This tutorial is aimed at people with limited knowledge of coding and cloud computing, but interested in getting their first program up and running on the cloud. It is based on serverless computing and all steps are done on IBM Cloud (you need to register first) using IBM Cloud Functions, which is based on the Open Source programming service OpenWhisk.
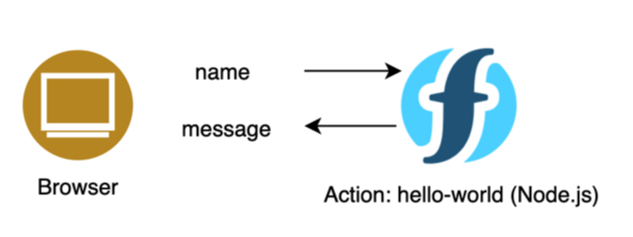
This tutotial contains 3 steps to create a simple program (also called function in serverless computing and action in Openwhisk). The way actions work is actually straightforward: they take some input parameters, process them and return something, e.g. a response message.
Several programming labguages are supported. In our case a Node.js function takes a string (a name) and returns a Hello, 'name' message.
In the first step we want to get on the IBM Cloud and start an action:
- go to IBM Cloud Functions
- click on Actions
- click on the blue Create button
- enter an Action Name, e.g. hello-world-web-action
- click on Create
- click on Invoke, you should see the result:
Results:
{
"message": "Hello World"
}
Congratulations!
The next steps is to process an input value (parameter) and return an output depending on the input parameter. If we provide a parameter value, we are greeted. Otherwise we get an error message.
- scroll up and replace the code with
function main({name}) {
var msg = 'You did not tell me who you are.';
if (name) {
msg = `Hello, ${name}!`
}
return {msg}
}
- Click on Save and Invoke; we did not provide a parameter so far, the initial value of msg is returned:
{
"msg": "You did not tell me who you are."
}
Now we want to provide an input parameter:
- scroll up and click on Change Input
- replace the content with
{ "name": "Hans"} - click on Save and Invoke; as we provided the name parameter, it is returned by this action as part of the variable msg:
{
"msg": "Hello, Hans!"
}
Up until now the action can be used by other services on the IBM Cloud, but it is not accessible to other programs elsewehere or to users who want to invoke the action with there internet browser. As a start only the return value needs to be changed slightly so it becomes HTML syntax that web browsers are able to understand:
function main({name}) {
var msg = 'You did not tell me who you are.';
if (name) {
msg = `Hello, ${name}!`
}
return {body: `<html><body><h3>${msg}</h3></body></html>`}
}
Now expose the action by defining it as a web action so it gets a URL:
- click om Endpoints on the left,
- click on Enable as Web Action,
- click on Save,
- copy the web action's URL (e.g. https://eu-de.functions.cloud.ibm.com/api/v1/web/a7200a8d-610b-4b00-9e58-05d850355555/brownbag/hello-world-web-action) into the clipboard and paste it into the Address Bar of the browser; the result is again
You did not tell me who you are..
We again need a parameter that we add to the URL:
- enter https://eu-de.functions.cloud.ibm.com/api/v1/web/a7200a8d-610b-4b00-9e58-05d850355555/brownbag/hello-world-web-action?name=Otto into the address bar and hit Enter The result is:
Hello, Otto!
References: