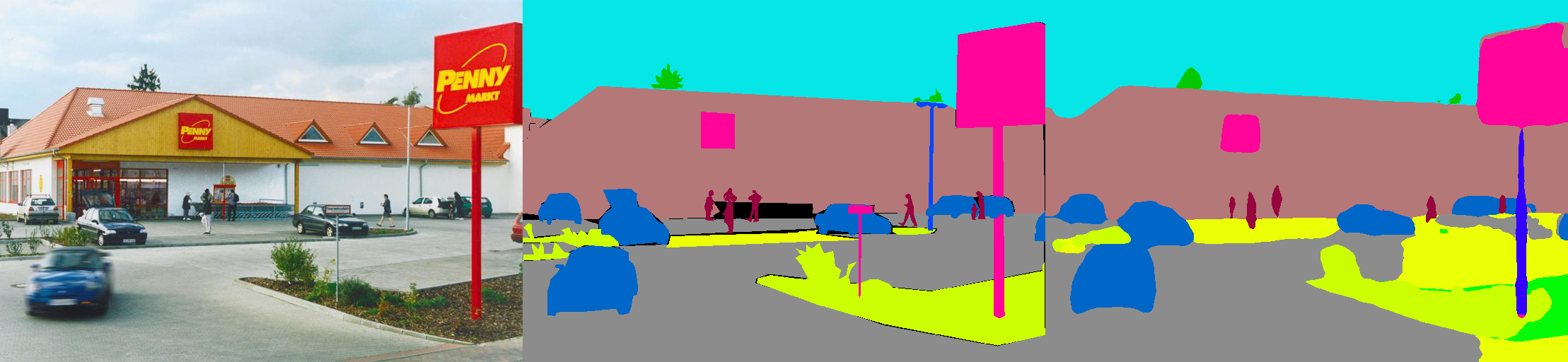
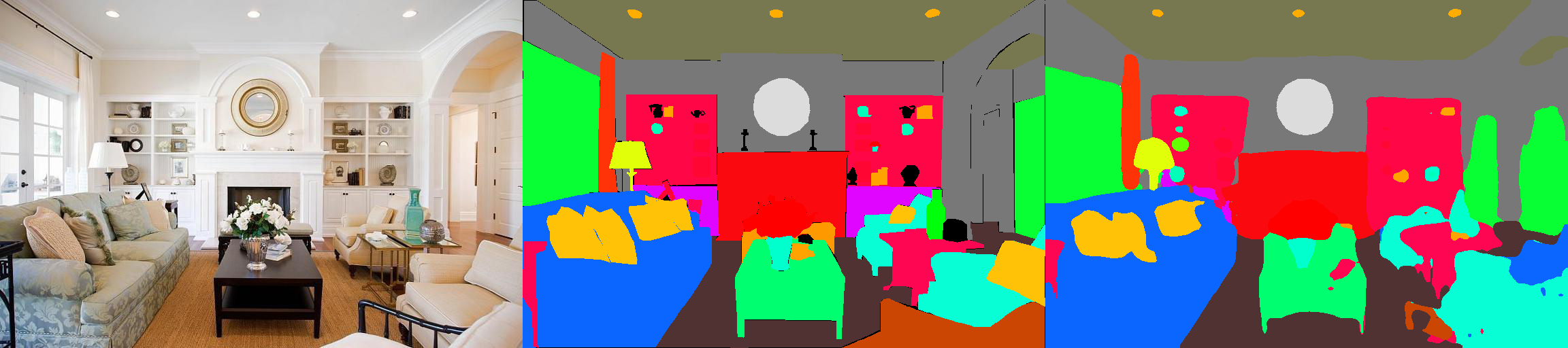
This is a PyTorch implementation of semantic segmentation models on MIT ADE20K scene parsing dataset.
ADE20K is the largest open source dataset for semantic segmentation and scene parsing, released by MIT Computer Vision team. Follow the link below to find the repository for our dataset and implementations on Caffe and Torch7: https://github.com/CSAILVision/sceneparsing
If you simply want to play with our demo, please try this link: http://scenesegmentation.csail.mit.edu You can upload your own photo and segment it!
All pretrained models can be found at: http://sceneparsing.csail.mit.edu/model/pytorch
[From left to right: Test Image, Ground Truth, Predicted Result]Color encoding of semantic categories can be found here: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1se8YEtb2detS7OuPE86fXGyD269pMycAWe2mtKUj2W8/edit?usp=sharing
- We use configuration files to store most options which were in argument parser. The definitions of options are detailed in
config/defaults.py.
This module computes the mean and standard-deviation across all devices during training. We empirically find that a reasonable large batch size is important for segmentation. We thank Jiayuan Mao for his kind contributions, please refer to Synchronized-BatchNorm-PyTorch for details.
The implementation is easy to use as:
- It is pure-python, no C++ extra extension libs.
- It is completely compatible with PyTorch's implementation. Specifically, it uses unbiased variance to update the moving average, and use sqrt(max(var, eps)) instead of sqrt(var + eps).
- It is efficient, only 20% to 30% slower than UnsyncBN.
For the task of semantic segmentation, it is good to keep aspect ratio of images during training. So we re-implement the DataParallel module, and make it support distributing data to multiple GPUs in python dict, so that each gpu can process images of different sizes. At the same time, the dataloader also operates differently.
Now the batch size of a dataloader always equals to the number of GPUs, each element will be sent to a GPU. It is also compatible with multi-processing. Note that the file index for the multi-processing dataloader is stored on the master process, which is in contradict to our goal that each worker maintains its own file list. So we use a trick that although the master process still gives dataloader an index for __getitem__ function, we just ignore such request and send a random batch dict. Also, the multiple workers forked by the dataloader all have the same seed, you will find that multiple workers will yield exactly the same data, if we use the above-mentioned trick directly. Therefore, we add one line of code which sets the defaut seed for numpy.random before activating multiple worker in dataloader.
UPerNet is a model based on Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) and Pyramid Pooling Module (PPM). It doesn't need dilated convolution, an operator that is time-and-memory consuming. Without bells and whistles, it is comparable or even better compared with PSPNet, while requiring much shorter training time and less GPU memory (e.g., you cannot train a PSPNet-101 on TITAN Xp GPUs with only 12GB memory, while you can train a UPerNet-101 on such GPUs). Thanks to the efficient network design, we will soon open source stronger models of UPerNet based on ResNeXt that is able to run on normal GPUs. Please refer to UperNet for details.
We split our models into encoder and decoder, where encoders are usually modified directly from classification networks, and decoders consist of final convolutions and upsampling.
Encoder:
- MobileNetV2dilated
- ResNet18dilated
- ResNet50dilated
- ResNet101dilated
Decoder:
- C1 (1 convolution module)
- C1_deepsup (C1 + deep supervision trick)
- PPM (Pyramid Pooling Module, see PSPNet paper for details.)
- PPM_deepsup (PPM + deep supervision trick)
- UPerNet (Pyramid Pooling + FPN head, see UperNet for details.)
IMPORTANT: We use our self-trained base model on ImageNet. The model takes the input in BGR form (consistent with opencv) instead of RGB form as used by default implementation of PyTorch. The base model will be automatically downloaded when needed.
| Architecture | MultiScale Testing | Mean IoU | Pixel Accuracy(%) | Overall Score | Inference Speed(fps) | Training Time(hours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNetV2dilated + C1_deepsup | No | 34.84 | 75.75 | 54.07 | 17.2 | 0.8 * 20 = 16 |
| Yes | 33.84 | 76.80 | 55.32 | 10.3 | ||
| MobileNetV2dilated + PPM_deepsup | No | 35.76 | 77.77 | 56.27 | 14.9 | 0.9 * 20 = 18.0 |
| Yes | 36.28 | 78.26 | 57.27 | 6.7 | ||
| ResNet18dilated + C1_deepsup | No | 33.82 | 76.05 | 54.94 | 13.9 | 0.42 * 20 = 8.4 |
| Yes | 35.34 | 77.41 | 56.38 | 5.8 | ||
| ResNet18dilated + PPM_deepsup | No | 38.00 | 78.64 | 58.32 | 11.7 | 1.1 * 20 = 22.0 |
| Yes | 38.81 | 79.29 | 59.05 | 4.2 | ||
| ResNet50dilated + PPM_deepsup | No | 41.26 | 79.73 | 60.50 | 8.3 | 1.67 * 20 = 33.4 |
| Yes | 42.14 | 80.13 | 61.14 | 2.6 | ||
| ResNet101dilated + PPM_deepsup | No | 42.19 | 80.59 | 61.39 | 6.8 | 3.82 * 25 = 95.5 |
| Yes | 42.53 | 80.91 | 61.72 | 2.0 | ||
| UperNet50 | No | 40.44 | 79.80 | 60.12 | 8.4 | 1.75 * 20 = 35.0 |
| Yes | 41.55 | 80.23 | 60.89 | 2.9 | ||
| UperNet101 | No | 42.00 | 80.79 | 61.40 | 7.8 | 2.5 * 25 = 62.5 |
| Yes | 42.66 | 81.01 | 61.84 | 2.3 |
The training is benchmarked on a server with 8 NVIDIA Pascal Titan Xp GPUs (12GB GPU memory), except for ResNet101dilated, which is benchmarked on a server with 8 NVIDIA Tesla P40 GPUS (22GB GPU memory), because of the insufficient memory issue when using dilated conv on a very deep network. The inference speed is benchmarked a single NVIDIA Pascal Titan Xp GPU, without visualization.
The code is developed under the following configurations.
- Hardware: >=4 GPUs for training, >=1 GPU for testing (set
[--gpus GPUS]accordingly) - Software: Ubuntu 16.04.3 LTS, CUDA>=8.0, Python>=3.5, PyTorch>=0.4.0
- Dependencies: numpy, scipy, opencv, yacs, tqdm
- Here is a simple demo to do inference on a single image:
chmod +x demo_test.sh
./demo_test.shThis script downloads a trained model (ResNet50dilated + PPM_deepsup) and a test image, runs the test script, and saves predicted segmentation (.png) to the working directory.
- To test on an image or a folder of images (
$PATH_IMG), you can simply do the following:
python3 -u test.py --imgs $PATH_IMG --gpu $GPU --cfg $CFG
- Download the ADE20K scene parsing dataset:
chmod +x download_ADE20K.sh
./download_ADE20K.sh- Train a model by selecting the GPUs (
$GPUS) and configuration file ($CFG) to use. During training, checkpoints by default are saved in folderckpt.
python3 train.py --gpus $GPUS --cfg $CFG - To choose which gpus to use, you can either do
--gpus 0-7, or--gpus 0,2,4,6.
For example, you can start with our provided configurations:
- Train MobileNetV2dilated + C1_deepsup
python3 train.py --gpus GPUS --cfg config/ade20k-mobilenetv2dilated-c1_deepsup.yaml- Train ResNet50dilated + PPM_deepsup
python3 train.py --gpus GPUS --cfg config/ade20k-resnet50dilated-ppm_deepsup.yaml- Train UPerNet101
python3 train.py --gpus GPUS --cfg config/ade20k-resnet101-upernet.yaml- You can also override options in commandline, for example
python3 train.py TRAIN.num_epoch 10.
- Evaluate a trained model on the validation set. Add
VAL.visualize Truein argument to output visualizations as shown in teaser.
For example:
- Evaluate MobileNetV2dilated + C1_deepsup
python3 eval_multipro.py --gpus GPUS --cfg config/ade20k-mobilenetv2dilated-c1_deepsup.yaml- Evaluate ResNet50dilated + PPM_deepsup
python3 eval_multipro.py --gpus GPUS --cfg config/ade20k-resnet50dilated-ppm_deepsup.yaml- Evaluate UPerNet101
python3 eval_multipro.py --gpus GPUS --cfg config/ade20k-resnet101-upernet.yaml
## Reference
If you find the code or pre-trained models useful, please cite the following papers:
Semantic Understanding of Scenes through ADE20K Dataset. B. Zhou, H. Zhao, X. Puig, T. Xiao, S. Fidler, A. Barriuso and A. Torralba. International Journal on Computer Vision (IJCV), 2018. (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.05442.pdf)
@article{zhou2018semantic,
title={Semantic understanding of scenes through the ade20k dataset},
author={Zhou, Bolei and Zhao, Hang and Puig, Xavier and Xiao, Tete and Fidler, Sanja and Barriuso, Adela and Torralba, Antonio},
journal={International Journal on Computer Vision},
year={2018}
}
Scene Parsing through ADE20K Dataset. B. Zhou, H. Zhao, X. Puig, S. Fidler, A. Barriuso and A. Torralba. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017. (http://people.csail.mit.edu/bzhou/publication/scene-parse-camera-ready.pdf)
@inproceedings{zhou2017scene,
title={Scene Parsing through ADE20K Dataset},
author={Zhou, Bolei and Zhao, Hang and Puig, Xavier and Fidler, Sanja and Barriuso, Adela and Torralba, Antonio},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
year={2017}
}