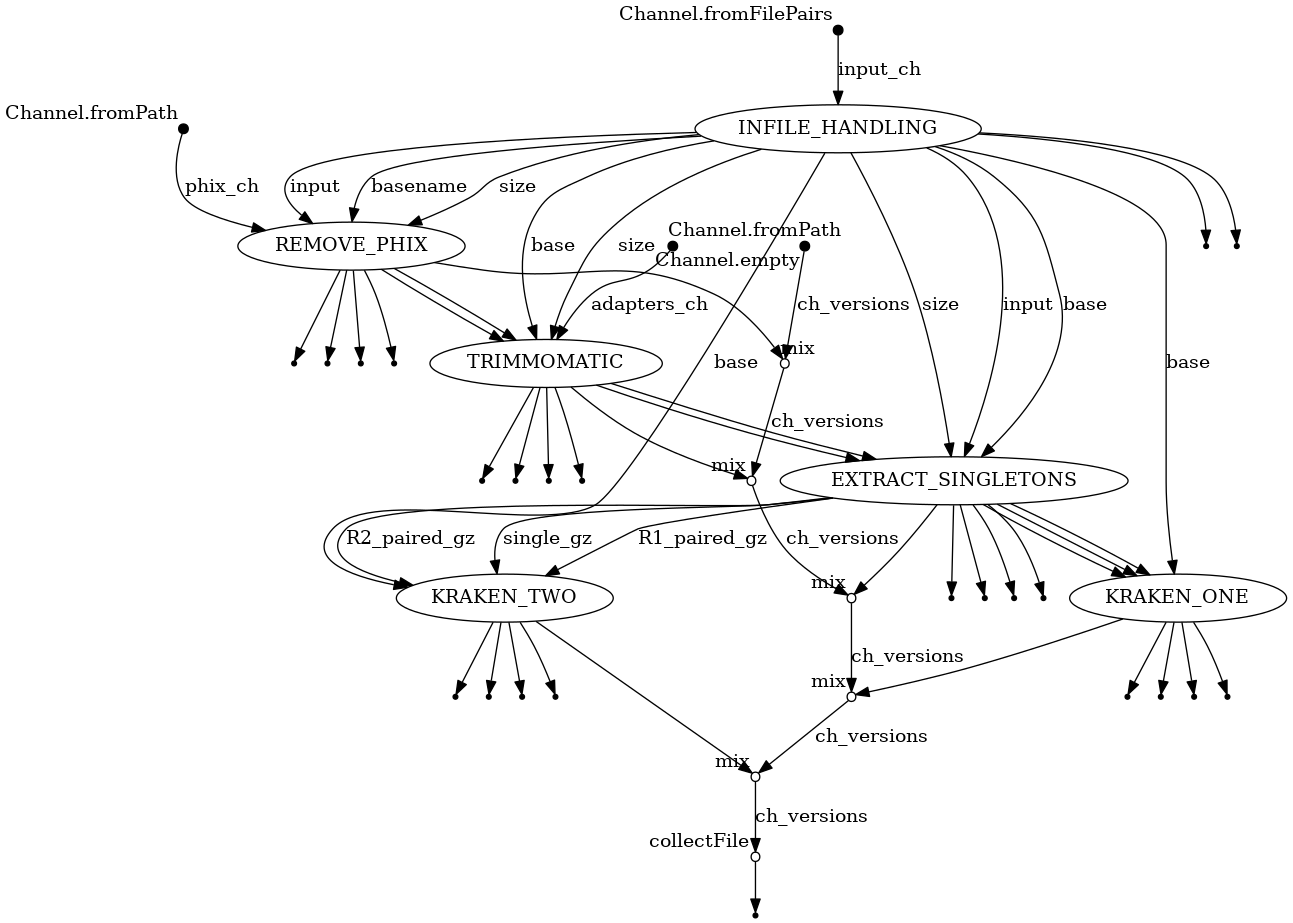
A schematic of the steps in the workflow.
- Nextflow
- Docker or Singularity
git clone https://github.com/gregorysprenger/wf-paired-illumina-read-clean.git
Example data are included in assets/test_data directory.
nextflow run \
-profile singularity main.nf \
--inpath assets/test_data \
--outpath results
Test data was generated by taking top 1 million lines of SRA data SRR16343585. (Note: This requires SRA toolkit)
fasterq-dump SRR16343585
head -1000000 SRR16343585_1.fastq > test_R1.fastq
head -1000000 SRR16343585_2.fastq > test_R2.fastq
gzip test_R*.fastq
# Add to $HOME/.bashrc
SINGULARITY_BASE=/scicomp/scratch/$USER
export SINGULARITY_TMPDIR=$SINGULARITY_BASE/singularity.tmp
export SINGULARITY_CACHEDIR=$SINGULARITY_BASE/singularity.cache
export NXF_SINGULARITY_CACHEDIR=$SINGULARITY_BASE/singularity.cache
mkdir -pv $SINGULARITY_TMPDIR $SINGULARITY_CACHEDIR
Reload .bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
Load nextflow
module load nextflow
- Identifies paired FastQ files in a given path
- Recognized extensions are: fastq.gz, fq.gz
- Remove PhiX from reads using bbduk
- Output:
- Total reads <*_raw.tsv>
- PhiX reads - <*_phix.tsv>
- Output:
- Adapter clipping and quality trimming using trimmomatic
- Output:
- Discarded reads and Singletons <*_trimmo.tsv>
- Output:
- Merge verlapping sister reads into singleton reads using flash
- Output:
- Paired and single reads: <*{R1,R2}.paired.fq.gz>, <*single.fq.gz>
- Number of overlapping reads <*overlap.tsv>
- Number of cleaned reads: <*clean-reads.tsv>
- Output:
- Binning of paired reads with kraken 1 and 2
- Output:
- Summary output <taxonomy{1,2}-reads.tab>
- Full kraken output <kraken{1,2}.tab.gz>
- Output: