Aeryn
Aeryn is a server app, written in Sinatra, used to invite new contributors to a GitHub organization team once they have a pull request merged.
State
This project works for production. However, by this point all of the Aeryn servers ran by the maintainers of this repo have moved to danger/peril with an aeryn.ts file.
Motivation
Moya's contributor guidelines explain in detail what we'll summarize here: we believe in giving push access to contributors after they have a pull request merged. On Moya's main repo, we've been practicing this since June 2015; the practice has led to an engaged, respectful community helping to improve the project.
But remembering to check every pull request, actually inviting new contributors, leaving them a comment – it's work that adds up. This project automates that process using GitHub WebHooks and the GitHub API.
Setup
There are a few prerequisites:
- A GitHub personal access token.
- The team ID of the GitHub org team to invite contributors to.
Personal Access Token
You'll need to create a new personal access token on whatever account will be inviting new contributors (this means the account needs admin writes). The access token needs the admin:org and public_repo scopes.
Team ID
The organization's Team ID is also required. This is a number that's not easily retrieved from GitHub's user interface. You can retrieve it by using curl and your personal access token from the previous step.
> curl -H "Authorization: token PUT_YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN_HERE" https://api.github.com/orgs/PUT_YOUR_ORG_NAME_HERE/teamsThat will return a JSON list of teams on the org. Pick the one you want to invite contributors to (here's an abridged sample of what that might look like).
[
{
"name": "Contributors",
"id": 1234567
}
]Deploy
The easiest way to deploy the app is to use Heroku. Click the following to get set up and provide necessary config values.
If you don't want to use Heroku, you can copy .env.sample to .env to set environment variables for your server. The variables themselves are described in the app.json file.
Configuring the WebHook
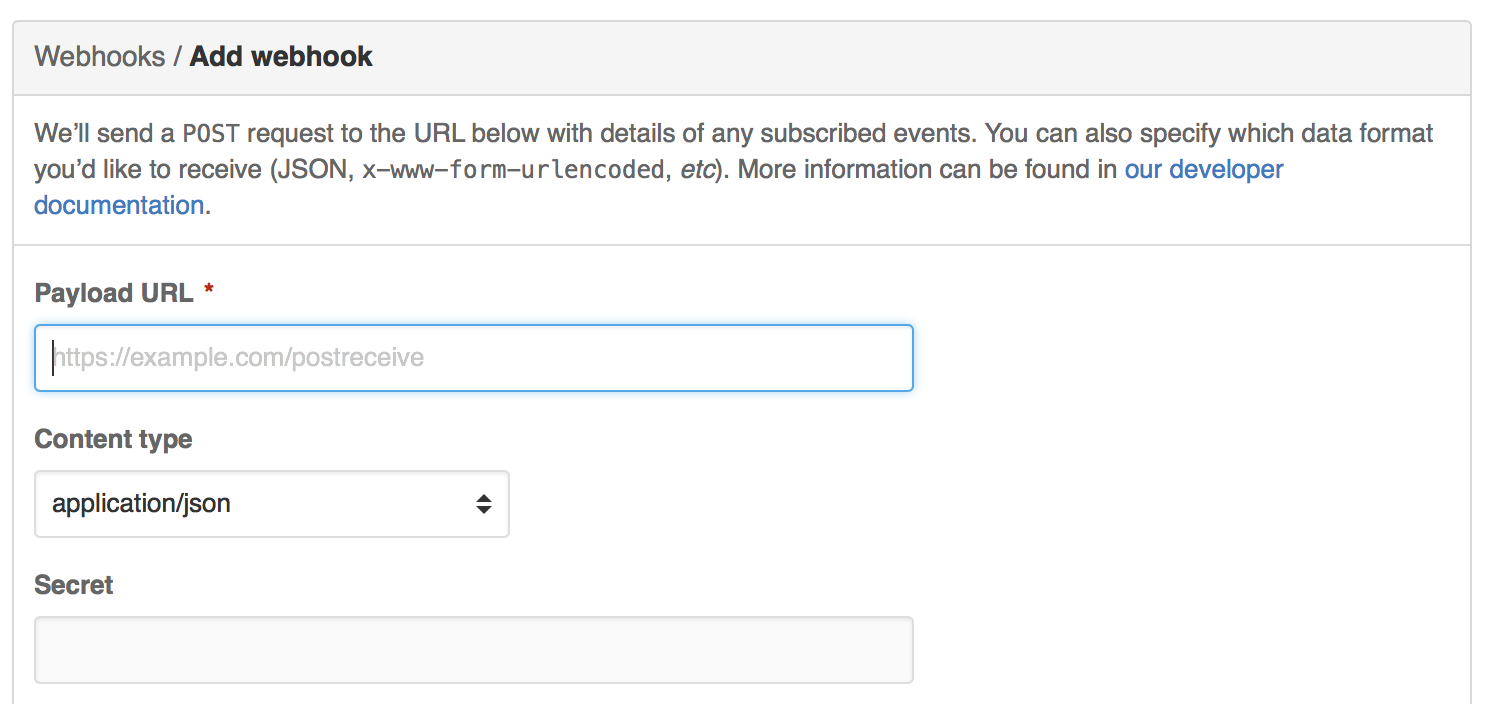
Once deployed, we need to point your GitHub repo(s) at the server. Go to your repository's settings page and WebHook tab, and create a new WebHook.
You'll need the server's address, as well as the WEBHOOK_ENDPOINT environment variable you set up earlier. So if your server is at https://example.com and the endpoint is /payload, then the Payload URL for the WebHook is https://example.com/payload.
You'll also need to specify a secret. This is a random string that GitHub will use to sign the requests sent to Aeryn, to make sure no one else can control the server but GitHub.
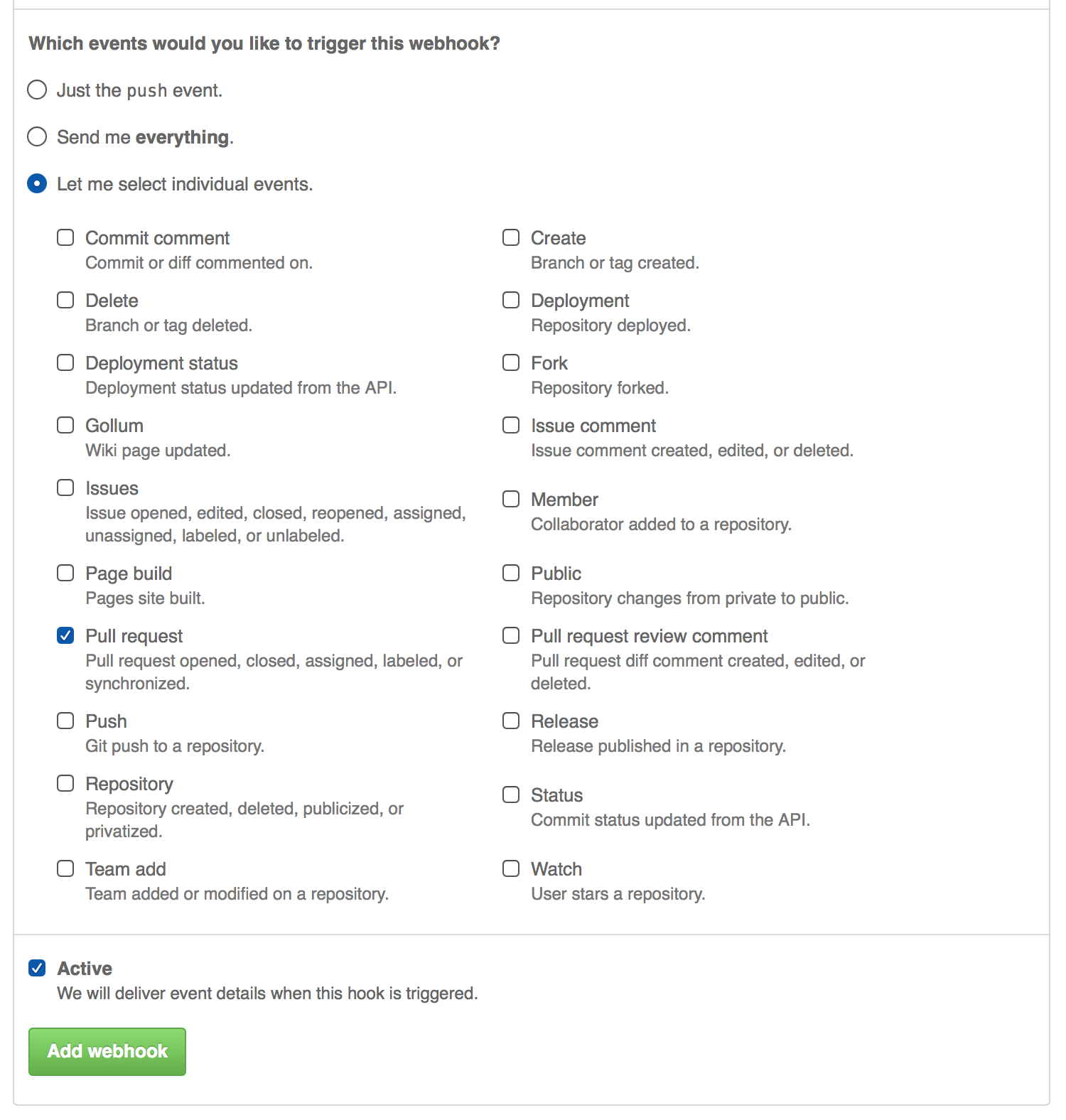
Only certain events need to trigger the WebHook, specifically the "Pull Request" event.
Once you've saved the WebHook, GitHub will send a ping to your server to see if everything is working. Aeryn should respond that everything is fine, and you'll see a nice green check under the WebHook settings:
If you don't see a green checkmark, it means that GitHub wasn't able to reach Aeryn. Double-check your environment variables and server config, and please feel free to open an issue.
Contributing
If you have trouble installing
ffiwhen runningbundle install, try runningbrew install coreutilsfirst.
This project is open source under the MIT license, which means you have full access to the source code and can modify it to fit your own needs.
This project subscribes to the Moya Contributors Guidelines which TLDR: means we give out push access easily and often. That's actually the whole point of this repo.
This repo subscribes to the Contributor Code of Conduct, based on the Contributor Covenant version 1.4.0. The maintainers take the code of conduct seriously.
Organizations using Aeryn
Check out this list of known organizations using Aeryn. Submit a pull request if you'd like to be added to the list!