The AWS Service Operator allows you to manage AWS resources using Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions.
Using the AWS Service Operator enables a gitops workflow to drive your infrastructure to the desired state leveraging Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions (CRD), the Kubernetes internal control loop, and AWS CloudFormation orchestration. Read more about "operators" here.
Make sure your Kubernetes cluster is up and running and you’ve configured your awscli for the approriate account and region you’ll be working in.
You will need to install an IAM management layer
such as kube2iam. This will allow you to use an AWS IAM role to manage a pod’s
access to AWS resources.
To get started with kube2iam go here or check out the
helm chart
The aws-service-operator runs as a pod in your Kubernetes cluster and listens for new aws type CRDs.
When a new CRD is created the operator will create the resource in AWS via CloudFormation and
create a Kubernetes Service for access within the cluster.
The `K8S_WORKER_NODE_IAM_ROLE` is the IAM role assigned to your kubernetes worker instances.
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name aws-service-operator-role \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--template-body file://configs/aws-service-operator-role.yaml \
--parameters \
ParameterKey=WorkerArn,ParameterValue=<K8S_WORKER_NODE_IAM_ROLE>Your resulting IAM role arn should look something like arn:aws:iam::<ACCOUNT_ID>:role/aws-service-operator
Before applying these resources make sure to replace the following placeholders with the approriate information in configs/aws-service-operator.yaml
-
<ACCOUNT_ID>- Your AWS Account ID -
<REGION>- The AWS Region you’re working in -
<CLUSTER_NAME>- The name of your cluster -
<BUCKET_NAME>- (optional) The operator stores certain things in s3 create a bucket or provide an existing bucket for the operator to usei.e. aws s3 mb s3://foobar -
<K8S_NAMESPACE>- (optional) This will scope kubernetes API calls to a specific namespace. If used consider adding a namespace to the resources defined inconfigs/aws-service-operator.yaml
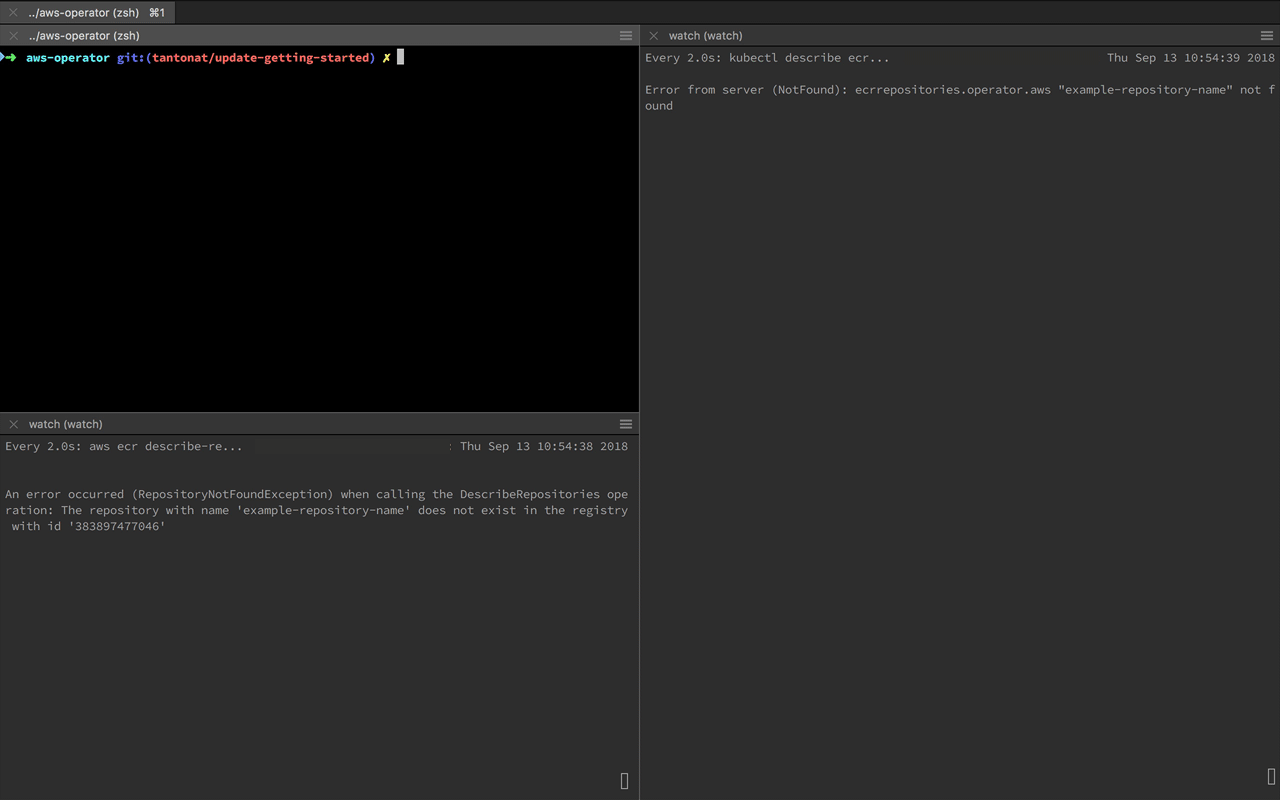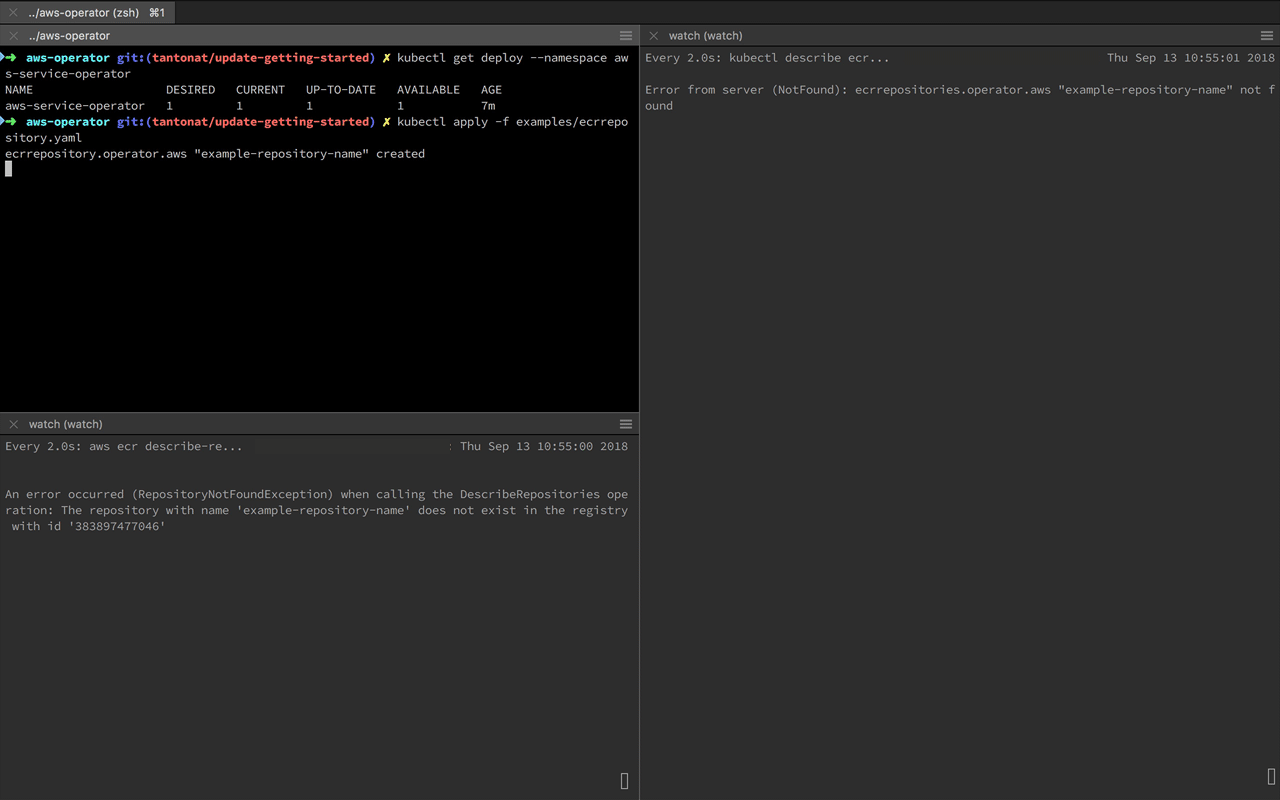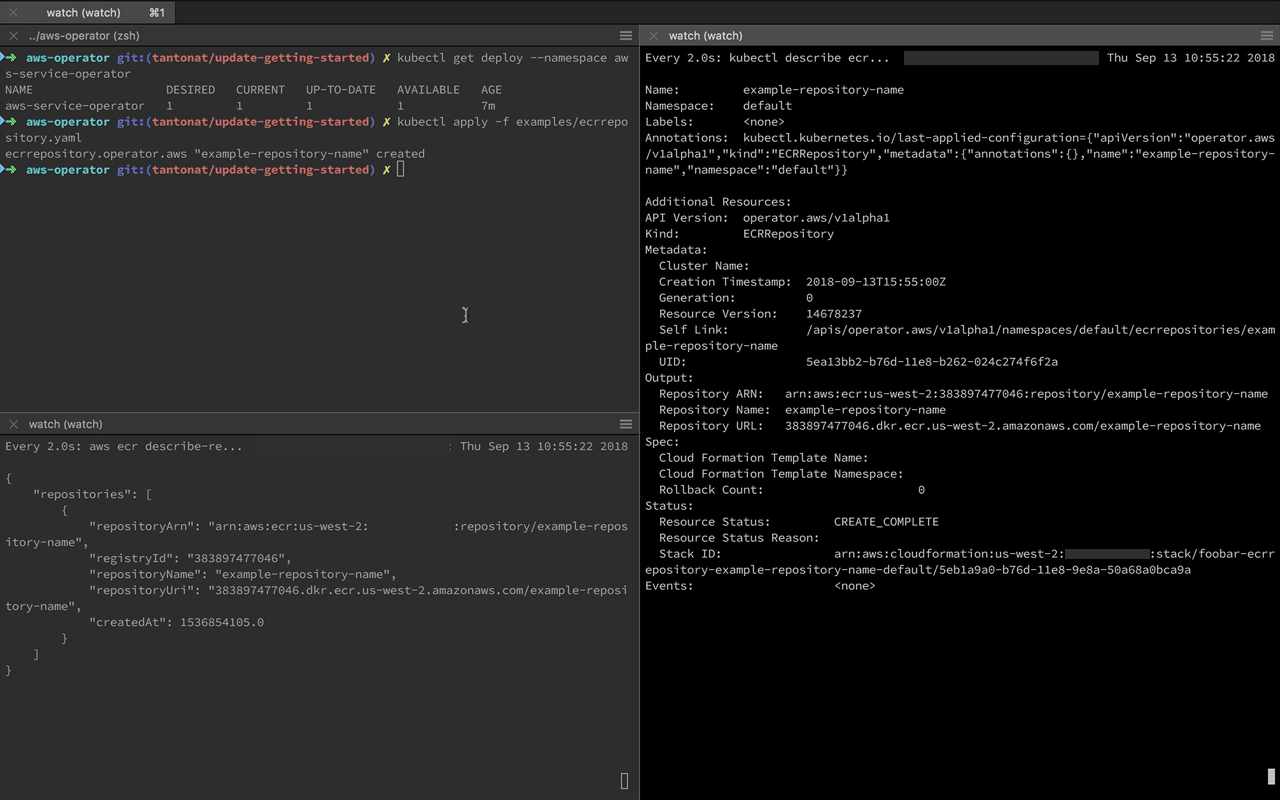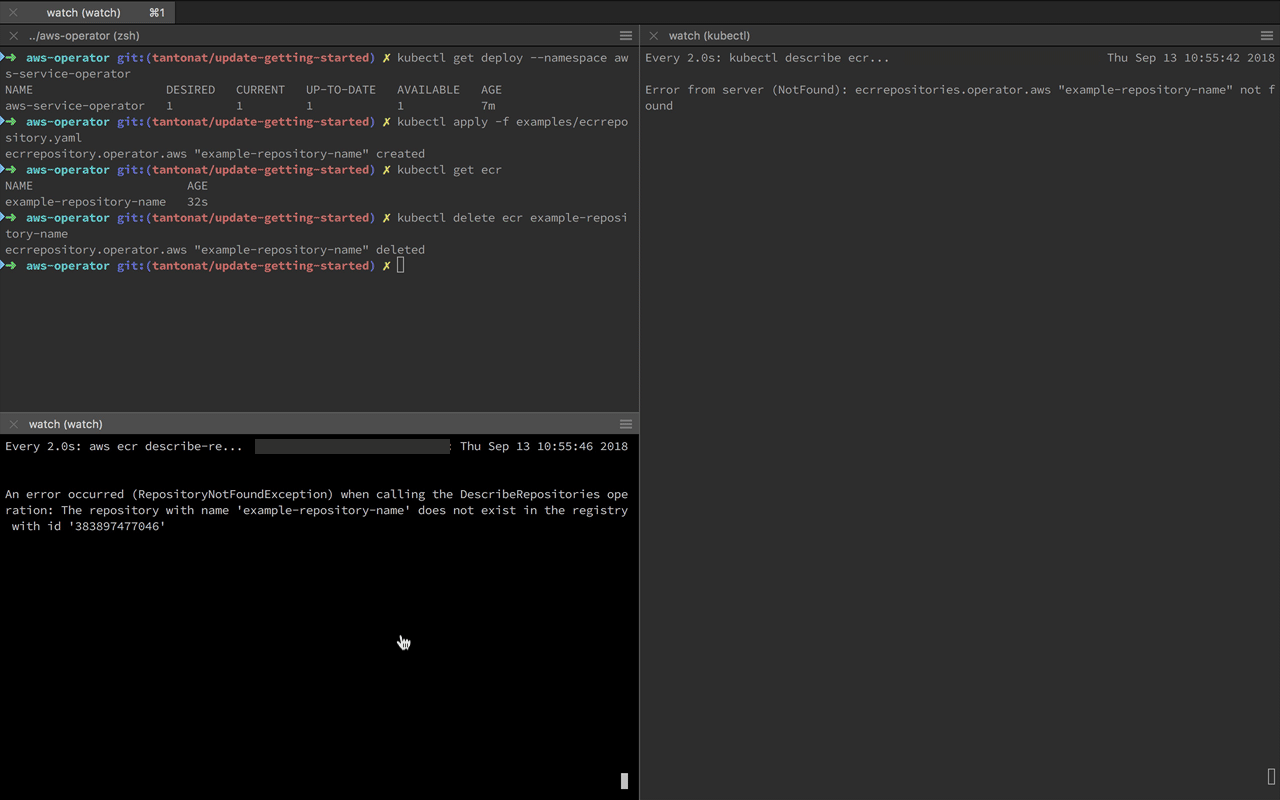
kubectl apply -f configs/aws-service-operator.yamlkubectl apply -f examples/cloudformationtemplateskubectl logs -f -n aws-service-operator deploy/aws-service-operatorkubectl apply -f examples/ecrrepository.yamlThe operator will communicate directly with CloudFormation to create the ECR repository using
the parameters you have passed in. If you’d like to see the progress you can
view the status directly via kubectl.
kubectl describe ecr example-repository-nameIf you would like to tear everything down - run the following commands.
IMPORTANT this will not remove anything you created with the AWS CLI (ECR repo for the operator itself, IAM roles etc.)
kubectl delete ecr example-repository-name
kubectl get crd | grep ".operator.aws" | awk '{print $1}' | xargs kubectl delete crd
kubectl delete -f configs/aws-service-operator.yaml- What is the difference between aws-service-operator (this project) and aws-servicebroker?
-
The operator approach is based on an active component that can react to changes and eventually will also support day 2 operations. See Issue #137 for more details, pull requests are most welcome.