climateR simplifies the steps needed to get climate data into R. At
its core it provides three main things:
- A climate catalog of over 100,000k datasets from over 2,000 data providers/archives. See (climateR::params)
nrow(params)
#> [1] 107857
length(unique(params$id))
#> [1] 2075
length(unique(params$asset))
#> [1] 4653-
A general toolkit for accessing remote and local gridded data files bounded by space, time, and variable constraints (
dap,dap_crop,read_dap_file) -
A set of shortcuts that implement these methods for a core set of selected catalog elements
remotes::install_github("mikejohnson51/AOI") # suggested!
remotes::install_github("mikejohnson51/climateR")library(AOI)
library(climateR)
library(tidyterra)
library(ggplot2)
library(terra)
library(tidyr)
library(sf)The climateR package is supplemented by the
AOI framework established in the
AOI R package.
To get a climate product, an area of interest must be defined:
AOI = aoi_get(state = "NC")
plot(AOI$geometry)Here we are loading a polygon for the state of North Carolina More examples of constructing AOI calls can be found here.
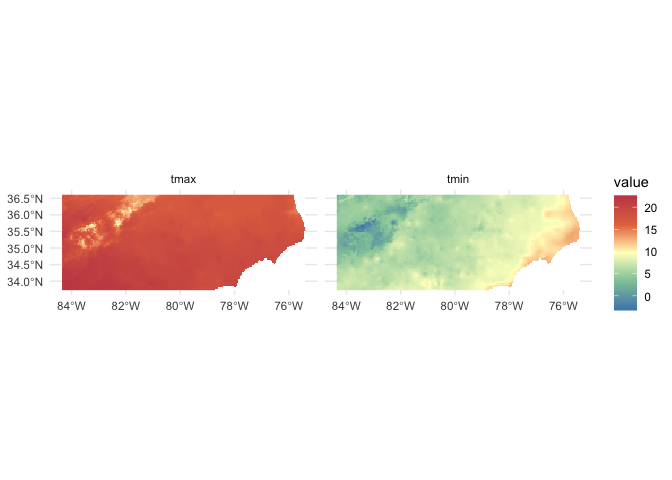
With an AOI, we can construct a call to a dataset for a parameter(s) and date(s) of choice. Here we are querying the PRISM dataset for maximum and minimum temperature on October 29, 2018:
system.time({
p = getPRISM(AOI, varname = c('tmax','tmin'), startDate = "2018-10-29")
})
#> user system elapsed
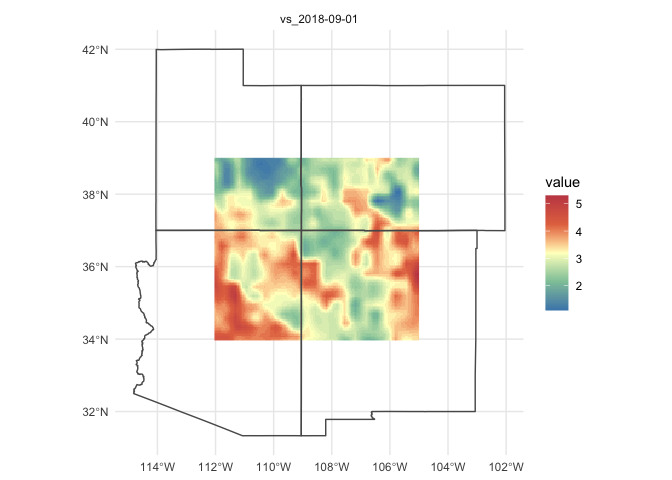
#> 0.406 0.040 1.681climateR offers support for sf, sfc, and bbox objects. Here we
are requesting wind velocity data for the four corners region of the USA
by bounding coordinates.
AOI = st_as_sfc(st_bbox(c(xmin = -112, xmax = -105, ymax = 39, ymin = 34), crs = 4326))
g = getGridMET(AOI,
varname = "vs",
startDate = "2018-09-01")
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = rast(g)) +
facet_wrap(~lyr) +
scale_fill_whitebox_c(
palette = "muted",
na.value = "white"
) +
geom_sf(data = AOI::aoi_get(state = c("CO", "NM", "AZ", "UT")), fill = NA) +
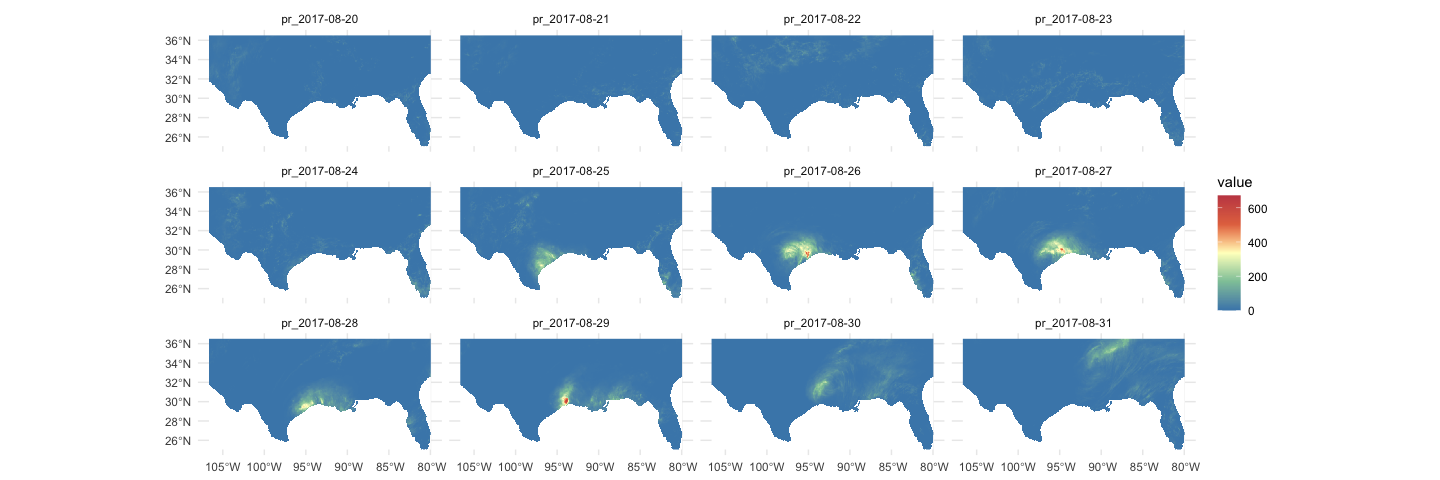
theme_minimal()In addition to multiple variables we can request variables through time, here let’s look at the gridMET rainfall for the Gulf Coast during Hurricane Harvey:
harvey = getGridMET(aoi_get(state = c("TX", "FL")),
varname = "pr",
startDate = "2017-08-20", endDate = "2017-08-31")
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = harvey$precipitation_amount) +
facet_wrap(~lyr) +
scale_fill_whitebox_c(
palette = "muted",
na.value = "white") +
theme_minimal()Some sources are downscaled Global Climate Models (GCMs). These allow you to query forecasted ensemble members from different models and/or climate scenarios. One example is from the MACA dataset:
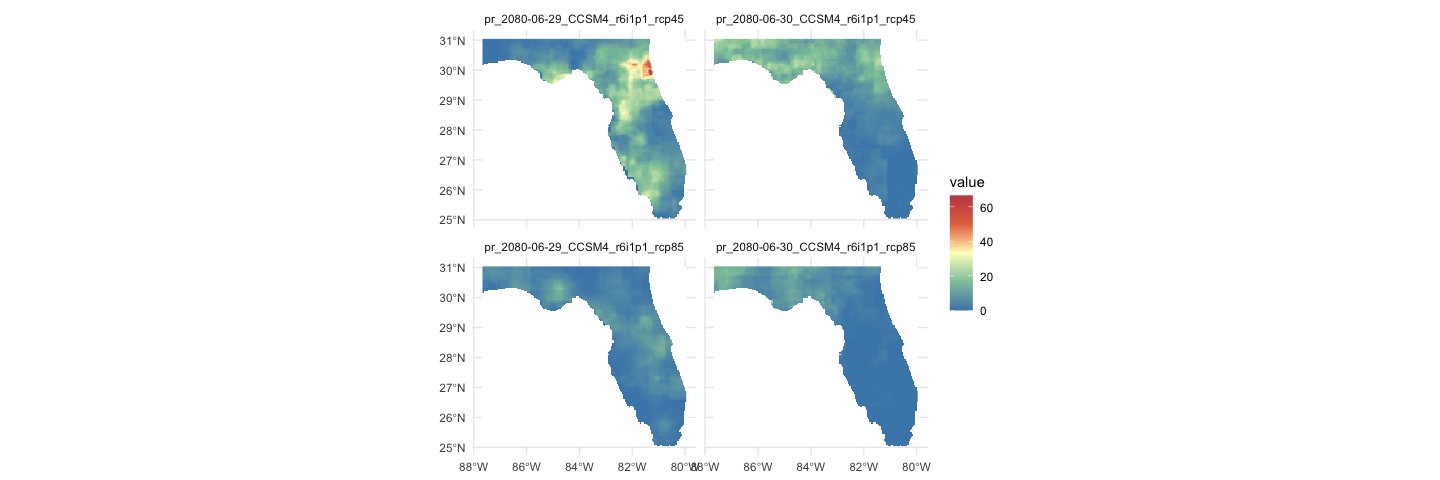
system.time({
m = getMACA(AOI = aoi_get(state = "FL"),
model = "CCSM4",
varname = 'pr',
scenario = c('rcp45', 'rcp85'),
startDate = "2080-06-29", endDate = "2080-06-30")
})
#> user system elapsed
#> 0.207 0.028 6.568ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = rast(m)) +
facet_wrap(~lyr) +
scale_fill_whitebox_c(
palette = "muted",
na.value = "white"
) + theme_minimal()Getting multiple models results is also quite simple:
models = c("BNU-ESM","CanESM2", "CCSM4")
temp = getMACA(AOI = aoi_get(state = "CO"),
varname = 'tasmin',
model = models,
startDate = "2080-11-29")
temp$air_temperature$mean = terra::app(temp$air_temperature, mean)
names(temp[[1]]) = c(models, "Ensemble Mean")
# Plot
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = temp$air_temperature) +
facet_wrap(~lyr) +
scale_fill_whitebox_c(
palette = "muted",
na.value = "white"
) + theme_minimal()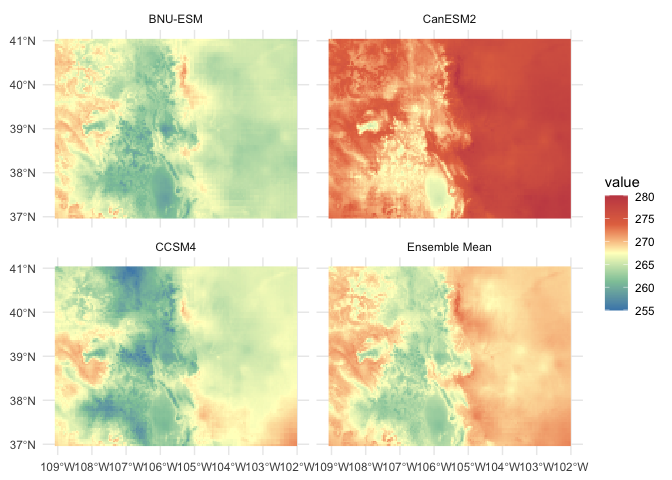 If
you don’t know your models, you can always grab a random set by
specifying a number:
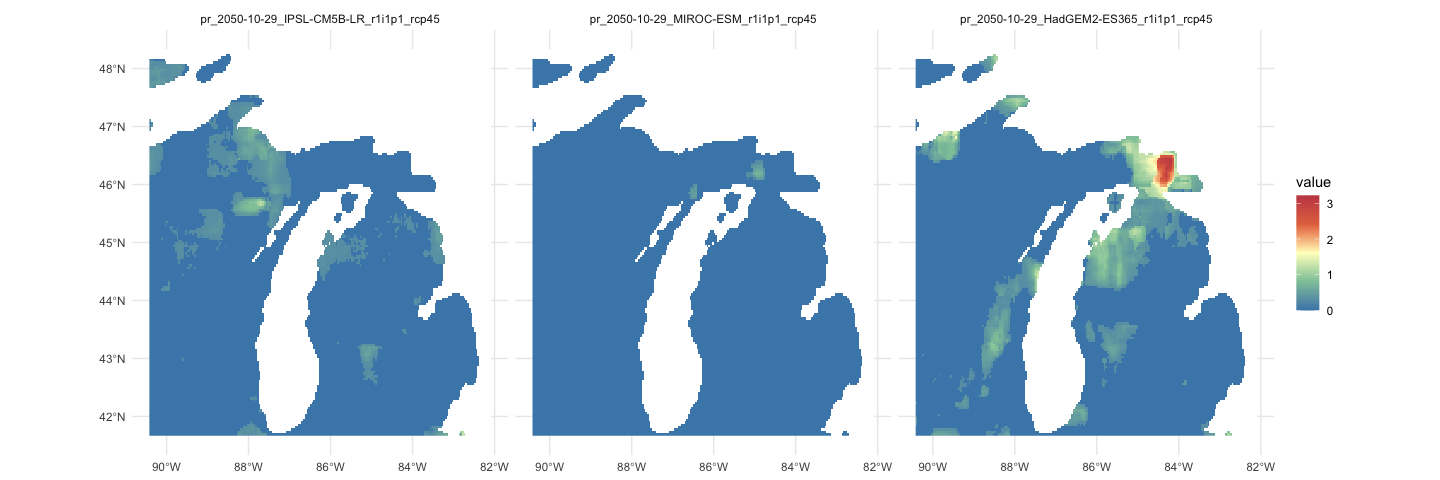
If
you don’t know your models, you can always grab a random set by
specifying a number:
random = getMACA(aoi_get(state = "MI"),
model = 3,
varname = "pr",
startDate = "2050-10-29")
# Plot
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = random$precipitation) +
facet_wrap(~lyr) +
scale_fill_whitebox_c(
palette = "muted",
na.value = "white"
) +
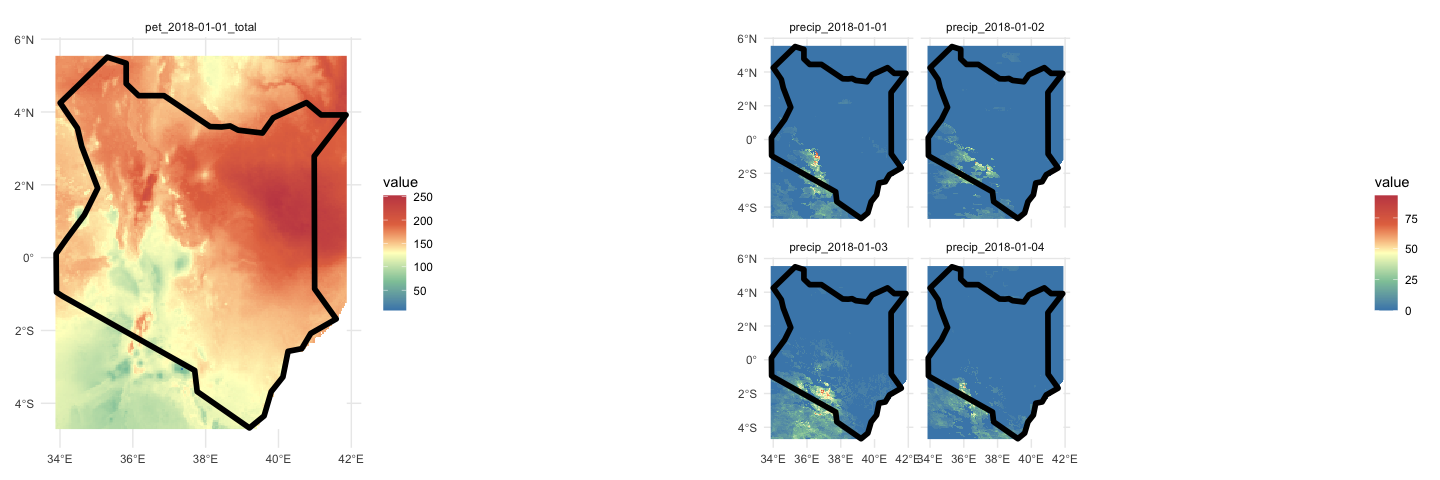
theme_minimal()Not all datasets are USA focused either. TerraClimate offers global, monthly data up to the current year for many variables, and CHIRPS provides daily rainfall data:
kenya = aoi_get(country = "Kenya")
tc = getTerraClim(kenya, varname = "pet", startDate = "2018-01-01")
chirps = getCHIRPS(kenya, startDate = "2018-01-01", endDate = "2018-01-04" )
library(patchwork)
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = tc$pet) +
facet_wrap(~lyr) +
scale_fill_whitebox_c(
palette = "muted",
na.value = "white"
) +
geom_sf(data = kenya, fill = NA, lwd = 2, col = "black") +
theme_minimal() +
ggplot() +
geom_spatraster(data = chirps$precip) +
facet_wrap(~lyr) +
scale_fill_whitebox_c(
palette = "muted",
na.value = "white"
) +
geom_sf(data = kenya, fill = NA, lwd = 2, col = "black") +
theme_minimal() Finally, data gathering is not limited to areal extents and can be retrieved as a time series at locations.
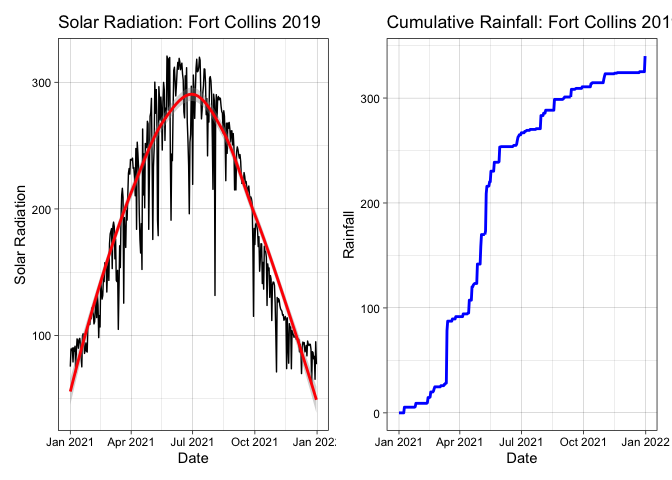
AOI =
ts = getGridMET(geocode('Fort Collins', pt = TRUE),
varname = c("pr", 'srad'),
startDate = "2021-01-01",
endDate = "2021-12-31")ggplot(data = ts, aes(x = date, y = srad)) +
geom_line() +
stat_smooth(col = "red") +
theme_linedraw() +
labs(title = "Solar Radiation: Fort Collins 2019",
x = "Date", y = "Solar Radiation") +
ggplot(data = ts, aes(x = date, y = cumsum(pr))) +
geom_line(color = "blue", lwd = 1) +
theme_linedraw() +
labs(title = "Cumulative Rainfall: Fort Collins 2019",
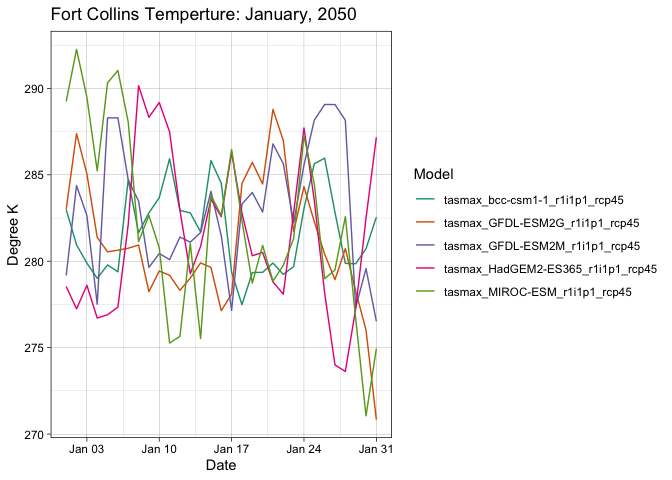
x = "Date", y = "Rainfall")future = getMACA(geocode("Fort Collins", pt = TRUE),
model = 5, varname = "tasmax",
startDate = "2050-01-01", endDate = "2050-01-31")
future_long = pivot_longer(future, -date)
ggplot(data = future_long, aes(x = date, y = value, col = name)) +
geom_line() +
theme_linedraw() +
scale_color_brewer(palette = "Dark2") +
labs(title = "Fort Collins Temperture: January, 2050",
x = "Date",
y = "Degree K",
color = "Model")Extracting data for a set of points is an interesting challenge. It turns it is much more efficient to grab the underlying raster stack and then extract time series as opposed to iterating over the locations:
- Starting with a set of locations in Colorado:
f = system.file("co/co_cities.rds", package = "climateR")
cities = readRDS(f)climateRwill grab the SpatRaster underlying the bounding area of the points
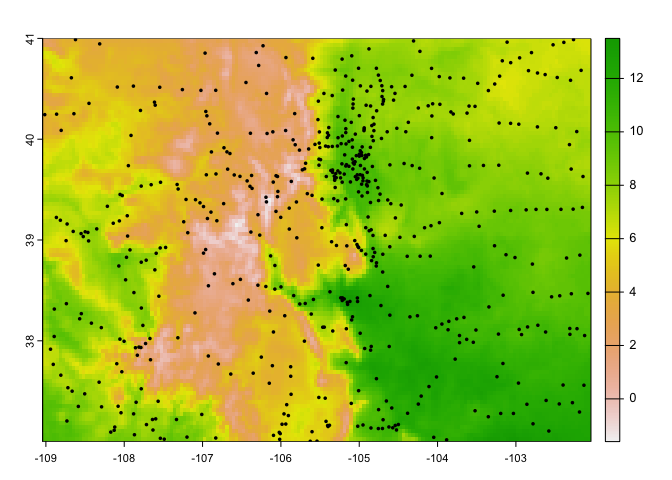
sites_stack = getTerraClim(AOI = cities,
varname = "tmax",
startDate = "2018-01-01",
endDate = "2018-12-31"){
plot(sites_stack$tmax[[1]])
plot(vect(cities), add = TRUE, pch = 16, cex = .5)
}- Use
extract_sitesto extract the times series from these locations. Theidparameter is the unique identifier from the site data with which to names the resulting columns.
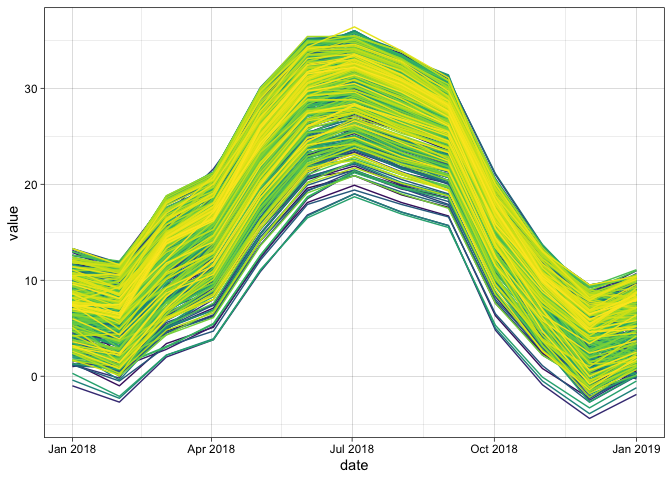
sites_wide = extract_sites(r = sites_stack, pts = cities, id = "NAME")
sites_wide[[1]][1:5, 1:5]
#> date ADAMSCITY AGATE AGUILAR AKRON
#> 1 2018-01-01 00:00:00 9.5 8.2 11.4 7.1
#> 2 2018-01-31 10:00:00 8.1 7.1 9.9 5.8
#> 3 2018-03-02 20:00:00 14.6 14.1 15.0 13.5
#> 4 2018-04-02 06:00:00 17.5 16.6 17.6 16.2
#> 5 2018-05-02 16:00:00 25.1 25.0 25.5 24.8To make the data ‘tidy’ simply pivot on the date column:
#> # A tibble: 6 × 3
#> date name value
#> <dttm> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 2018-01-01 00:00:00 ADAMSCITY 9.5
#> 2 2018-01-01 00:00:00 AGATE 8.2
#> 3 2018-01-01 00:00:00 AGUILAR 11.4
#> 4 2018-01-01 00:00:00 AKRON 7.1
#> 5 2018-01-01 00:00:00 ALAMOSA 5.2
#> 6 2018-01-01 00:00:00 ALLENSPARK 6.1