Reference implementation of "An Algorithm for Routing Vectors in Sequences" (Heinsen, 2022), and an earlier variant, "An Algorithm for Routing Capsules in All Domains" (Heinsen, 2019), for computing a sequence of capsules (e.g., vectors, matrices) that best explain (e.g., predict, generate) a given input sequence.
A toy example is helpful for conveying quickly what the algorithm does:
import torch
from heinsen_routing import EfficientVectorRouting as Routing
model = torch.nn.Sequential(
Routing(n_inp=10000, n_out=1000, d_inp=1024, d_out=2048),
Routing(n_inp= 1000, n_out= 100, d_inp=2048, d_out=3072),
Routing(n_inp= 100, n_out= 10, d_inp=3072, d_out=4096),
)
x_inp = torch.randn(10_000, 1024) # 10,000 vectors of size 1024 (e.g., embedded tokens)
x_out = model(x_inp) # 10 vectors of size 4096 that best explain x_inpFor instructions to route very long sequences (e.g., 1,000,000+ token embeddings in 18GB of VRAM), see here. For an example of end-to-end credit assignment, see here. For replicating published results, see here.
pip install git+https://github.com/glassroom/heinsen_routing
Alternatively, you can download a single file to your project directory: heinsen_routing.py.
The only dependency is PyTorch.
Our routing algorithm takes a sequence of n_inp input capsules and computes a new sequence of n_out output capsules. A capsule is a group of artificial neurons, such as a vector or a matrix, representing the properties of an entity in a context (e.g., a word in a paragraph, an object in an image, a topic in a conversation). Each input and output capsule represents (i.e., is a symbol for) a different entity.
The algorithm is iterative. In each iteration, we update the state of all output capsules in parallel. Each output capsule maximizes "bang per bit," the difference between a net benefit to use and net cost to ignore data, by better explaining (e.g., predicting, generating) the input capsules. The output sequence's final state maximizes "bang per bit" by best explaining the input sequence.
The algorithm is differentiable. When you train it with stochastic gradient descent, it learns to compute the output sequence that best explains the input sequence, in order to minimize the training loss you specify.
This repository contains three variants of our routing algorithm, implemented as PyTorch modules:
EfficientVectorRouting is the efficient implementation proposed in "An Algorithm for Routing Vectors in Sequences" (Heinsen, 2022). It incorporates optimizations that reduce parameter count, memory use, and computation by orders of magnitude compared to the other two variants, making it the best choice for most use cases. This README focuses primarily on this PyTorch module. If you're not sure which module you should use, we recommend this one. See the next section for sample usage.
DefinableVectorRouting implements the general form of "An Algorithm for Routing Vectors in Sequences" (Heinsen, 2022). It requires you to define, instantiate, and pass at initialization four PyTorch modules named A, F, G, and S (corresponding to neural networks A, F, G, and S in the paper), which specify routing behavior. In principle, you could define A, F, G, and S to replicate EfficientVectorRouting's behavior -- but not its optimizations. See the module's docstring for sample usage.
GenerativeMatrixRouting implements the original variant, "An Algorithm for Routing Capsules in All Domains" (Heinsen, 2019). It routes matrices as the capsules, and uses Gaussian mixture models to generate the output matrices, weighted by separate activations that maximize "bang per bit." This module is the least scalable of the three, so we now recommend using it mainly for small-scale tasks. See the module's docstring for sample usage.
EfficientVectorRouting takes a sequence of input vectors [..., n_inp, d_inp] and computes a sequence of output vectors [..., n_out, d_out], where "..." denotes zero or more preserved dimensions. Each vector is a capsule representing a different entity. The output sequence maximizes "bang per bit" by best predicting (i.e., explaining) the given input sequence:
import torch
from heinsen_routing import EfficientVectorRouting as Routing
batch_sz = 4
n_inp, d_inp = (2000, 1024) # input seqs will have 2000 vectors of size 1024
n_out, d_out = (1000, 2048) # we will route them to 1000 vectors of size 2048
model = Routing(n_inp=n_inp, n_out=n_out, d_inp=d_inp, d_out=d_out)
x_inp = torch.randn(batch_sz, n_inp, d_inp) # shape is [batch_sz, n_inp, d_inp]
x_out = model(x_inp) # shape is [batch_sz, n_out, d_out]If you set d_out equal to 1, EfficientVectorRouting routes each sequence of input vectors to a sequence of one-dimensional vectors, or scalars, which you can concatenate into a single vector. Each scalar value is a capsule representing a different entity:
import torch
from heinsen_routing import EfficientVectorRouting as Routing
batch_sz = 4
n_inp, d_inp = (1000, 1024) # input seqs will have 1000 vectors of size 1024
d_vec = 2048 # we will route each seq to a vector of size 2048
model = Routing(n_inp=n_inp, n_out=d_vec, d_inp=d_inp, d_out=1)
x_inp = torch.randn(batch_sz, n_inp, d_inp) # shape is [batch_sz, n_inp, d_inp]
x_out = model(x_inp).squeeze(-1) # shape is [batch_sz, d_vec]If you set n_inp equal to -1, EfficientVectorRouting routes input sequences of any length, limited only by available memory, to output sequences of fixed length. If the order of input vectors matters, embed position information in them beforehand. Train the module with input sequences of varying lengths and it will learn to predict (explain) them. Here, we route sequences of random length:
import torch
from heinsen_routing import EfficientVectorRouting as Routing
batch_sz = 4
n_inp, d_inp = ( -1, 1024) # length of input seq will vary
n_out, d_out = (1000, 1024) # length of output seq is fixed
model = Routing(n_inp=n_inp, n_out=n_out, d_inp=d_inp, d_out=d_out)
random_len = torch.randint(1, 10_000, []).item()
x_inp = torch.randn(batch_sz, random_len, d_inp) # seqs of random length; order unimportant
x_out = model(x_inp) # seqs of fixed lengthNote: When n_inp is set to -1, EfficientVectorRouting treats every input vector as being in the same shared feature space (i.e., each element represents the same feature in all input vectors). In contrast, when n_inp is fixed, the module treats each input vector differently, so each input vector may be in a different feature space (i.e., the same element may represent a different feature in each input vector).
EfficientVectorRouting's memory footprint is linear in each of n_inp, n_out, d_inp, and d_out, giving you fine-grained control over memory consumption. To route input sequences of greater length, you can reduce the length of the output sequence, and vice versa. For example, here we route an input sequence with 1,000,000 vectors at full (32-bit) precision, keeping track of gradients for backpropagation, consuming under ~18GB of memory (on a recent Nvidia GPU, excluding ~1GB of PyTorch and CUDA overhead):
import torch
from heinsen_routing import EfficientVectorRouting as Routing
n_inp, d_inp = (1_000_000, 1024) # very long input seq
n_out, d_out = ( 100, 1024) # short output seq
model = Routing(n_inp=n_inp, n_out=n_out, d_inp=d_inp, d_out=d_out) # uses ~6GB of memory
x_inp = torch.randn(n_inp, d_inp) # uses ~4GB of memory
x_out = model(x_inp) # uses ~8GB of memoryA handy technique for routing very long sequences is to route them twice: First to a short hidden sequence of larger vectors representing "summaries," and then to an output sequence with the desired shape. The motivation is to reduce the computation incurred and memory allocated by the execution of n_inp Softmax functions, each over n_out proposed output vectors, in each iteration of the first routing. Here, we apply this technique to route 250,000 to 1,000 vectors of size 1024 at 32-bit precision, keeping track of gradients, requiring only ~5.6GB of memory (on a recent Nvidia GPU, excluding ~1GB of PyTorch and CUDA overhead):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from heinsen_routing import EfficientVectorRouting as Routing
n_inp, d_inp = (250_000, 1024) # very long input seq
n_hid, d_hid = ( 100, 10240) # short hidden seq of higher-dimensional "summaries"
n_out, d_out = ( 1000, 1024) # output seq with final desired shape
model = nn.Sequential(
Routing(n_inp=n_inp, n_out=n_hid, d_inp=d_inp, d_out=d_hid), # "summarize"
Routing(n_inp=n_hid, n_out=n_out, d_inp=d_hid, d_out=d_out), # "rewrite"
)
x_inp = torch.randn(n_inp, d_inp)
x_out = model(x_inp)Note: If the long input sequences have varying lengths, or if your application will work well with all input vectors in each sequence being in the same feature space, you can set n_inp to -1 to reduce parameter count and memory footprint. For example, in the code snippet above, you can replace model with:
model = nn.Sequential(
Routing(n_inp=-1, n_out=n_hid, d_inp=d_inp, d_out=d_hid), # "summarize"
Routing(n_inp=-1, n_out=n_out, d_inp=d_hid, d_out=d_out), # "rewrite"
)and the memory required to route 250,000 to 1,000 vectors of size 1024 at 32-bit precision, keeping track of gradients, shrinks to ~3.9GB (on a recent Nvidia GPU, excluding ~1GB of PyTorch and CUDA overhead).
You can apply EfficientVectorRouting recurrently, inducing it each time to compute a new sequence that best predicts (explains) the previously computed sequence. You can also apply recurrent routings as residuals, inducing the module to compute new residual sequences that best predict (explain) the recurrent accumulation of all previous sequences. For example:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from heinsen_routing import EfficientVectorRouting as Routing
class RecurrentResidualRoutings(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_emb, d_emb, n_iters, seq_compression_factor=8):
super().__init__()
n_hid = max(2, n_emb // seq_compression_factor)
self.n_iters = n_iters
self.normalize = nn.LayerNorm(d_emb)
self.residualize = nn.Sequential(
Routing(n_inp=n_emb, n_out=n_hid, d_inp=d_emb, d_out=d_emb),
Routing(n_inp=n_hid, n_out=n_emb, d_inp=d_emb, d_out=d_emb),
)
def forward(self, x):
for _ in range(self.n_iters):
x = self.normalize(x)
x = x + self.residualize(x)
return x
batch_sz = 4
n_emb, d_emb = (1000, 1024)
model = RecurrentResidualRoutings(n_emb, d_emb, n_iters=5)
x_inp = torch.randn(batch_sz, n_emb, d_emb)
x_out = model(x_inp)You can mask input vectors differently for each output vector by passing a boolean mask of shape [n_inp, n_out] as an input to the forward pass. True values mask input vector data and False values don't. For example, here we use masking to restrict EfficientVectorRouting to model only causal relationships over an ordered sequence of vectors, each representing a token. For each output vector in a given position, the module can route data only from input vectors located in up to that position:
import torch
from heinsen_routing import EfficientVectorRouting as Routing
batch_sz = 4
n_tok, d_tok = (100, 1024)
causal_mask = torch.tril(torch.ones(n_tok, n_tok), diagonal=-1).bool()
model = Routing(n_inp=n_tok, n_out=n_tok, d_inp=d_tok, d_out=d_tok)
tok_embs = torch.randn(batch_sz, n_tok, d_tok) # normally provided by a model
pos_embs = torch.randn(n_tok, d_tok) # normally provided by a model
x_inp = torch.nn.functional.layer_norm(tok_embs + pos_embs, [d_tok])
x_out = model(x_inp, mask=causal_mask)Note: The mask does not have to be square. For example, you can specify a causal mask of shape [n_ltc + n_tok, n_tok], where n_ltc is a specified number of vectors providing long-term context to all tokens, n_ltc + n_tok is the number of input vectors, and n_tok is the number of output vectors.
Each instance of EfficientVectorRouting internally computes a credit assignment matrix of shape [..., n_inp, n_out], consisting of the credit assigned to each input vector by each output vector. To obtain the credit assignments, instantiate the module with return_dict=True, and it will return a dictionary with output vectors as key 'x_out' and credit assignments as key 'phi'. For example:
import torch
from heinsen_routing import EfficientVectorRouting as Routing
batch_sz = 4
n_inp, d_inp = (100, 1024)
n_out, d_out = ( 10, 1024)
model = Routing(n_inp=n_inp, n_out=n_out, d_inp=d_inp, d_out=d_out, return_dict=True)
x_inp = torch.randn(batch_sz, n_inp, d_inp)
outputs = model(x_inp)
x_out = outputs['x_out'] # [batch_sz, n_out, d_out] output vectors
phi = outputs['phi'] # [batch_sz, n_inp, n_out] credit assigned to input by output vecsThe credit assignments are additive, like Shapley values, and composable on their own, independently of data transformations, making it possible to compute end-to-end credit assignments over a network of routings, as explained in Subsection 3.2 of the paper. For "how-to" recipes to compute end-to-end credit assignments over common compositions, including residual layers, see Appendix A of the same paper. For example:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from heinsen_routing import EfficientVectorRouting as Routing
class SequentialRoutingsWithCreditAssignments(nn.Module):
"""
Apply routings sequentially and compute end-to-end credit assignments
by following the recipe for sequential routings in Appendix A of "An
Algorithm for Routing Vectors in Sequences" (Heinsen, 2022).
"""
def __init__(self, kwds_by_routing, eps=1e-5):
super().__init__()
self.eps = eps
self.routings = nn.ModuleList(
[Routing(**kwds, return_dict=True) for kwds in kwds_by_routing]
)
def forward(self, x):
prod = None
for routing in self.routings:
outputs = routing(x)
x = outputs['x_out']
phi = outputs['phi']
prod = phi if prod is None else prod @ phi # chain of matrix products
prod = prod / (prod.std() + self.eps) # scale the matrix products
return x, prod
kwds_by_routing = [
{ 'n_inp': 500, 'n_out': 400, 'd_inp': 1024, 'd_out': 1024, },
{ 'n_inp': 400, 'n_out': 300, 'd_inp': 1024, 'd_out': 1024, },
{ 'n_inp': 300, 'n_out': 200, 'd_inp': 1024, 'd_out': 1024, },
{ 'n_inp': 200, 'n_out': 100, 'd_inp': 1024, 'd_out': 1024, },
]
model = SequentialRoutingsWithCreditAssignments(kwds_by_routing)
x_inp = torch.randn(kwds_by_routing[0]['n_inp'], kwds_by_routing[0]['d_inp'])
x_out, credit_assignments = model(x_inp)If you run the code above, x_out will have shape [100, 1024], computed by the last routing, and credit_assignments will have shape [500, 100], consisting of the end-to-end credit assigned to the first routing's 500 input vectors by the final routing's 100 output vectors.
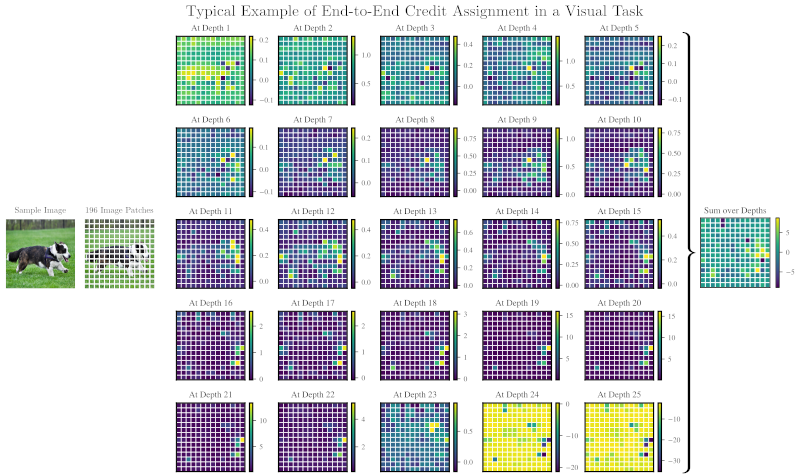
Here is a typical example of end-to-end credit assignment, in this case obtained from three sequential routings trained to route a sequence of hidden states at all depths in a BEiT Transformer to a sequence of predicted scores for ImageNet-1k classification. We show the end-to-end credit asigned to every pixel patch at every level of Transformer depth by the top predicted score, corresponding to the label "Cardigan Welsh Corgi." The credit assignments are additive, so we sum them over all depths to obtain the credit assigned to each pixel patch. As you can see, our algorithm assigns credit end-to-end to the dog's body in shallower layers, and to its nose, mouth, ears, and paws in deeper layers, explaining the top predicted score ("Cardigan Welsh Corgi"):
The code and a pretrained model necessary for recreating the visualization above are online (see here). For a higher-resolution version and a more in-depth explanation of this visualization, see the paper.
Q: "Is it true that EfficientVectorRouting can route sequences with 1,000,000+ vectors in a single GPU/TPU?"
A: Yes. See here.
Q: "Can I use EfficientVectorRouting in a Transformer? CNN? RNN? Autoencoder? Generative model? Any model?"
A: Yes. EfficientVectorRouting is a general-purpose PyTorch module.
Q: "Can I use EfficientVectorRouting instead of self-attention as a component of models?"
A: Yes. There is in fact a connection between the query-key-value self-attention mechanism used in Transformers and the algorithm implemented by EfficientVectorRouting: Transformer self-attention is a special case of modern Hopfield networks with bipartite structure, a class of dense associative memories which are in turn a special case of the routing algorithm we propose in "An Algorithm for Routing Vectors in Sequences." EfficientVectorRouting is one possible implementation of our algorithm.
Q: "Can I use EfficientVectorRouting to classify a sequence of token embeddings?"
A: Yes. Route the sequence to a vector (see here) and use the vector's elements as the predicted classification scores. In training, the module will learn to compute scores that minimize classification error and simultaneously best predict (explain) the sequence being classified.
Note: If the number of classes is large (say, more than a few thousand classes), it may be more efficient to route the sequence to a hidden vector, and then apply a linear transformation to that hidden vector to predict classification scores, as is conventional.
Q: "Can I use EfficientVectorRouting to build "deep autoencoders for sequences"?
A: Yes. You can build deep autoencoders that apply multiple EfficientVectorRouting layers to encode an input sequence to progressively shorter sequences and then progressively decode the shortest sequence back to the original length, in a typical "bowtie" arrangement. The autoencoders can of course be variational, using the reparametrization trick to sample the inner shortest sequence from a specified distribution.
Q: "Is it true that each output vector computed by EfficientVectorRouting can have its own feature space?"
A: Yes. Each output vector is computed in a different basis, possibly representing different features (i.e., the same element may represent different features in different vectors). The number of representable features can be as large as n_out × d_out. This increase in representational capacity may enable you to work with shorter sequences and/or smaller vector sizes than otherwise necessary. See Subsection 3.1 of the paper.
Note: If you treat every output vector as being in the same shared feature space (e.g., if you always apply the same transformations to all output vectors, instead of different transformations to each one), you can induce all vector bases to represent the same features. If that's what you want, great -- but if not, please exercise a bit of care to avoid doing it unintentionally!
Q: "Can I set n_inp to -1 in EfficientVectorRouting even if all input sequences have the same length?"
A: Yes, but note that when you set n_inp to -1, EfficientVectorRouting treats all input vectors as being in the same shared feature space (i.e., each element represents the same feature in all input vectors). If all input vectors are indeed in the same shared feature space, then, yes, it makes sense to set n_inp to -1 even if input sequence length is fixed. Note: Setting n_inp to -1 may cause the module to incur more computation, depending on the shape of input and output sequences.
Q: "Is it true that I can get end-to-end credit assignments over a network of EfficientVectorRouting layers?"
A: Yes. To compute end-to-end credit assignments, follow the "how-to" recipes in Appendix A of the paper -- or make sure you thoroughly understand how the credit assignments work before straying away from the proven recipes. For a discussion of credit assignments, see Subsection 3.2 of the same paper. For a concrete example of end-to-end credit assignment, see here.
Q: "Is it true that EfficientVectorRouting implements a model of associative memory?"
A: Yes. In Subsection 3.3 of the paper, we describe input vectors as keys to content-addressable memory values and biases, and output vectors as queries whose states are iteratively updated until they stabilize in a local maximum of a "bang per bit" landscape (or, equivalently, a local minimum of an energy landscape). We also show that with significant simplifications, the routing algorithm implemented by EfficientVectorRouting reduces to modern Hopfield networks with bipartite structure, a class of dense associative memories of which Transformer self-attention is a notable special case.
Q: "Is it true that EfficientVectorRouting implements a "block" in a model of a Society of Mind (Minsky, 1986)?"
A: Yes. In Subsection 3.4 of of the paper, we describe output vectors as multidimensional agents competing against each other to use or ignore scarce resources in a block via knowledge lines, or K-lines, in a model of a Society of Mind. Agents iteratively improve the shares of each scarce resource they use or ignore by better predicting (i.e., explaining) it. Note that when Minsky was working on ``The Society of Mind," published in 1986, he was certainly aware of early models of associative memory, including Hopfield networks (formulated by John Hopfield in 1982 and 1984, building on prior work going back to the early 1970's) and restricted Boltzmann machines (first proposed as the "Harmonium" by Paul Smolensky in 1986).
To replicate the results published in "An Algorithm for Routing Vectors in Sequences" (Heinsen, 2022), follow the intructions here: https://github.com/glassroom/heinsen_routing_2022_paper.
To replicate the results published in "An Algorithm for Routing Capsules in All Domains" (Heinsen, 2019), follow the intructions here: https://github.com/glassroom/heinsen_routing_2019_paper.
We have tested the code in this repository only on Ubuntu Linux 20.04 with Python 3.8+.
If our work is helpful to your research, please cite it:
@misc{heinsen2022algorithm,
title={An Algorithm for Routing Vectors in Sequences},
author={Franz A. Heinsen},
year={2022},
eprint={2211.11754},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG}
}
@misc{heinsen2019algorithm,
title={An Algorithm for Routing Capsules in All Domains},
author={Franz A. Heinsen},
year={2019},
eprint={1911.00792},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG}
}
We conceived and implemented this routing algorithm to be a component (i.e., a layer) of larger models that are in turn part of our AI software, nicknamed Graham. Most of the original work we do at GlassRoom tends to be either proprietary in nature or tightly coupled to internal code, so we cannot share it with outsiders. In this case, however, we were able to isolate our code and release it as stand-alone open-source software without having to disclose any key intellectual property. We hope others find our work and our code useful.