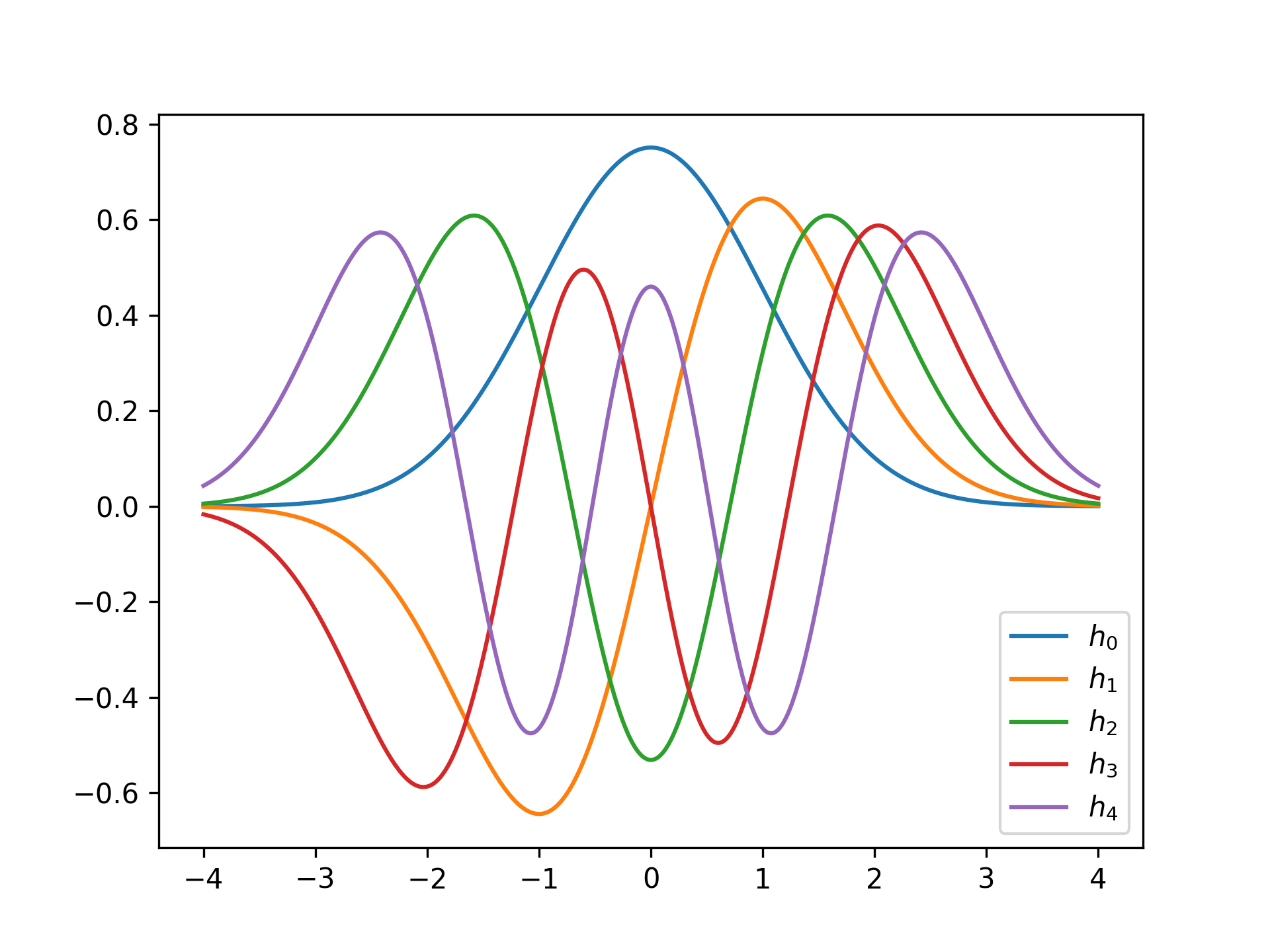
A Hermite function series module.
from hermitefunction import HermiteFunction
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(-4, +4, 1000)
for n in range(5):
f = HermiteFunction(n)
plt.plot(x, f(x), label=f'$h_{n}$')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()pip install git+https://github.com/goessl/vector.git
pip install hermite-function
This package provides a single class, HermiteFunction, to handle Hermite function series.
HermiteFunction extends Vector from the vector module and therefore provides all Hilbert space operations from coefficient access through indexing, over norm calculation to arithmetic.
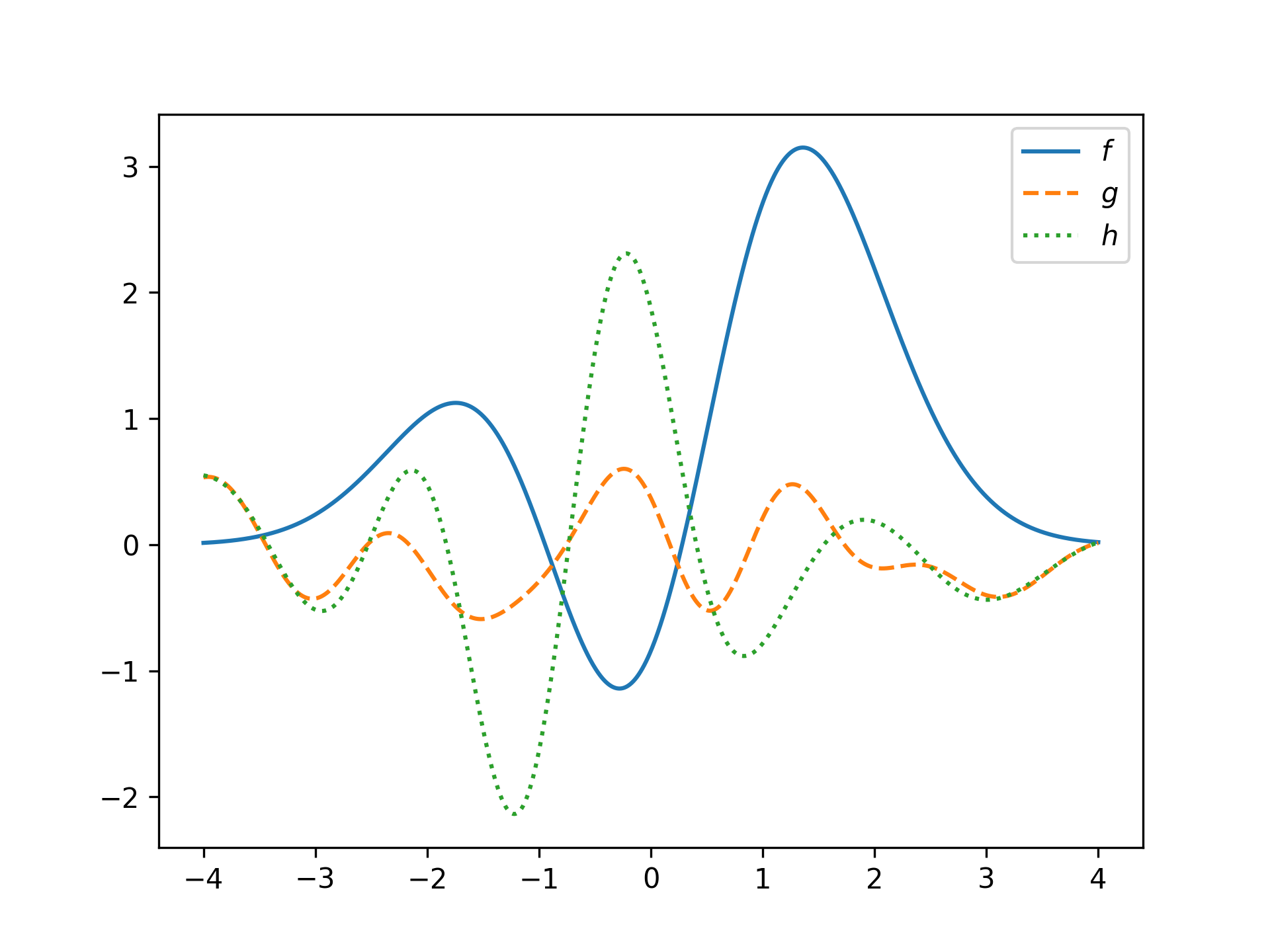
A series can be initialized in three ways:
- With the constructor
HermiteFunction(coef), that takes a non-negative integer to create a pure Hermite function with the given index, or an iterable of coefficients to create a Hermite function series. - With the random factories
HermiteFunction.rand(deg)&HermiteFunction.randn(deg, normed=True)for a random Hermite function series of a given degree. - By fitting data with
HermiteFunction.fit(X, y, deg).
f = HermiteFunction((1, 2, 3))
g = HermiteFunction.randn(15)
h = HermiteFunction.fit(x, g(x), 10)
plt.plot(x, f(x), label='$f$')
plt.plot(x, g(x), '--', label='$g$')
plt.plot(x, h(x), ':', label='$h$')
plt.legend()
plt.show()Methods for functions:
- evaluation with
f(x), - differentiation to an arbitrary degree
f.der(n), - integration
f.antider(), - Fourier transformation
f.fourier()& - getting the degree of the series
f.degare implemented.
f_p = f.der()
f_pp = f.der(2)
plt.plot(x, f(x), label=rf"$f \ (\deg f={f.deg})$")
plt.plot(x, f_p(x), '--', label=rf"$f' \ (\deg f'={f_p.deg})$")
plt.plot(x, f_pp(x), ':', label=rf"$f'' \ (\deg f''={f_pp.deg})$")
plt.legend()
plt.show()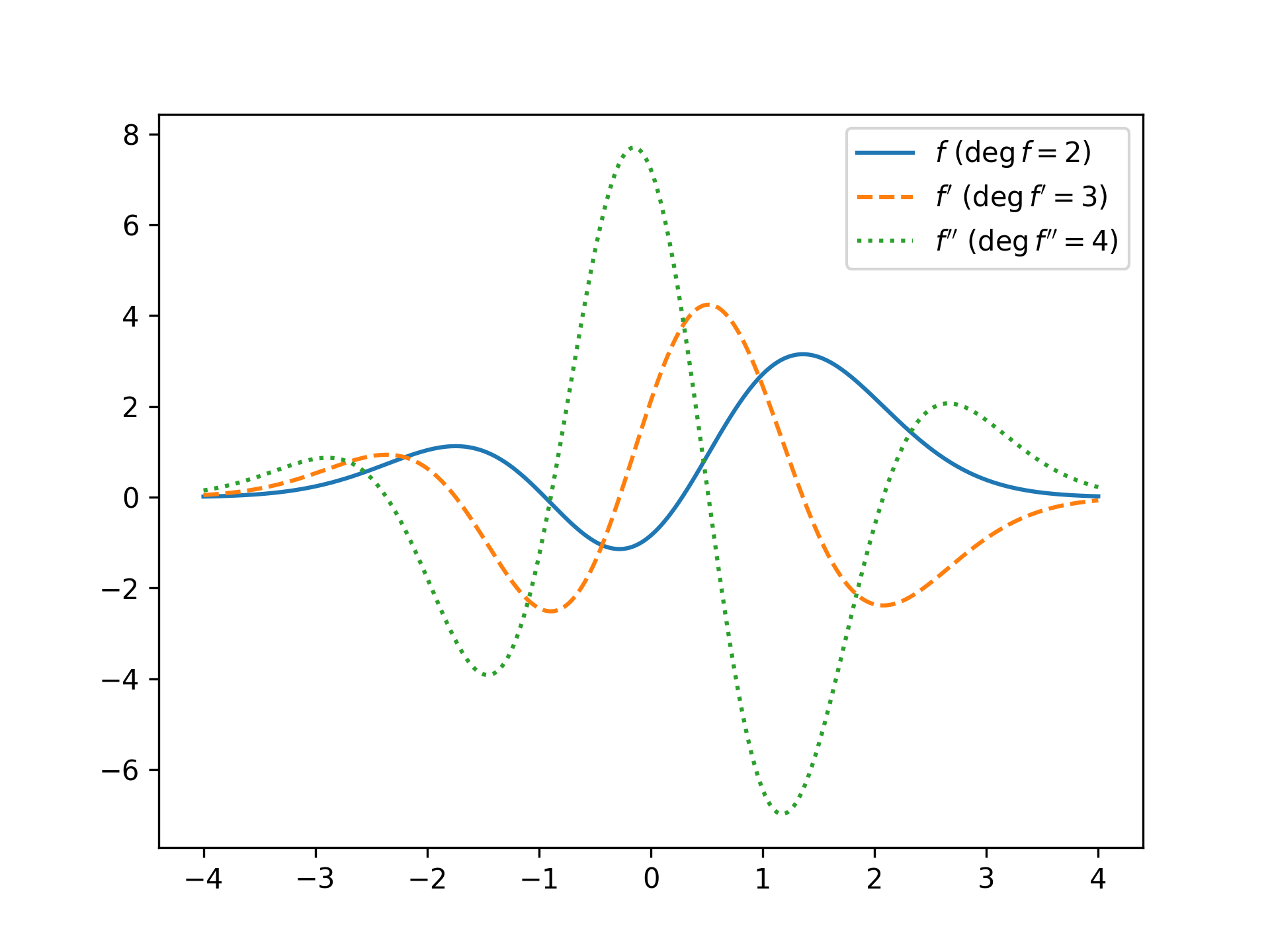 Hilbert space operations inherited from vector
Hilbert space operations inherited from vector
g = HermiteFunction(4)
h = f + g
i = 0.5 * f
plt.plot(x, f(x), label='$f$')
plt.plot(x, g(x), '--', label='$g$')
plt.plot(x, h(x), ':', label='$h$')
plt.plot(x, i(x), '-.', label='$i$')
plt.legend()
plt.show()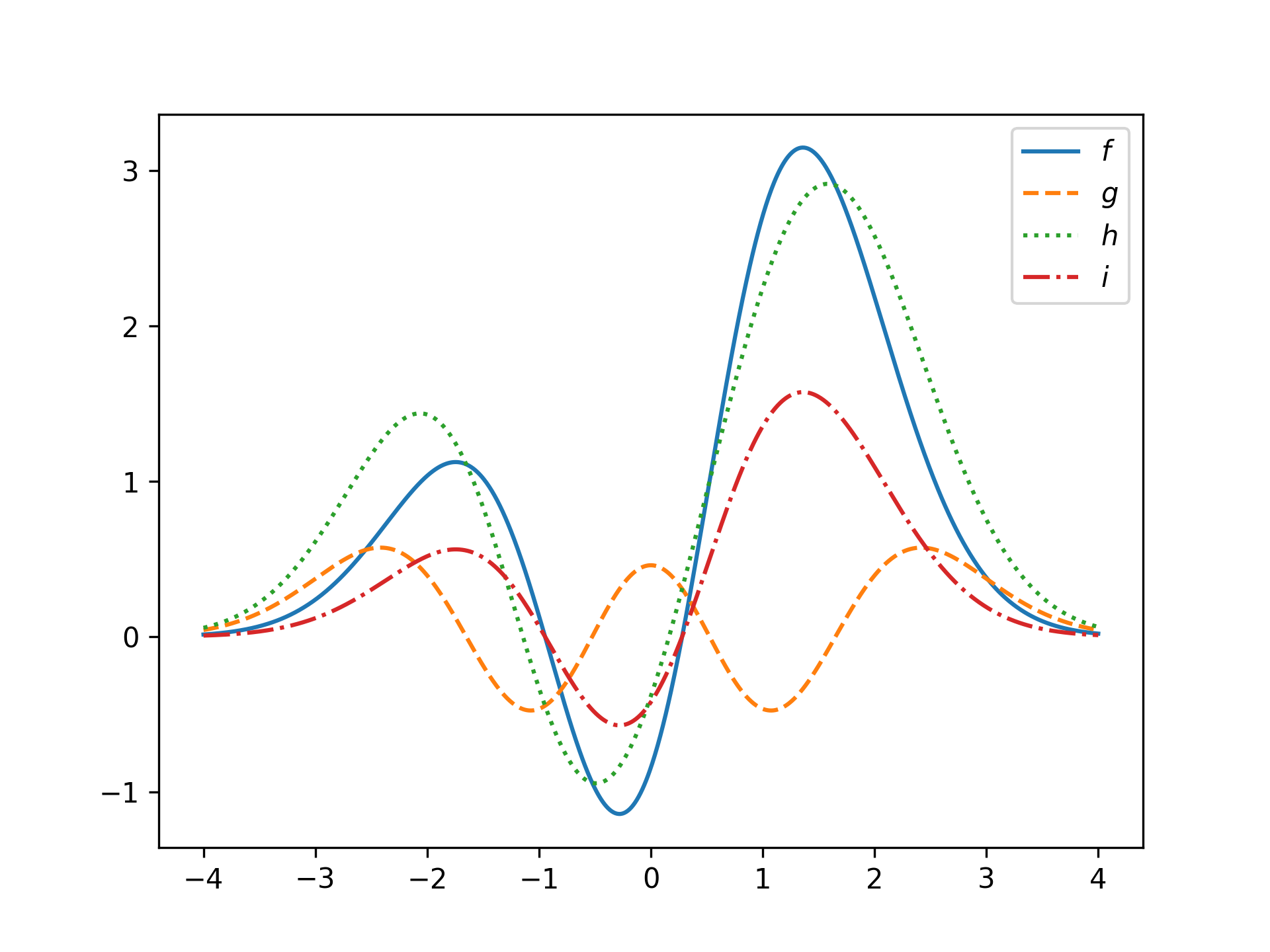 Because this package was intended as a tool to work with quantum mechanical wavefunctions, the expectation value for the kinetic energy is also implemented (
Because this package was intended as a tool to work with quantum mechanical wavefunctions, the expectation value for the kinetic energy is also implemented (
f.kinIn the following let
where
from Wikipedia - Hermite functions.
With
With the same relation as above we get
which can be applied from the highest to the lowest order. For
Copyright (c) 2022 Sebastian Gössl
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.