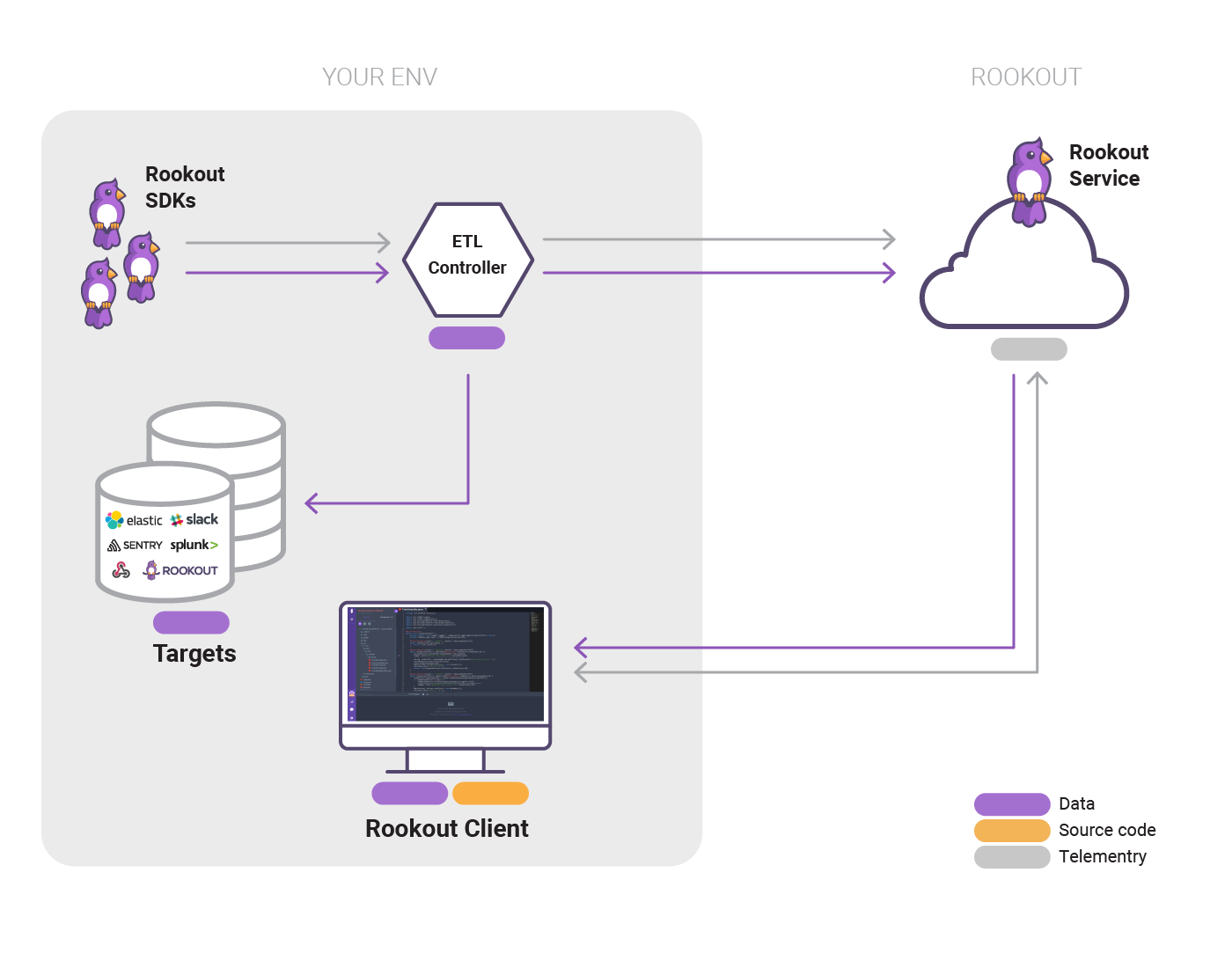
This project will use rookout live debuging tool to debug two flask applications. for on premise k8s cluster we will use docker-desktop k8s cluster. The build and deployment of aplications would be in gitops percipels using argocd, argoEvents and argoWorkflows.
The local cluster will use ngnix controller for external traffic. conroller's service will be expose on 443 and 80 by ngnix loadbalancer. cert-manager will auto generate self-signed certificates.
External DNS server will not be used. all domains will be configurated locally in /etc/host and resloved to localhost. by the domain ngnix controller will route to the right service using ingress.
Domains:
webhook.example - used to trigger argoWorkflow in /flaskapp .
webapp.example - rookout's flask application.
datastore.example - external domain for datastore componenet.
controller.example - external domain for controller.
argowf.example - argoWorkflow UI.
flask-app.example - my flask application.
argocd.example - argoCD UI.
For using rookout localy, we will use ETL conroller and datastore. only metadata will pass to rookout cloud and all the information would be stored locally in datastore component. The deployment would be using argoCD application and helm charts.
Each of flask webapps intiating connection to rookout's ETL controller using SDK. for that purpose the container will be injected with enviorment variables which the process expect. the veriables are:
ROOKOUT_TOKEN: value manual pre-injected secret (rookout-token) to argocd namespace (key token)
ROOKOUT_CONTROLLER_HOST: ws://rookout-controller.argocd.svc.cluster.local
ROOKOUT_CONTROLLER_PORT: 7488 us the websockt
ROOKOUT_REMOTE_ORIGIN: each application with it's remote git repo.
I will use to webapplication.
flask-app: https://github.com/GoshaDo/BestFW
webapp: The dockerfile edited and the repo wasn't forked, those changes was performed to support arm64 chip. base image have been changed to python:3.8-slim and "apt-get install g++ -y " step added. repo: https://github.com/Rookout/tutorial-python
We will use argo stack, ArgoEvents, ArgoWorkflows, ArgoCD. ArgoEvents will detect and store webhook requests to preconfigured domain and path. ArgoWorkflows will use sensor to watch for sutied event and trigger workflow (pipeline).
The pipline will clone or pull the repo and build new image using kaniko (We want to avoud mapping docker stock due to security issues) then delivery the new image and the tag to dockerhub. the workflow will automaticly update this repo tag value at /argocd/app/values.yaml. Then argoCD will auto-sync with the envriorment.
- Lunch docker-desktop k8s cluster using GUI.
- install following charts:
helm install --namespace argocd --create-namespace argocd ./charts/argocd
helm install --namespace ingress-nginx --create-namespace ingress-nginx ./charts/ingress-nginx
- Deploy safley rookout token as k8s secret
kubectl create secret generic rookout-token --from-literal=token=[SENSTIVE] -n argocd
- edit sudo vim /etc/hosts with
127.0.0.1 webhook.example
127.0.0.1 webapp.example
127.0.0.1 datastore.example
127.0.0.1 controller.example
127.0.0.1 argowf.example
127.0.0.1 flask-app.example
127.0.0.1 argocd.example
- create ssh keys using ssh-keygen. chmod to 400 and configure public key in github repo, and inject private key using :
kubectl create secret generic git-creds --from-file=ssh-private-key=/Users/gosha/.ssh/github -n argocd
- deploy dockerhub auth secret for your's container registrey.
export DOCKER_USERNAME=goshad
export DOCKER_PASSWORD=[SENSTIVE]
export DOCKER_SERVER=https://index.docker.io/v1/
kubectl create -n argocd secret docker-registry regcred \
--docker-server=${DOCKER_SERVER} \
--docker-username=${DOCKER_USERNAME} \
--docker-password=${DOCKER_PASSWORD}
- expose using ngrok
ngrok http webhook.example:80
- automatic deployment by changing the tag of flask-app in argocd/apps/value.yaml file after build and pushing to dockerhub.
- intergrating integration test in staging enviorment before. if failed will revert changes by updating back the value.yaml file
- seperate applications and infra to diffrent namespaces.