Implementation of paper - YOLOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information
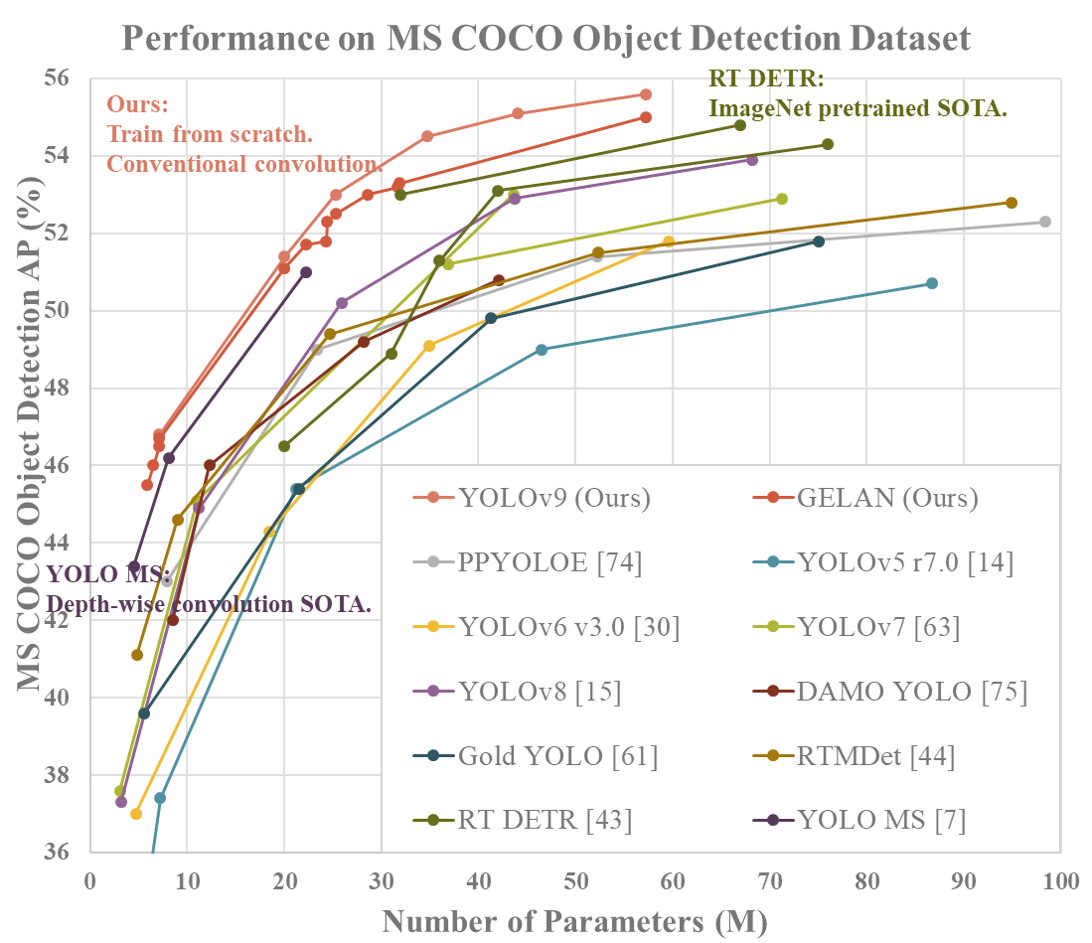
MS COCO
| Model | Test Size | APval | AP50val | AP75val | Param. | FLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv9-S | 640 | 46.8% | 63.4% | 50.7% | 7.2M | 26.7G |
| YOLOv9-M | 640 | 51.4% | 68.1% | 56.1% | 20.1M | 76.8G |
| YOLOv9-C | 640 | 53.0% | 70.2% | 57.8% | 25.5M | 102.8G |
| YOLOv9-E | 640 | 55.6% | 72.8% | 60.6% | 58.1M | 192.5G |
Expand
Custom training: WongKinYiu#30 (comment)
ONNX export: WongKinYiu#2 (comment) WongKinYiu#40 (comment)
TensorRT inference: WongKinYiu#34 (comment) WongKinYiu#79 (comment)
Hugging Face demo: WongKinYiu#45 (comment)
CoLab demo: WongKinYiu#18
ONNXSlim export: WongKinYiu#37
YOLOv9 ByteTrack: WongKinYiu#78 (comment)
AnyLabeling tool: WongKinYiu#48 (comment)
Docker environment (recommended)
Expand
# create the docker container, you can change the share memory size if you have more.
nvidia-docker run --name yolov9 -it -v your_coco_path/:/coco/ -v your_code_path/:/yolov9 --shm-size=64g nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:21.11-py3
# apt install required packages
apt update
apt install -y zip htop screen libgl1-mesa-glx
# pip install required packages
pip install seaborn thop
# go to code folder
cd /yolov9yolov9-c.pt yolov9-e.pt gelan-c.pt gelan-e.pt
# evaluate yolov9 models
python val_dual.py --data data/coco.yaml --img 640 --batch 32 --conf 0.001 --iou 0.7 --device 0 --weights './yolov9-c.pt' --save-json --name yolov9_c_640_val
# evaluate gelan models
# python val.py --data data/coco.yaml --img 640 --batch 32 --conf 0.001 --iou 0.7 --device 0 --weights './gelan-c.pt' --save-json --name gelan_c_640_valYou will get the results:
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.530
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.702
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.578
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.362
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.585
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.693
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 1 ] = 0.392
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 10 ] = 0.652
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.702
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.541
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.760
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.844
Data preparation
bash scripts/get_coco.sh- Download MS COCO dataset images (train, val, test) and labels. If you have previously used a different version of YOLO, we strongly recommend that you delete
train2017.cacheandval2017.cachefiles, and redownload labels
Single GPU training
# train yolov9 models
python train_dual.py --workers 8 --device 0 --batch 16 --data data/coco.yaml --img 640 --cfg models/detect/yolov9-c.yaml --weights '' --name yolov9-c --hyp hyp.scratch-high.yaml --min-items 0 --epochs 500 --close-mosaic 15
# train gelan models
# python train.py --workers 8 --device 0 --batch 32 --data data/coco.yaml --img 640 --cfg models/detect/gelan-c.yaml --weights '' --name gelan-c --hyp hyp.scratch-high.yaml --min-items 0 --epochs 500 --close-mosaic 15Multiple GPU training
# train yolov9 models
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --master_port 9527 train_dual.py --workers 8 --device 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 --sync-bn --batch 128 --data data/coco.yaml --img 640 --cfg models/detect/yolov9-c.yaml --weights '' --name yolov9-c --hyp hyp.scratch-high.yaml --min-items 0 --epochs 500 --close-mosaic 15
# train gelan models
# python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 4 --master_port 9527 train.py --workers 8 --device 0,1,2,3 --sync-bn --batch 128 --data data/coco.yaml --img 640 --cfg models/detect/gelan-c.yaml --weights '' --name gelan-c --hyp hyp.scratch-high.yaml --min-items 0 --epochs 500 --close-mosaic 15Under construction.
@article{wang2024yolov9,
title={{YOLOv9}: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information},
author={Wang, Chien-Yao and Liao, Hong-Yuan Mark},
booktitle={arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.13616},
year={2024}
}
@article{chang2023yolor,
title={{YOLOR}-Based Multi-Task Learning},
author={Chang, Hung-Shuo and Wang, Chien-Yao and Wang, Richard Robert and Chou, Gene and Liao, Hong-Yuan Mark},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.16921},
year={2023}
}
Parts of code of YOLOR-Based Multi-Task Learning are released in the repository.