This document describes how to deploy the infrastructure needed to evaluate the performance of an NLP Tool submitted to the NLP Sandbox.
One of the feature of the NLP Sandbox is the ability for NLP developers to submit their NLP Tool once and then have it evaluated on multiple Data Hosting Sites.
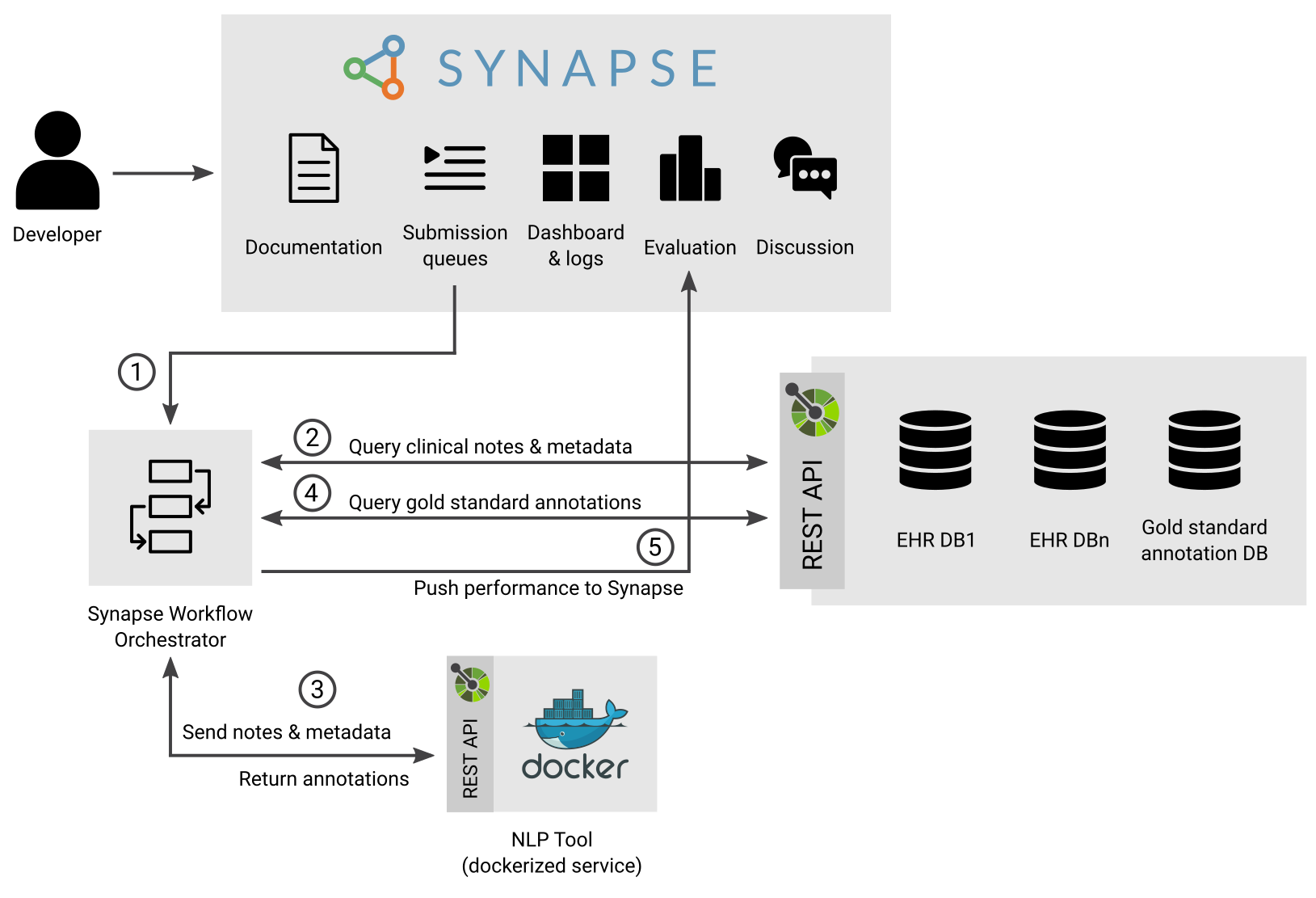
The figure below represents how the infrastructure deployed on a Data Hosting Site evaluates the performance of a tool submitted by a developer to the NLP Sandbox.
The submission workflow is composed of these steps:
- An NLP Developer submits an NLP tool for evaluation using the NLP Sandbox web client or command line interface (CLI). The submission is added to one of the submission queues of the NLP Sandbox depending on the NLP Task selected by the NLP Developer.
- The Synapse Workflow Orchestrator query one or more submissions queues for submissions to process. The Orchestrator that runs on a Data Hosting Site only query submissions that it can evaluate based on the type of data stored in the Data Node(s) available (XXX: clarify the case where there are multiple Data Nodes).
- If there is a
RECEIVEDsubmission, the Orchestrator will start running a workflow with the submission as its input. The steps to the workflow is outlined in workflow.cwl.- Starts the NLP Tool (web service) to evaluate
- Queries N clinical notes from the Data Node.
- Sends the N clinical notes to the NLP Tool and receives the predictions.
- Repeats Steps 4 and 5 until all the clinical notes included in a given dataset have been processed by the NLP Tool.
- Stops the NLP Tool.
- Queries the gold standard from the Data Node.
- Evaluates the performance of the predictions by comparing them to the gold standard.
- Sends the performance measured to the NLP Sandbox backend server.
- The NLP Developer and the community review the performance of the NLP Tool.
To be a NLP sandbox data hosting site, the site must be able to host 4 main technology stacks via Docker. Here are the requirements:
- Docker: ver 19.03.0+ or higher
- Docker-compose: ver 1.25.5 or higher
- Data Node
- Synapse Workflow Orchestrator
- ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana)
- NLP Tools (E.g. Date-Annotators)
Ideally for performance, the Data Node, Synapse Workflow Orchestrator and ELK are hosted on different servers (e.g. ec2 instances), but these can technically be deployed on one server/machine.
- Clone and start the data node. This step should already be done by the cloudformation script for Sage Bionetworks.
git clone https://github.com/nlpsandbox/data-node.git cd data-node cp .env.example .env docker-compose up -d - Push data into the data-node.
# set up conda or pipenv environment pip install nlpsandbox-client # Pushes challenge data python scripts/push_challenge_data.py # Pushes small subset of data python scripts/push_small_dataset.py
View Submission workflow for what this tool does.
- Obtain/Create a Service Account (TBD)
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/Sage-Bionetworks/SynapseWorkflowOrchestrator.git cd SynapseWorkflowOrchestrator - Copy the example template
cp .envTemplate .envand configure. Sage Bionetworks uses the service accountnlp-sandbox-botand theseEVALUTION_TEMPLATES, but these will be different per data hosting site.SYNAPSE_USERNAME=nlp-sandbox-bot # The data hosting site will have to created their own synapse service account. SYNAPSE_PASSWORD= EVALUATION_TEMPLATES={"queueid": "syn25585023"} # The queueid will be provided to the site by Sage Bionetworks. syn25585023 is the internal workflow synapse id. WORKFLOW_OUTPUT_ROOT_ENTITY_ID=synid # This value will be provided to the site by Sage Bionetworks. # WES_ENDPOINT=http://localhost:8082/ga4gh/wes/v1 # This needs to be commented - Start the orchestrator
docker-compose up -d
- Optional: Start portainerer This is an open source tool for managing container-based software applications (e.g. provides a GUI to view Docker images and running containers).
docker volume create portainer_data docker run -d -p 8000:8000 -p 9000:9000 --name=portainer --restart=always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v portainer_data:/data portainer/portainer-ce
- If hosting ELK on a different instance from running submissions: Add the following section to the
docker-compose.yaml. TheROUTE_URISwill be different from theSage Bionetworkssite.Wherelogspout: image: bekt/logspout-logstash restart: on-failure environment: - ROUTE_URIS=logstash://10.23.60.253:5000 # Only for Sage Bionetworks - LOGSTASH_TAGS=docker-elk volumes: - /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
10.23.60.253is the IP Address of your external ELK Server - Load example data in the data node.
- Inform Sage Bionetworks of data node endpoint ip so config.yml can be modified.
A solution to track Docker container logs are a requirement to be a data hosting site. The reason for this is because the tool services submitted by participants are hosted as Docker containers and if there are issues with the service, the logs will have to be returned to participants. We suggest using ELK stack (instructions below), but there are plenty of other methods you can use to capture Docker logs.
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/nlpsandbox/docker-elk.git cd docker-elk docker-compose up -d - Only use the free version of ELK. This can be configured here
- Change the
elastic passwordsin each of these locations:docker-compose.ymlkibana/config/kibana.ymllogstash/config/logstash.ymlelasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
- Running all the services on one machine:
- Make sure to update the
kibanaport in thedocker-compose.ymlor else there is a chance that you will run intoport already allocatederror.ports: - "80:5601" # Change 80 to an open port
- Use the logspout extension to capture Docker container logs.
This will automatically start logspout for you and you won't have to add it to the
docker-compose -f docker-compose.yml -f extensions/logspout/logspout-compose.yml up
SynapseWorkflowOrchestrator
- Make sure to update the
- Clone and start the date annotator. This step should already be done by the cloudformation script for Sage Bionetworks.
If running all services on one machine: must make sure
git clone https://github.com/nlpsandbox/date-annotator-example.git cd date-annotator-exampleportis changed to avoidport already allocatederror.Start the serviceports: - "80:80" # Change the first 80 to an open port
docker-compose up -d
This repository will host the CWL workflow and tools required to set up the model-to-data challenge infrastructure for NLP Sandbox
For more information about the tools, please head to ChallengeWorkflowTemplates
pip3 install cwltool- A synapse account / configuration file. Learn more here
- A Synapse submission to a queue. Learn more here
- workflow.cwl
If there are updates to the api version or dataset version, the workflow inputs
have to be editted
- id: dataset_name type: string default: "2014-i2b2" # change this - id: dataset_version type: string default: "20201203" # change this - id: api_version type: string default: "1.0.1" # change this
cwltool workflow.cwl --submissionId 12345 \
--adminUploadSynId syn12345 \
--submitterUploadSynId syn12345 \
--workflowSynapseId syn12345 \
--synaspeConfig ~/.synapseConfigwhere:
submissionId- ID of the Synapse submission to processadminUploadSynId- ID of a Synapse folder accessible only to the submission queue administratorsubmitterUploadSynId- ID of a Synapse folder accessible to the submitterworkflowSynapseId- ID of the Synapse entity containing a reference to the workflow file(s)synapseConfig- filepath to your Synapse credentials