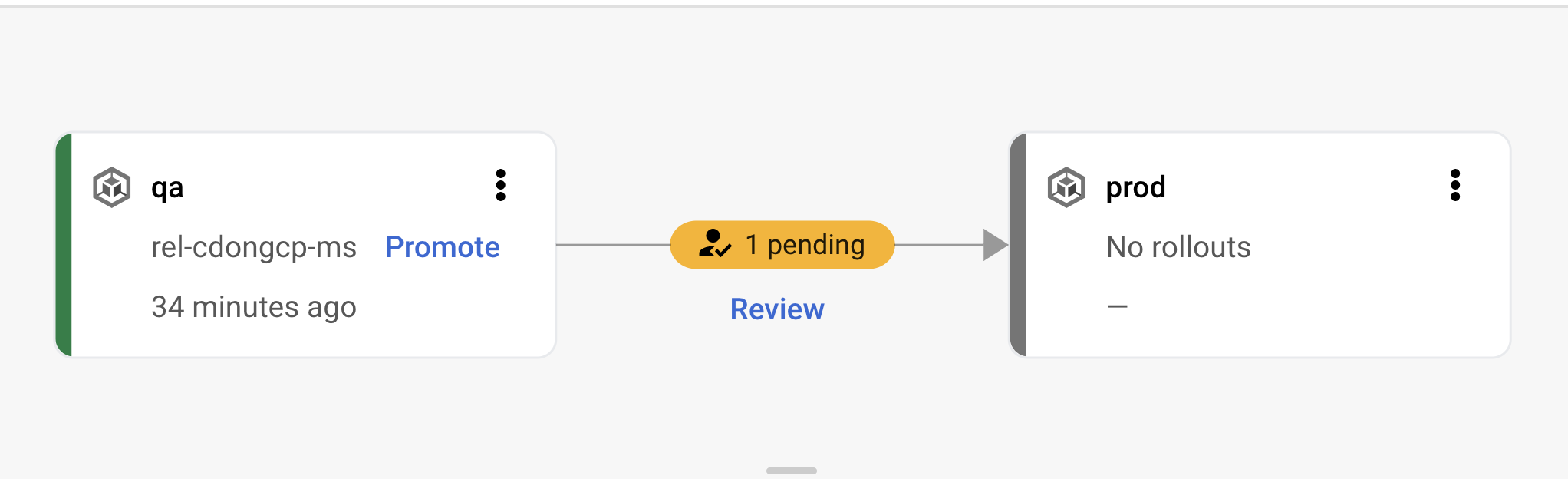
- After the build completes you will see an approval request in the Cloud Deploy pipeline
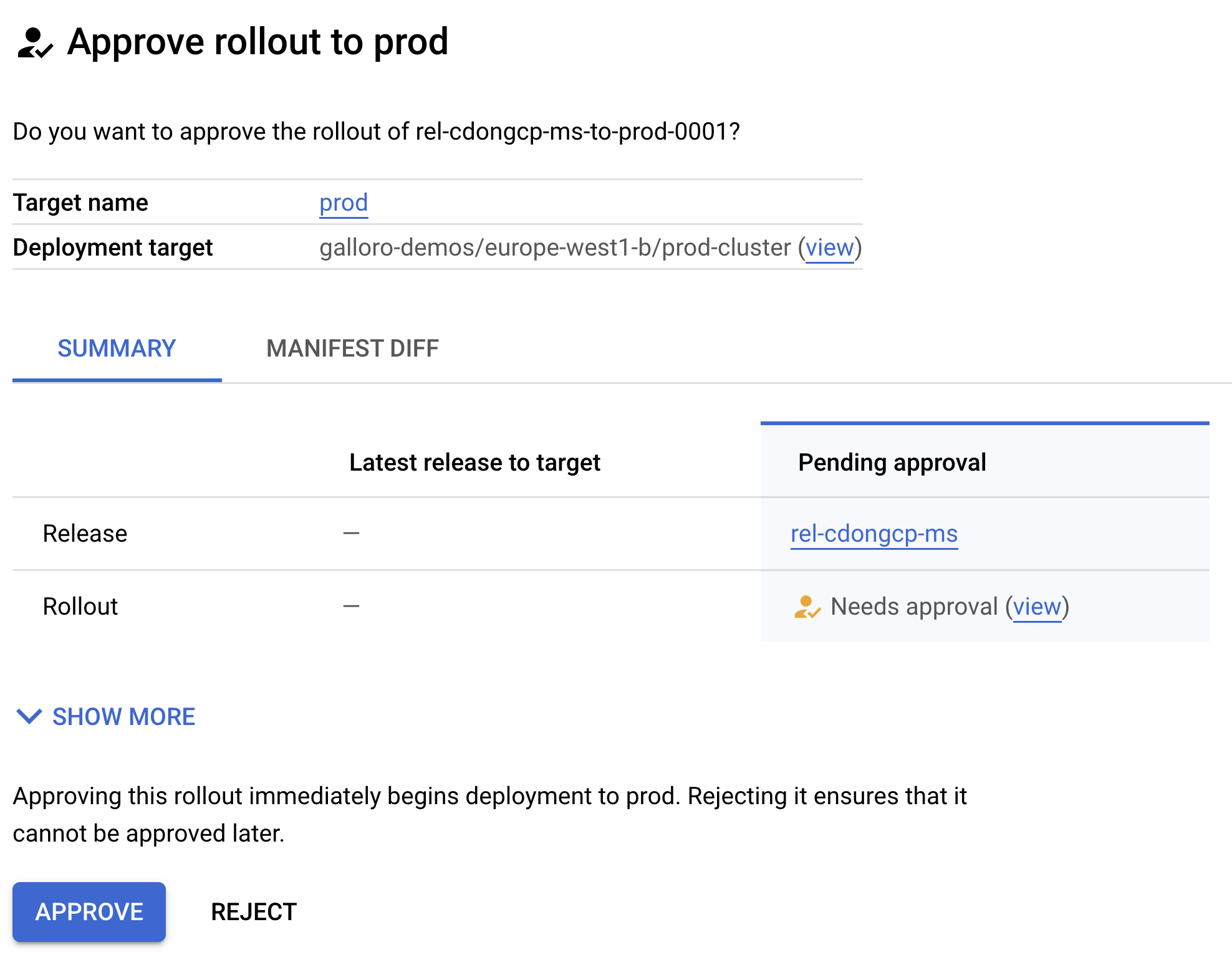
- Click on Review, you will see a rollout that Needs approval, click on Review again
- Click on the Approve button
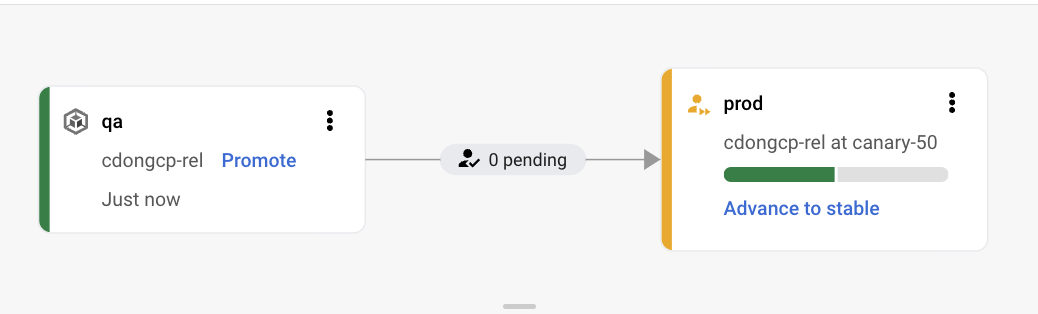
- If you go back to the Delivery Pipeline visualization in Cloud Deploy you will see the rollout deployed to canary phase
- Get the Gateway resource IP of your prod cluster and execute the following command from a terminal (replace x.x.x.x with your gateway IP address):
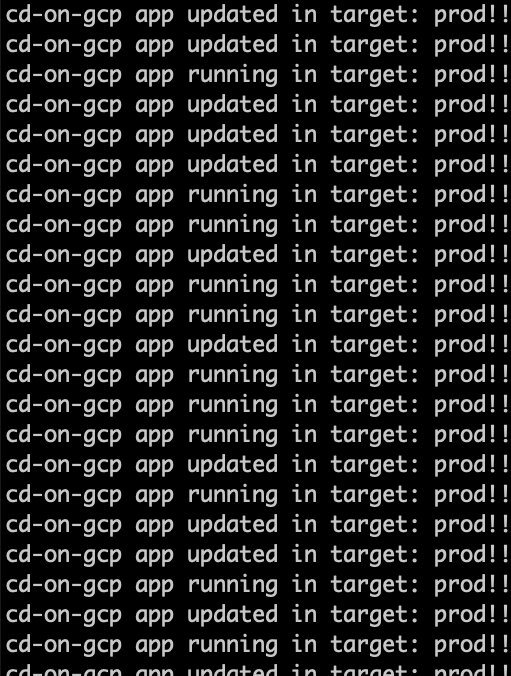
"while true;do curl x.x.x.x;done", you should see responses both from the old and new (canary) version since your canary strategy has been set at 50% in the delivery pipeline, keep the curl command running.
-
Click on Advance to stable, then click Advance, your rollout will advance to the stable phase and your application will be completely replaced with the updated version as you can see from the curl responses.
-
If you go back to the Delivery Pipeline visualization in Cloud Deploy you will see the rollout deployed in prod.
- If you get with a browser to the IP of your Gateway in the prod cluster, you will see the updated version of your application deployed in the prod environemnt: