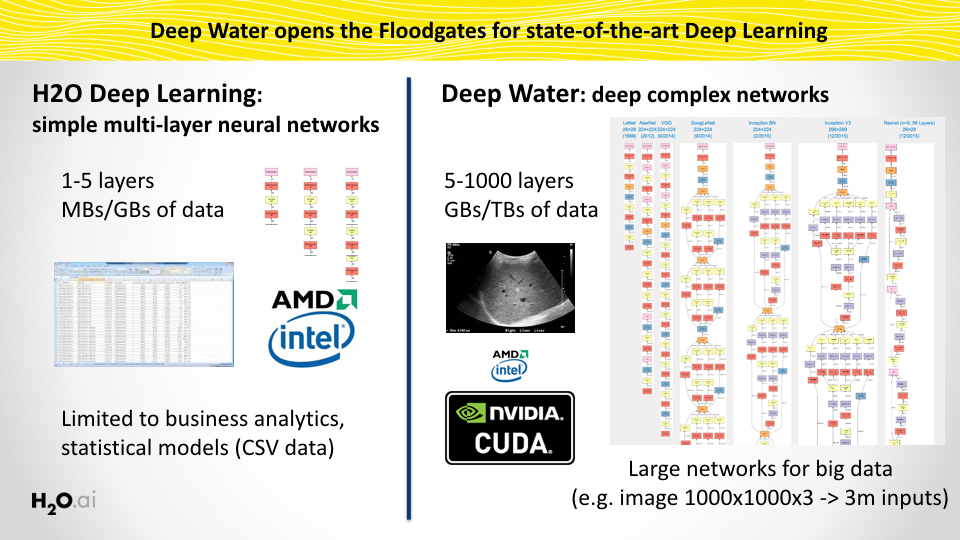
- Native implementation of Deep Learning models for GPU-optimized backends (MXNet, Caffe, TensorFlow, etc.)
- State-of-the-art Deep Learning models trained from the H2O Platform
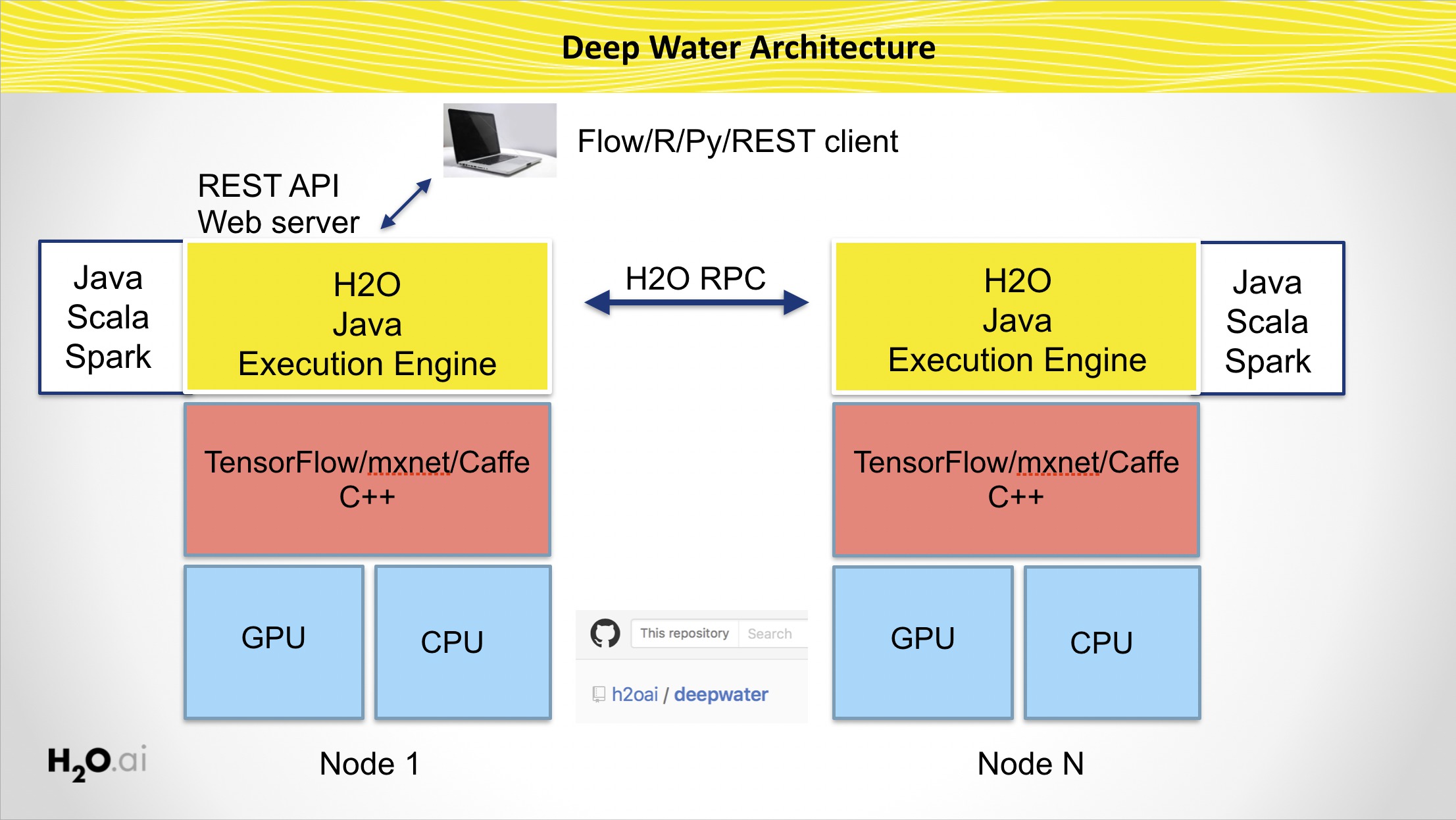
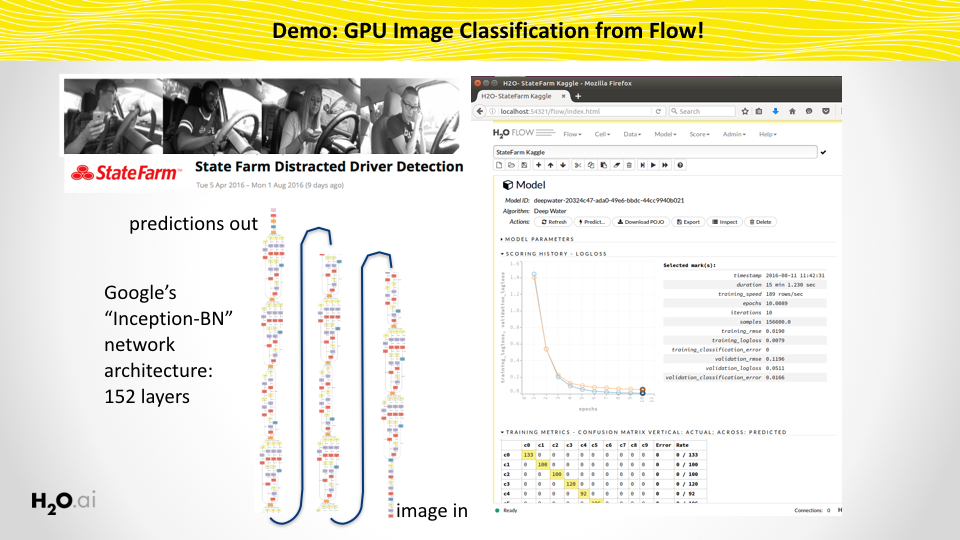
- Train user-defined or pre-defined deeplearning models for image/text/H2OFrame classification from Flow, R, Python, Java, Scala or REST API
- Behaves just like any other H2O model (Flow, cross-validation, early stopping, hyper-parameter search, etc.)
- The next best thing after sliced bread
- Under development
- An oil drilling platform
Check out a sample of cool Deep Learning Jupyter notebooks!
The downloadable packages below are built for the following system specifications:
- Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
- NVIDIA Display driver at least 367
- CUDA 8.0.44 or later (we recommend the latest version) in /usr/local/cuda
- CUDNN 5.1 (placed inside of lib and include directories in /usr/local/cuda/)
To use the GPU, please set the following environment variables:
export CUDA_PATH=/usr/local/cuda
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$CUDA_PATH/lib64:$LD_LIRBARY_PATH
- Required to run python Jupyter notebooks:
H2O Deep Water enabled Python 2.7/3.5 module
-- install via
pip install <file> - To build custom MXNet networks from Python:
Matching MXNet Python 2.7 egg
-- install via
easy_install <file> - To build custom TensorFlow networks from Python:
Matching TensorFlow Python 2.7 wheel
-- install via
pip install <file>
- Required to run R examples:
H2O Deep Water enabled R package
-- install via
R CMD INSTALL <file>
- To build custom Tensorflow networks from R: Matching TensorFlow R package (unofficial from RStudio) -- follow link for installation instructions
- To run from Flow only: H2O Standalone h2o.jar
-- launch via
java -jar h2o.jarfor image tasks we recommendjava -Xmx30g -jar h2o.jar
If you are interested in running H2O Deep Water on a different infrastructure, see the DIY build instructions below.
java -jar h2o.jar
Example Java GPU-enabled unit tests.
Example Python GPU-enabled unit tests. Check out a sample of cool Deep Learning Python Jupyter notebooks!
Example R GPU-enabled unit tests. Check out a sample of cool Deep Learning R Jupyter notebooks!
Coming soon.
We have a pre-built image for Amazon Web Services's EC2 environment:
- AMI ID: ami-97591381
- AMI Name: h2o-deepwater-ami-latest
- AWS Region: US East (N. Virginia)
- Recommended instance type: p2.xlarge
The AMI image contains the Docker Image described below. Once started,
login to the shell prompt. It's a good idea to update the docker image
with docker pull opsh2oai/h2o-deepwater to ensure that you have the
most recent version. Then start the docker image, either with the
provided shell script or with nvidia-docker run -it --net host opsh2oai/h2o-deepwater.
Start H2O with java -Xmx30g -jar /opt/h2o.jar &. Connect to port 54321.
Start Jupyter with jupyter notebook --allow-root --ip=* &.
Connect to the link shown, with your IP exchanged for localhost.
We have a GPU-enabled Docker image and one the CPU only. Both are available on Docker Hub.
For both images you need to install Docker, see http://www.docker.com
- Optional Step. Make docker run without sudo. Instructions for Ubuntu 16.04:
sudo groupadd dockersudo gpasswd -a ${USER} dockersudo service docker restart- log out then log in, or
newgrp docker
To use the GPU-enabled Docker image you need a Linux machine with at least one GPU, a GPU driver, and with docker and nvidia-docker installed.
An NVIDIA GPU with a Compute Capability of at least 3.5 is necessary. See https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus .
If you use Amazon Web Services (AWS), a good machine type to use is the P2 series. Note that G2 series machines have GPUs that are too old.
If you have used these docker images before, please run docker pull IMAGENAME to ensure
that you have the latest version.
-
Install nvidia-docker, see https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker . Note that you can only use Linux machines with one or more NVIDIA GPUs:
- GNU/Linux x86_64 with kernel version > 3.10
- Docker >= 1.9 (official docker-engine, docker-ce or docker-ee only)
- NVIDIA GPU with Architecture > Fermi (2.1) and Compute Capability >= 3.5
- NVIDIA drivers >= 340.29 with binary nvidia-modprobe
-
Download and run the H2O Docker image
nvidia-docker run -it --rm --net host -v $PWD:/host opsh2oai/h2o-deepwater- You now get a prompt in the image:
#. The directory you started from is avaiable as/host - Start H2O with
java -jar /opt/h2o.jar - Python, R and Jupyter Notebooks are available
exitorctrl-dcloses the image
To use the CPU-enabled Docker image you just need to have Docker installed. Note that this image is significantly slower than the GPU image, which is why we don't recommend it.
- Download and run the H2O Docker image:
- On Linux:
docker run -it --rm --net host -v $PWD:/host opsh2oai/h2o-deepwater-cpu - On MacOS:
docker run -it --rm -p 54321:54321 -p 8080:8080 -v $PWD:/host opsh2oai/h2o-deepwater-cpu - You now get a prompt in the image:
#. The directory you started from is avaiable as/host - Start H2O with
java -jar /opt/h2o.jar - Python, R and Jupyter Notebooks are available
exitorctrl-dcloses the image
- On Linux:
Download the Deep Water overview slides.
If you want to use Deep Water in H2O-3, you'll need to have a .jar file that includes backend support for at least one of MXNet, Caffe or TensorFlow.
Instructions to build TensorFlow
Coming soon.
From the top-level of the deepwater repository, do
./gradlew build -x test
This will create the following file: build/libs/deepwater-all.jar
You need to check out the h2o-3.
Copy the freshly created jar file build/libs/deepwater-all.jar from the previous step to H2O-3's library h2o-3/lib/deepwater-all.jar (create the directory if it's not there) and you're done!
./gradlew build -x test
This H2O version will now have GPU Deep Learning support!
To use the GPU, please make sure to set your path to your CUDA installation:
export CUDA_PATH=/usr/local/cuda
sudo pip install h2o-3/h2o-py/dist/h2o-3.11.0.99999-py2.py3-none-any.whl
If you want to build your own MXNet models from Python or R, install the MXNet wheel (which was built together with MXNet above):
sudo easy_install deepwater/thirdparty/mxnet/python/dist/mxnet-0.7.0-py2.7.egg
R CMD INSTALL deepwater/thirdparty/mxnet/mxnet_0.7.tar.gz
The release process bundles all defined submodules and push them into Maven central via Sonatype repository provider. The released artifacts are Java 6 compatible.
The release can be invoked for all modules by:
./gradlew -PdoRelease -PbuildOnlyBackendApi -PdoJava6Bytecode=true -Prelease.useAutomaticVersion=true releaseThe process performs the following steps:
- Updates
gradle.propertiesand removesSNAPSHOTand increases minor version (can be changed) - Creates a new release commit and tags it with release tag. (See
gradle/release.gradlefile to override the default template.) - Builds
- Verifies compatibility of used API with Java 6 API
- Bytecode rewrite to be compatible with Java 6
- Generation of artifact metadata
- Pushes artifacts into staging area at https://oss.sonatype.org/
The process needs to be finished manually by:
- Logging in to https://oss.sonatype.org/#stagingRepositories
- Performing the actions "Close" and "Release" for the
ai.h2ostaging area- Note: Be careful because the area can contain more artifacts from different H2O projects.
Note: The release process creates two new commits and a new tag with the release version. However, the process does not push it to a remote repository, so it is necessary to perform a remote update manually using
git push --tagsor update thegradle/release.gradlesettings and remove the--dry-runoption from thepushOptionsfield.