Use RabbitMQ to distribute tasks to multiple workers
One process will create task messages. Multiple worker processes will share the work.
- Fork this starter repo into your GitHub.
- Clone your repo down to your machine.
- View / Command Palette - then Python: Select Interpreter
- Select your conda environment.
- Read the RabbitMQ Tutorial - Work Queues
- Read the code and comments in this repo.
- Open a terminal window in VS Code.
- Use the built-in Python utility venv to create a new virtual environment named
.venvin the current directory.
python3 -m venv .venvVerify you get a new .venv directory in your project. We use .venv as the name to keep it away from our project files.
In the same VS Code terminal window, activate the virtual environment.
- On Linux/MacOS, run:
source .venv/bin/activate
Verify you see the virtual environment name (.venv) in your terminal prompt.
On a mac terminal, start the RabbitMQ server.
- On MacOS, run
brew services start rabbitmq
RabbitMQ comes with an admin panel. When you run the task emitter, reply y to open it.
(Python makes it easy to open a web page - see the code to learn how.)
-
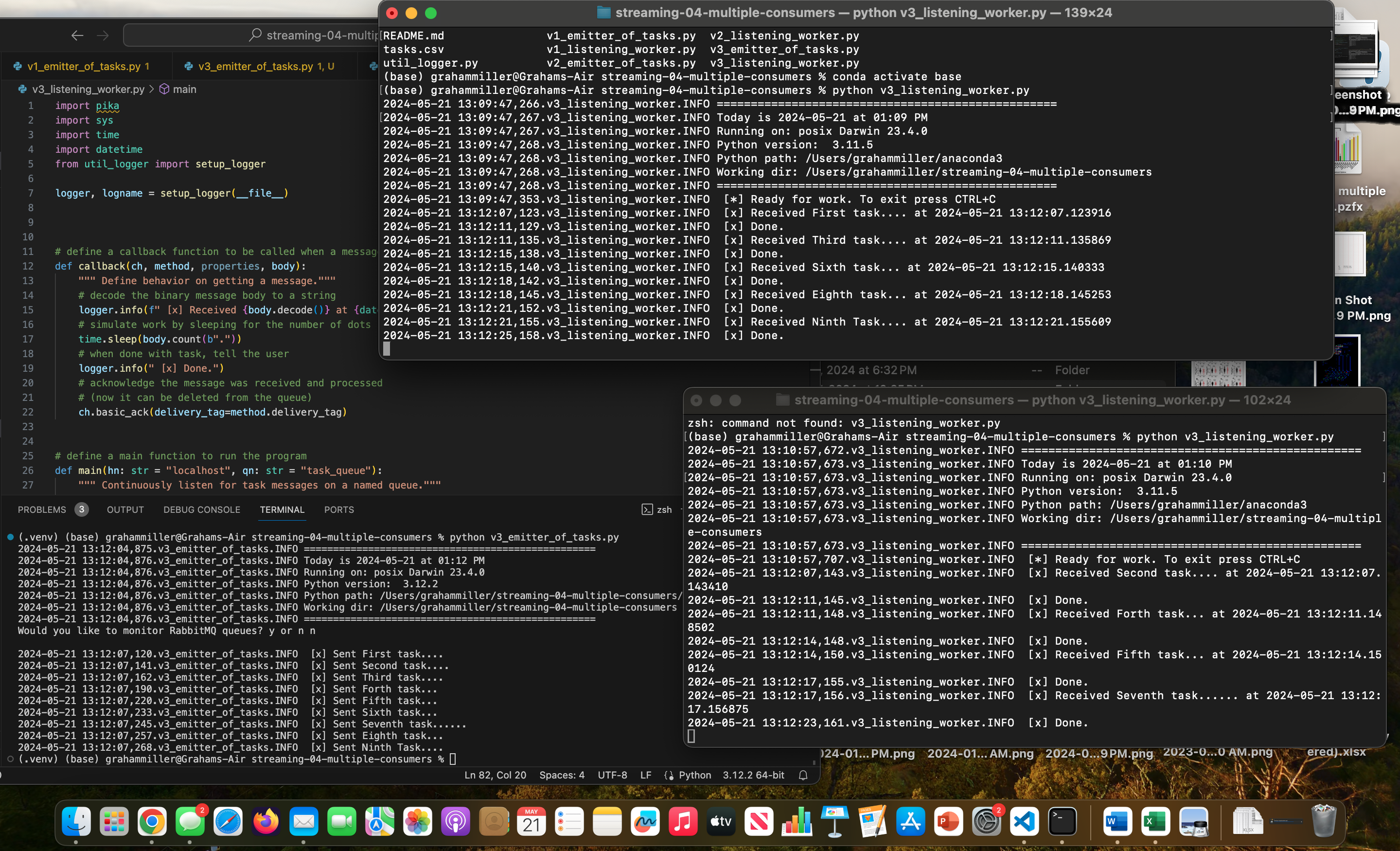
Run the different versions of the listening_worker.py in a seperate terminal
-
For version 3, activate two serperate local terminals, the directions to open two consumer terminals are as follows:
- open two seperate terminals on the local machine
- use
cd /Users/grahammiller/streaming-04-multiple-consumers, or wherever your consumer terminals are located on your machine - run
lsin the terminal to see a list of all the files within this folder - run
conda activate baseto activate the base environment - run code
python v3_listening_worker.py, or whatever your consumer/worker is named in both terminals. Now both terminals are listening for messages.
- Run the different emitter_of_tasks.py in the VS Code terminal
- Open the terminal in VS Code and run
python v3_emitter_of_tasks.pyto send the tasks to the RabbitMQ queue
See a running example with at least 3 concurrent process windows here: