This repository provides the software for control of the AR3 arm with ros_control and MoveIt. I hope to provide fellow robotic arm enthusiasts with a starting point to explore using ROS for controlling the arm. The baseline implementation is designed to accomodate the original hardware and firmware, including the message structures for communication. Moving forward, I will do my best to continue to keep it accessible. I plan to explore some interesting concepts that I have in mind for on-arm vision, grippers and human-robot interaction and I will share my projects here if possible.
You may also wish to check out some hardware modifications that I've made for joint encoders at ar3_hardware_mods.
-
ar3_control
- Controlling the arm through the MoveIt user interfaces
- Provides demo for the move group interface
-
ar3_description
- Hardware description of arm, urdf etc.
-
ar3_hardware_interface
- ROS interface for the hardware driver, built on the ros_control framework
- Manages joint offsets, limits and conversion between joint and actuator messages
-
ar3_hardware_drivers
- Handles communication with the motor controllers
-
ar3_microcontrollers
- Firmware for the motor controller ie. Teensy
-
ar3_moveit_config
- MoveIt module for motion planning
- Controlling the arm through Rviz
-
ar3_gazebo
- Simulation on Gazebo
Actively developed and tested on ROS Melodic on Windows 10 with limited testing on Ubuntu 18.04.
-
Install ROS Melodic and MoveIt for Windows 10
-
Create the ROS workspace
ie. ar3_wsmd C:\ar3_ws\src && C:\ar3_ws\src -
Clone this repository into the workspace
src:git clone https://github.com/ongdexter/ar3_core.git .The workspace directory should be as such:
ar_ws +-- src | +-- ar3_control | +-- ar3_description | +-- ... -
Build the workspace:
cd ~/ar3_ws catkin_make -
Source the workspace
call C:\ar3_ws\setup.batYou can add this to the ROS Command Window shortcut that you created during the ROS installation, by appending
&& c:\ar3_ws\devel\setup.batto the shortcut target, so that it is automatically run each time a new terminal is opened.
-
Install ROS Melodic and MoveIt for Ubuntu 18.04
-
Create the ROS workspace
ie. ar3_wsmkdir -p ~/ar3_ws/src && cd "$_" -
Clone this repository into the workspace
src:git clone https://github.com/ongdexter/ar3_core.git .The workspace directory should be as such:
ar_ws +-- src | +-- ar3_control | +-- ar3_description | +-- ... -
Install workspace dependencies:
cd ~/ar3_ws rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y -
Build the workspace:
catkin_make -
Source the workspace:
source ~/ar3_ws/devel/setup.bashYou can add this to your .bashrc so that it is automatically run each time a new terminal is opened:
echo "source ~/ar3_ws/devel/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc -
Enable serial port access if you haven't already done so:
sudo addgroup $USER dialoutYou will need to log out and back in for changes to take effect.
-
Hardware interface
- Set the serial port and baudrate in
ar3_hardware_interface/config/hardware_driver.yaml
- Set the serial port and baudrate in
-
Teensy Sketch
- Both teensy sketches provided are compatible with the default hardware. Refer to the module for more information.
There are two modules that you will always need to run:
-
Arm module - this can be for either a real-world or simulated arm
- For controlling the real-world arm, you will need to run the
ar3_hardware_interfacemodule - For the simulated arm, you will need to run the
ar3_gazebomodule - Either of the modules will load the necessary hardware descriptions for MoveIt
- For controlling the real-world arm, you will need to run the
-
MoveIt module - the
ar3_moveit_configmodule provides the MoveIt interface and RViz GUI, and thear3_controlmodule provides the MoveIt user interface for programmatically setting goals
The various use cases of the modules and instructions to run them are described below:
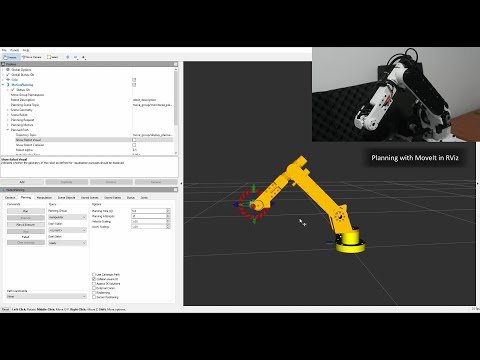
If you are unfamiliar with MoveIt, it is recommended to start with this to explore planning with MoveIt in RViz. This contains neither a real-world nor a simulated arm but just a model loaded within RViz for visualisation.
- The robot description, moveit interface and RViz will all be loaded in the single demo launch file
roslaunch ar3_moveit_config demo.launch
-
Start the
ar3_hardware_interfacemodule, which will load configs and the robot descriptionroslaunch ar3_hardware_interface ar3_hardware_bringup.launchThe hardware interface will also start the hardware driver and initialise communication with the Teensy. You can skip the joint encoder calibration sequence with the
use_existing_calibrationsargument when starting the node
ie.roslaunch ar3_hardware_interface ar3_hardware_bringup.launch use_existing_calibrations:=true. -
Start MoveIt and RViz
roslaunch ar3_moveit_config ar3_moveit_bringup.launch
You can now plan in RViz and control the real-world arm. Joint commands and joint states will be updated through the hardware interface.
- Start the
ar3_gazebomodule, which will start the Gazebo simulator and load the robot descriptionroslaunch ar3_gazebo ar3_gazebo_bringup.launch - Start Moveit and RViz
roslaunch ar3_moveit_config ar3_moveit_bringup.launch
You can now plan in RViz and control the simulated arm.
It is recommended to run this demo with the simulated arm first to make sure that the programmed goals are safe for your environment (and your arm). Needless to say, the same applies when programming your own tasks.
This is a demo modified from the official MoveIt tutorials. As opposed to manually setting goals through RViz, the move group interface allows us to programmatically plan and execute movements, and provides more functionality such as specifying path constraints and planning Cartesian movements. This also enables much more complex tasks, planning around obstacles etc.
- Start the
ar3_gazebomodule, which will start the Gazebo simulator and load the robot description
For controlling the real-world arm, you will just need to runar3_hardware_interfaceinstead ofar3_gazeboas described above.roslaunch ar3_gazebo ar3_gazebo_bringup.launch - Start Moveit and RViz
roslaunch ar3_moveit_config ar3_moveit_bringup.launch - Start the move group demo
Follow the command-line instructions to step through the demo. See
roslaunch ar3_control move_group_demo.launchar3_controlfor more details.