RPC (Remote Procedure Call) is an inter-process communication that exchanges information between various distributed systems (servers). It is a protocol that one program can use to request a service from a program located on some other node/server/computer/system on the network without having to understand the network's details.
In simple words, a computer A can call a function(procedures) in another computer B remotely. Hence, Remote Procedure Call.
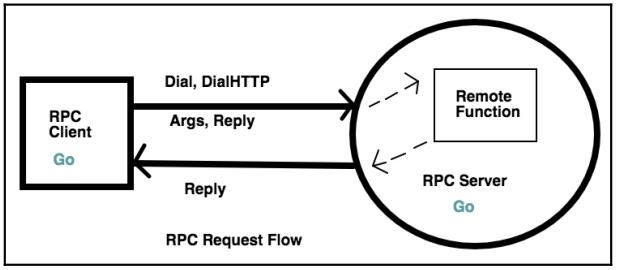
The basic steps for the entire process are as:
- Client (system
A) decides the function name and arguments to send - Client send the same to the
RPC Serverby dialing the connection - The RPC server receives the function name and arguments
- RPC server invokes/executes the function on the remote system
B - The client collects the data from the request
As you can see, it is a synchronous process.
Go provides a library for both RPC Server and RPC Client In the above diagram, the client sends the arguments and the reply pointer. Since it is a pointer, the server can modify it as per the request. The client will then use the data filled into the pointer.
Let us now create an RPC server that will send the UTC server time to the RPC client. We will use net/rpc and net/http standard packages for this example.
NOTE The RPC Server and RPC Client should agree upon:
- Arguments passed
- Value Returned
And must have exactly same types for both server and client
Let us create an Args struct to hold the arguments received from the client and TimeServer type using which we will register our function on RPC server for clients to run it.
type Args struct {}
type TimeServer int64Now let us create the GiveTimeServer function which will be invoked from the client.
func (t *TimeServer) GiveServerTime(args *Args, reply *int64) error {
// Set the value at the pointer got from the client
*reply = time.Now().Unix()
return nil
}Now let us register the methods listening on type TimeServer on the RPC server:
/* server.go */
func main() {
timeserver := new(TimeServer)
// Register the timeserver object upon which the GiveServerTime
// function will be called from the RPC server (from the client)
rpc.Register(timeserver)
// Registers an HTTP handler for RPC messages
rpc.HandleHTTP()
// Start listening for the requests on port 1234
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", "0.0.0.0:1234")
if err !=nil {
log.Fatal("Listener error: ", err)
}
// Serve accepts incoming HTTP connections on the listener l, creating
// a new service goroutine for each. The service goroutines read requests
// and then call handler to reply to them
http.Serve(listener, nil)
}That's it from the server side.
We will create the struct for Args (its empty in this example). And a reply variable which must have SAME type as that of server.
/* client.go */
package main
import (
"log"
"net/rpc"
)
type Args struct {}
func main() {
// Address to this variable will be sent to the RPC server
// Type of reply should be same as that specified on server
var reply int64
args := Args{}
// DialHTTP connects to an HTTP RPC server at the specified network
client, err := rpc.DialHTTP("tcp", "0.0.0.0:1234")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Client connection error: ", err)
}
// Invoke the remote function GiveServerTime attached to TimeServer pointer
// Sending the arguments and reply variable address to the server as well
err = client.Call("TimeServer.GiveServerTime", args, &reply)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("Client invocation error: ", err)
}
// Print the reply from the server
log.Printf("%d", reply)
}That was pretty straight forward. We just created a client and connected it to the host and port on which server is listening on.
Then we used the Call function to invoke a function tied to the TimeServer type and passed in args and &reply pointer.
Now let us start the server.go program.
$ go run server.go
Now let us start the client.go program and as soon as we do that, we will see the server's reply of it's current UTC time:
$ go run client.go
2021/09/04 18:36:37 1630760797 // 👈
That's it. It's that simple. I hope you guys understood how the client and server connection works via RPC server. In future blogs, we will dive deeper into the same topic and cover more on RPC and also GRPC.