A package for calculating submatricies, minors, adjugate- and cofactor matricies.
import numpy as np
from adjugate import adj
M = np.random.rand(4, 4)
adjM = adj(M)
M, adjM(array([[0.46445212, 0.90776864, 0.5617845 , 0.46365445],
[0.23096052, 0.37817574, 0.19684724, 0.26416446],
[0.8157284 , 0.35109541, 0.29357478, 0.63978973],
[0.97616731, 0.71221494, 0.18073805, 0.7949908 ]]),
array([[ 0.04081465, -0.13855441, 0.00220198, 0.0204637 ],
[ 0.01427584, -0.02328107, -0.02248499, 0.01750541],
[ 0.01310092, -0.00671938, 0.02476545, -0.02533861],
[-0.06588407, 0.19251526, 0.01180968, -0.02407058]]))
pip install adjugateThis package provides four functions:
submatrix(M, i, j)
Removes the i-th row and j-th column of M. Multiple indices or slices can be provided.
from adjugate import submatrix
M = np.arange(16).reshape(4, 4)
M, submatrix(M, 1, 2)(array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15]]),
array([[ 0, 1, 3],
[ 8, 9, 11],
[12, 13, 15]]))
minor(M, i, j)
Calculates the (i, j) minor of M.
from adjugate import minor
M = np.random.rand(4, 4)
minor(M, 1, 2)-0.2140487789380897
adj(M)
Calculates the adjugate of M.
M, adj(M)(array([[0.08665864, 0.99394655, 0.12535963, 0.26405097],
[0.5579125 , 0.86322768, 0.89414941, 0.568058 ],
[0.67013036, 0.84454395, 0.47131153, 0.19339756],
[0.66467323, 0.85295762, 0.13306573, 0.5569822 ]]),
array([[-0.23323852, -0.12057808, 0.24929258, 0.14698786],
[ 0.21400119, -0.06933021, 0.09234215, -0.06280701],
[-0.03500821, 0.21404878, 0.04025053, -0.21568468],
[-0.04102134, 0.19892593, -0.44852065, 0.29057721]]))
cof(M)
Calculates the cofactor matrix of M.
from adjugate import cof
M, cof(M)(array([[0.08665864, 0.99394655, 0.12535963, 0.26405097],
[0.5579125 , 0.86322768, 0.89414941, 0.568058 ],
[0.67013036, 0.84454395, 0.47131153, 0.19339756],
[0.66467323, 0.85295762, 0.13306573, 0.5569822 ]]),
array([[-0.23323852, 0.21400119, -0.03500821, -0.04102134],
[-0.12057808, -0.06933021, 0.21404878, 0.19892593],
[ 0.24929258, 0.09234215, 0.04025053, -0.44852065],
[ 0.14698786, -0.06280701, -0.21568468, 0.29057721]]))
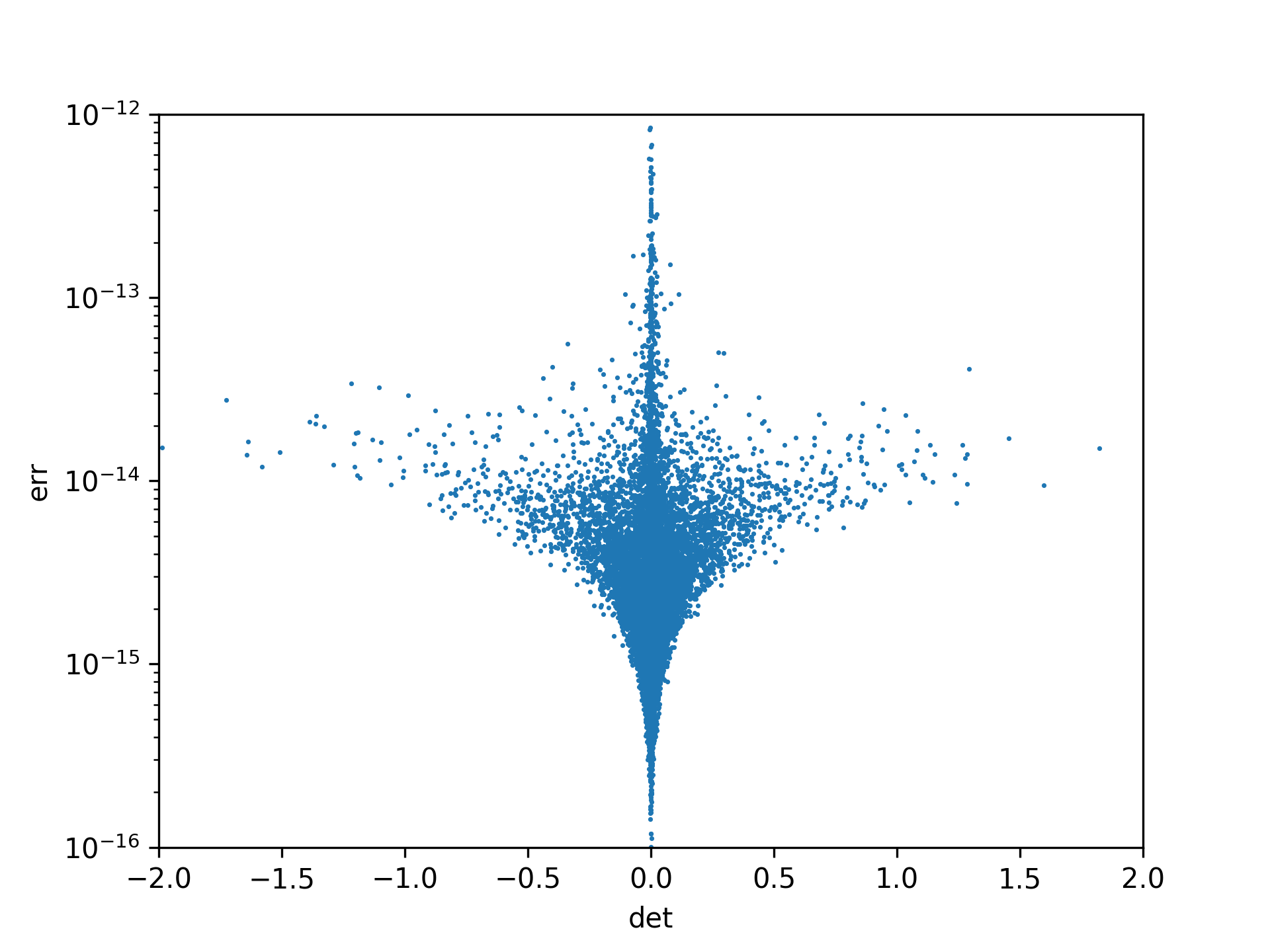
If you know that you matrix is invertible, then np.linalg.det(M) * np.linalg.inv(M) might be a faster choice (O(3) instad of O(5)). But this is in general, especially as the determinant approaches zero, not possible or precise:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
N = 20
dets, errs = [], []
for _ in range(10000):
M = np.random.rand(N, N)
dets += [np.linalg.det(M)]
errs += [np.linalg.norm(adj(M)-np.linalg.det(M)*np.linalg.inv(M))]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(dets, errs, marker='o', s=(72./fig.dpi)**2)
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_xlim(-2, +2)
ax.set_ylim(1e-16, 1e-12)
ax.set_xlabel('det')
ax.set_ylabel('err')
plt.show()