In this CTF we gonna analyze .pcap from scenario where user accidentally clicked on button to Enable Content in word document received by email. SOC team immediately received alert from endpoint which tried to establish suspicious outbound connection. Click here to navigate to room.
Upon booting up the target machine, open Wireshark and load the file from Desktop/Analysis/carnage.pcap . Lets dive in:
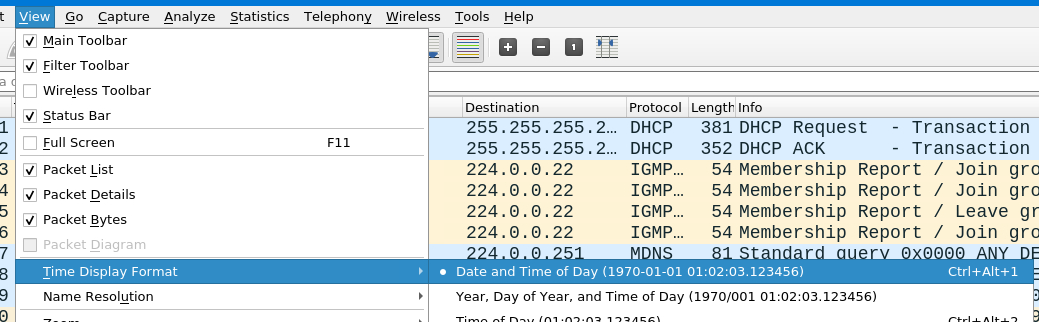
First we need to adjust the Time Display Format in Wireshark navigating to View>Time Display Format > Date and Time of Day.
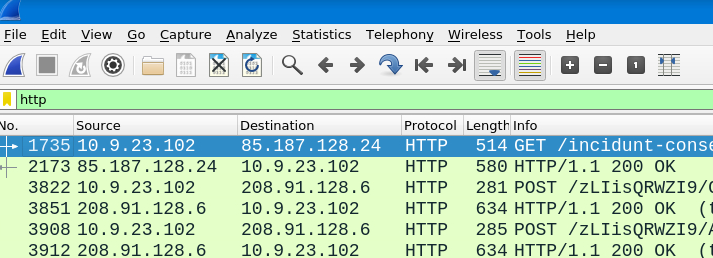
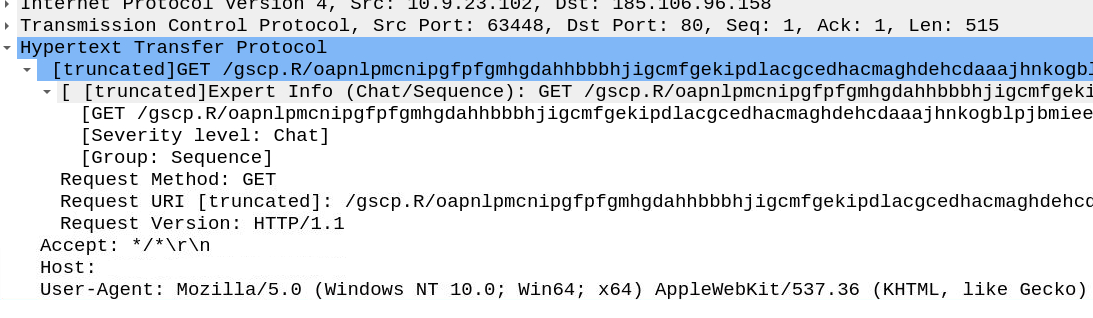
Once this is adjusted we have far better overview about timeline - lets now filter for HTTP traffic and check the very first packet - i hide the Time column to avoid spoiling.
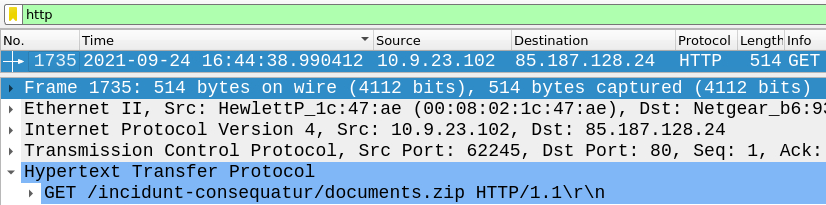
Answer: 2021-09-24 16:44:38
Very first http packet is also GET response - navigate to the info section on the top left to GET the answer.
Answer: documents.zip
Lets navigate to the first HTTP packet header right below GET section to get our answer.
Answer: attirenepal.com
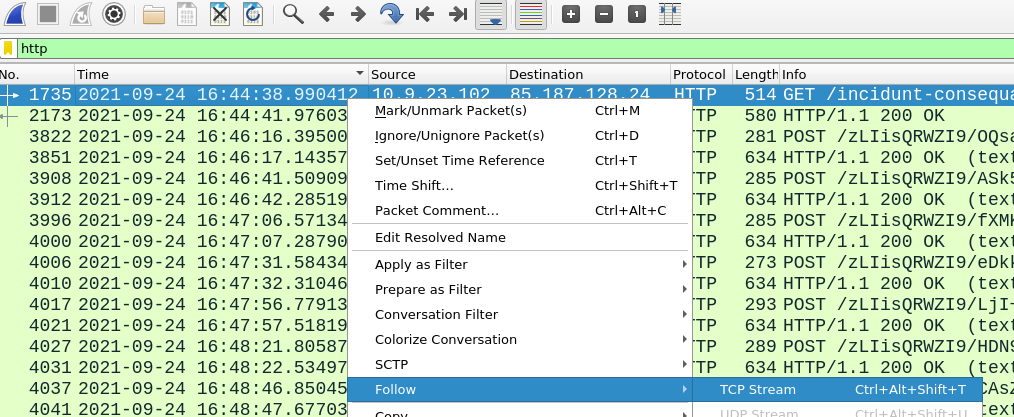
Following the same TCP stream and using link below to find .zip file we will spot the name easily.
Answer: chart-1530076591.xls
Lets use very popular Wireshark feature - follow TCP stream and inspect the traffic.
Lets investigate 2nd packet where we received OK from web server. There is header field Server which is name of our webserver.
Answer: LiteSpeed
Pretty straight-forward - using same stream but looking for server version.
Answer: PHP/7.2.34
Malicious files were downloaded to the victim host from multiple domains. What were the three ****domains involved with this activity?
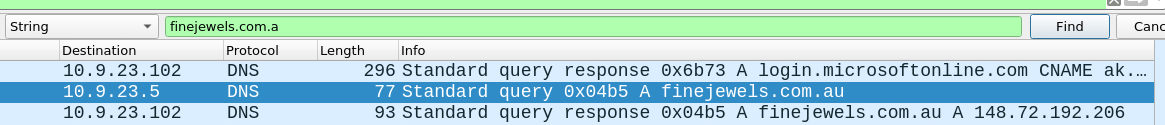
This was pain to even realize where to search, upon checking the hint i narrowed the search to the specified timeframe and used DNS filter to search for domains which were resolved. Used this query
(frame.time>="2021-09-24 16:45:11") && (frame.time<="2021-09-24 16:45:30") && dns
Answer: finejewels.com.au, thietbiagt.com, new.americold.com
Which certificate authority issued the SSL certificate to the first domain from the previous question?
First lets find the IP address of the domain - using basic search for the first domain from previous answer.
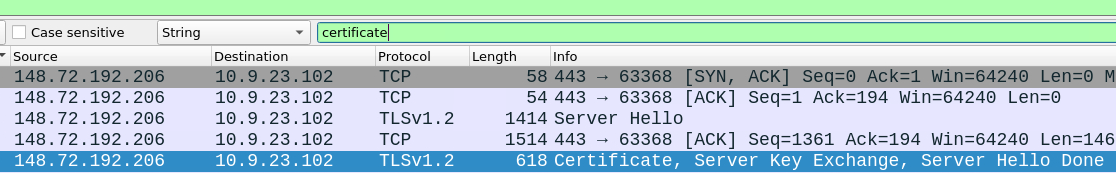
Lets use this IP address in source IP filter - server sends certificate as inbound traffic - and filter for certificate
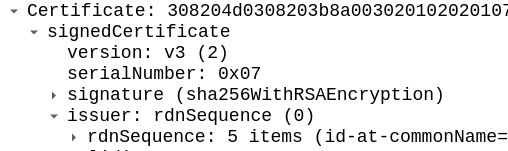
Perfect, all we need to do is now check the TLS header and look for CA.
Answer: godaddy
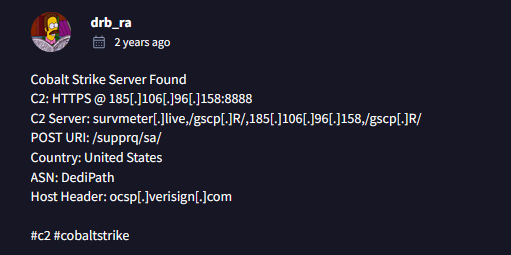
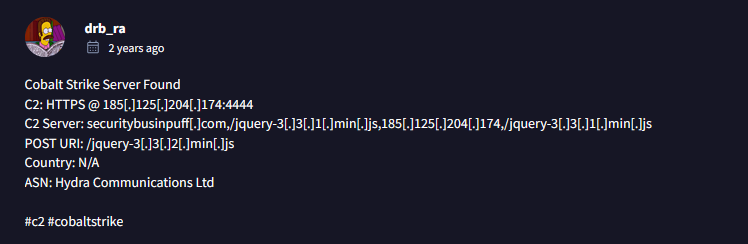
What are the two IP addresses of the Cobalt Strike servers? Use VirusTotal (the Community tab) to confirm if IPs are identified as Cobalt Strike C2 servers. (answer format: enter the IP addresses in sequential order)
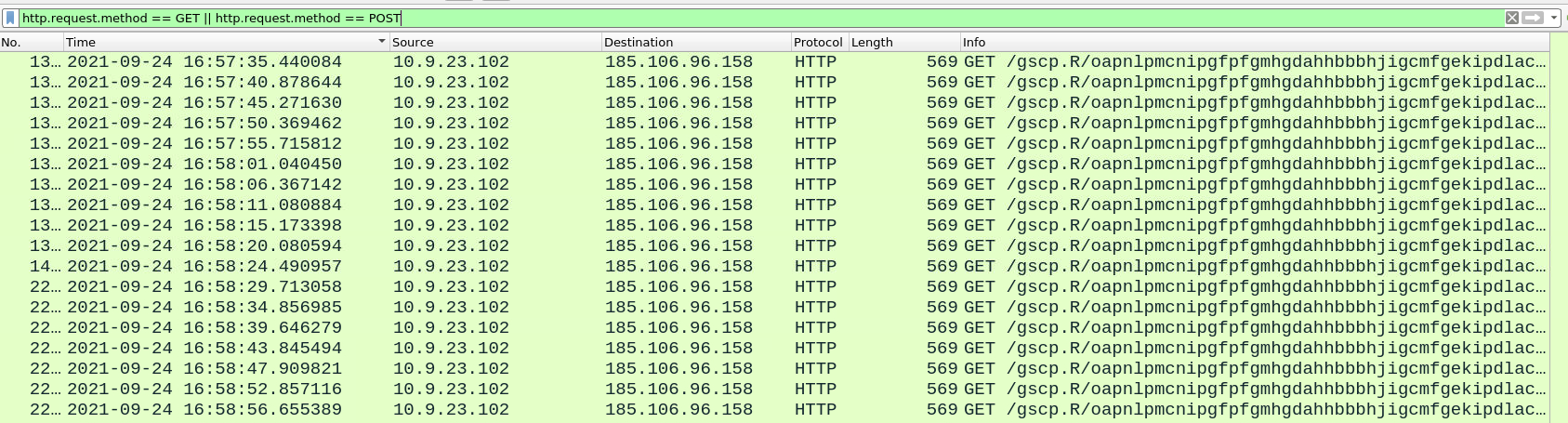
Cobalt Strike's Command and Control (C2) servers are pivotal components in its architecture, used for managing compromised systems or "beacons" remotely. These servers receive data from and send commands to beacons embedded in targeted networks. This setup allows attackers or penetration testers to control and coordinate actions across infiltrated systems, execute commands, exfiltrate data, and deploy further payloads. Two main methods used by C2 servers are POST and GET - lets narrow the search for this two using following filter
http.request.method == GET || http.request.method == POST
Upon applying the filter there is spike of GET responses to the single IP address.
Lets doublecheck our address 185.106.96.158 with VirusTotal and navigate to Community tab.
Very good, IP address confirmed as c2 by members of the InfoSec community, first one is done.
Lets exclude our first IP address from filter and recheck the results.
http.request.method == GET || http.request.method == POST && ip.dst != 185.106.96.158
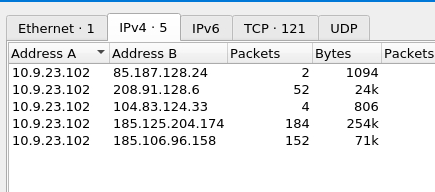
Checking the other IP’s none of them seems to be marked as C2. Ok have a step back and use a feature of Wireshark called Conversations along with http traffic filter for broader spectrum.
Once opened use Limit to display filter feature at very bottom, this will narrow the search only for http traffic - which will rapidly speed up our analysis - now we have few IP’s to check.
We have already verified the last one, lets see the 2nd from bottom within Virus Total > Community.
Success, we identified the 2nd one as well.
Answer: 185.106.96.158,185.125.204.174
We will filter for destination IP along with http using this following filter
ip.dst == 185.106.96.158 && http
Once we narrow the search we will open one of the GET packets and inspect the header fields.
Answer: ocsp.verisign.com
What is the domain name for the first IP address of the Cobalt Strike server? You may use VirusTotal to confirm if it's the Cobalt Strike server (check the Community tab).
Navigate to the Virus Total to Relations tab to get the answer. Also you can filter for dns packets ****in Wireshark and use the IP address to get the resolution.
Answer: survmeter.live
What is the domain name of the second Cobalt Strike server IP? You may use VirusTotal to confirm if it's the Cobalt Strike server (check the Community tab).
Virus Total, dns, IP and repeat.
Answer: securitybusinpuff.com
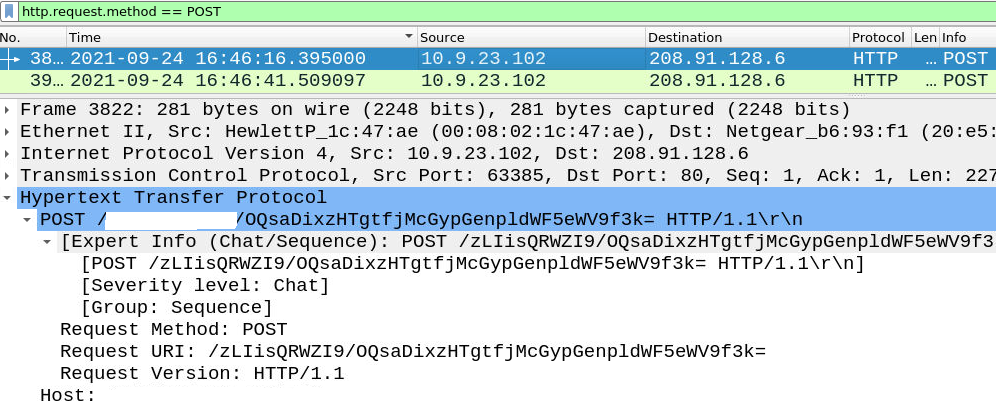
In this case i used Hint cus a was bit confused by the question asked - and post-infection traffic refers to POST-infection. Lets use our filter to narrow down POST requests.
http.request.method == POST
Pick any of the POST packet and inspect the HTTP header.
Answer: maldivehost.net
What are the first eleven characters that the victim host sends out to the malicious domain involved in the post-infection traffic?
Using the same filter, we will check the very first POST request and again inspect HTTP header.
See for yourself.
Answer: 281
Navigating to the TCP stream from same filter we will observe HTTP headers for the answer.
Answer: Apache/2.4.49 (cPanel) OpenSSL/1.1.1l mod_bwlimited/1.4
The malware used an API to check for the IP address of the victim’s machine. What was the date and time when the ****DNS ****query for the IP check domain occurred? (answer format: yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss UTC)
I used very difficult approach at first but the answer is pretty simple. Assuming there is any api in the name of service involved lets observe DNS traffic and search for api.
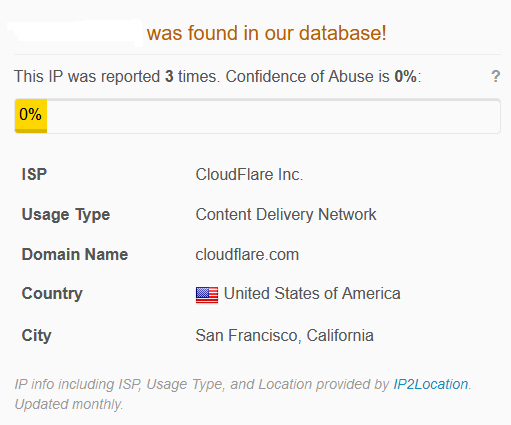
Our first result is shown, lets verify it via AbuseIPDB.
We have positive match that api is marked as malicious, now extract the timestamp for correct answer.
Answer: 2021-09-24 17:00:04
Answer lies here.
Answer: api.ipify.org
Looks like there was some malicious spam (malspam) activity going on. What was the first MAIL FROM address observed in the traffic?
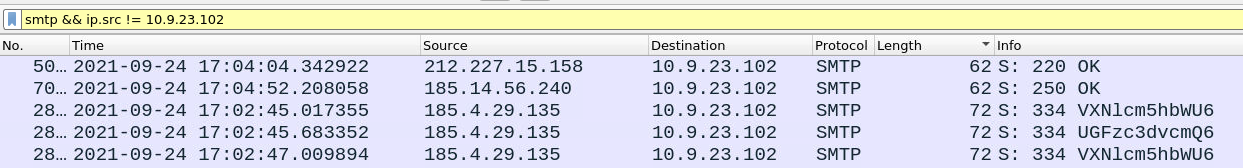
Malspam, or malicious spam, refers to unsolicited emails used to distribute malware. These emails often appear legitimate and use social engineering tactics to trick recipients into opening attachments or clicking on links that contain malicious payloads. This means we are looking for email which contains an attachment or source IP address is marked as malicious across Thread Intelligence webs such VirusTotal or AbuseIP. Since we are looking for inbound smtp traffic lets filter for smtp and exclude client IP address 10.9.23.102. Using this filter:
smtp && ip.src != 10.9.23.102
Good, now sort the frame size from highest>lowest to determine if we are dealing with the malicious attachment or not.
The highest inbound email had 300 bytes which is very low for any attachment so we can exclude this approach and focus more on email content and source IP address. Lets sort the packets from oldest > newest and start checking. Upon checking the first packets this thread of packets seemed off to me
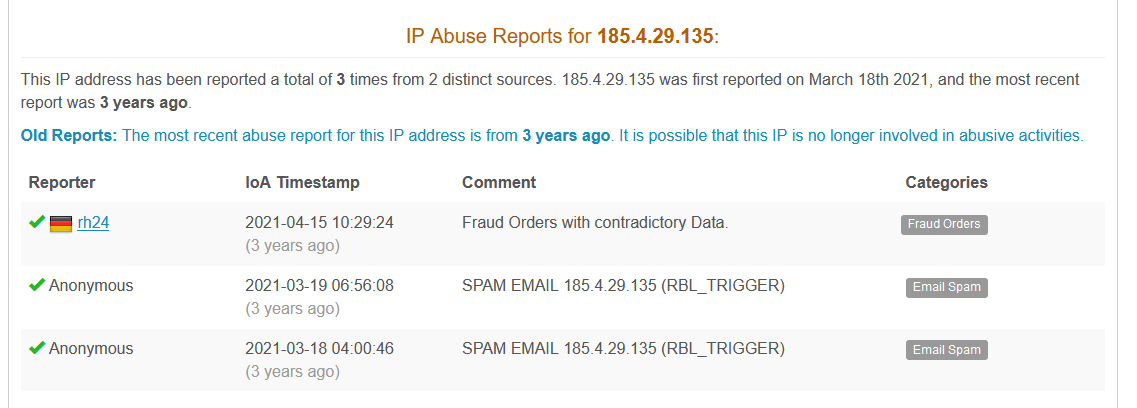
Email is informing us that our SMTP service is disabled - ok lets verify the IP address using AbuseIPDB.
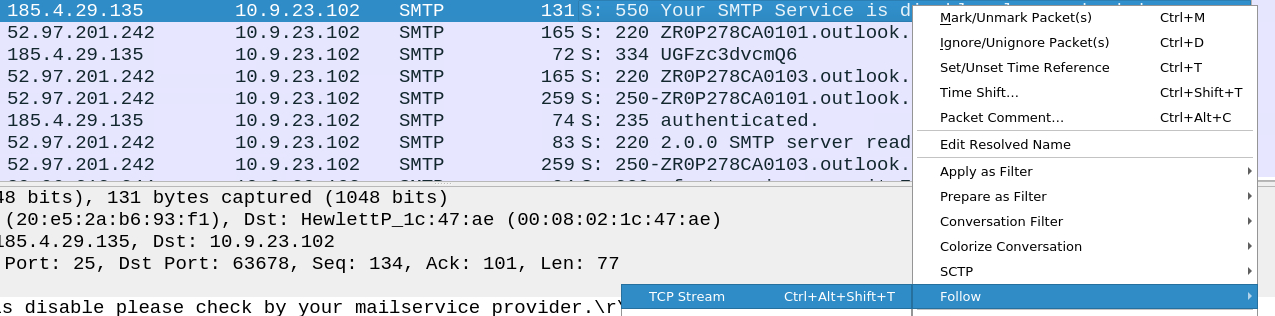
AbuseIPDB confirmed the malicious intend and also showed us the category - Email Spam. Lets dive into TCP stream and recheck the MAIL FROM
Upon checking the stream, recheck the address.
Answer: farshin@mailfa.com
Use smtp as filter and check at the very bottom where Wireshark displays the count.
Answer: 1439
And that’s a wrap, thanks for audience.