Farpatch is a hardware debugger that is powered off of the VTref pin of a debug port and presents a wifi interface. This enables debugging JTAG and SWD remotely in systems that otherwise might be difficult to reach.
It is powered by the blackmagic project.
This was originally based on blackmagic-espidf for ESP8266 and has undergone extensive rework.
- Powered by the target using
VTref - Compatible with 1.8V - 5V targets
- Built-in web server with serial terminal
- RTT support for serial-over-debug
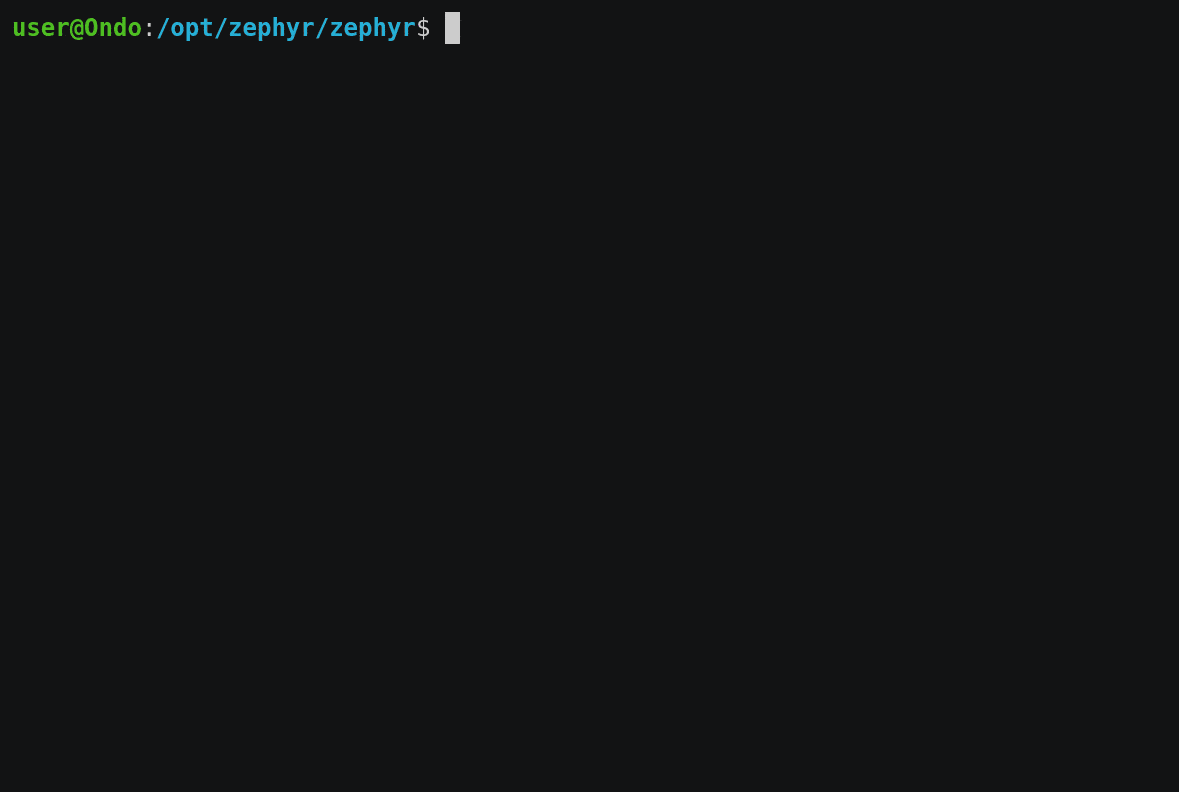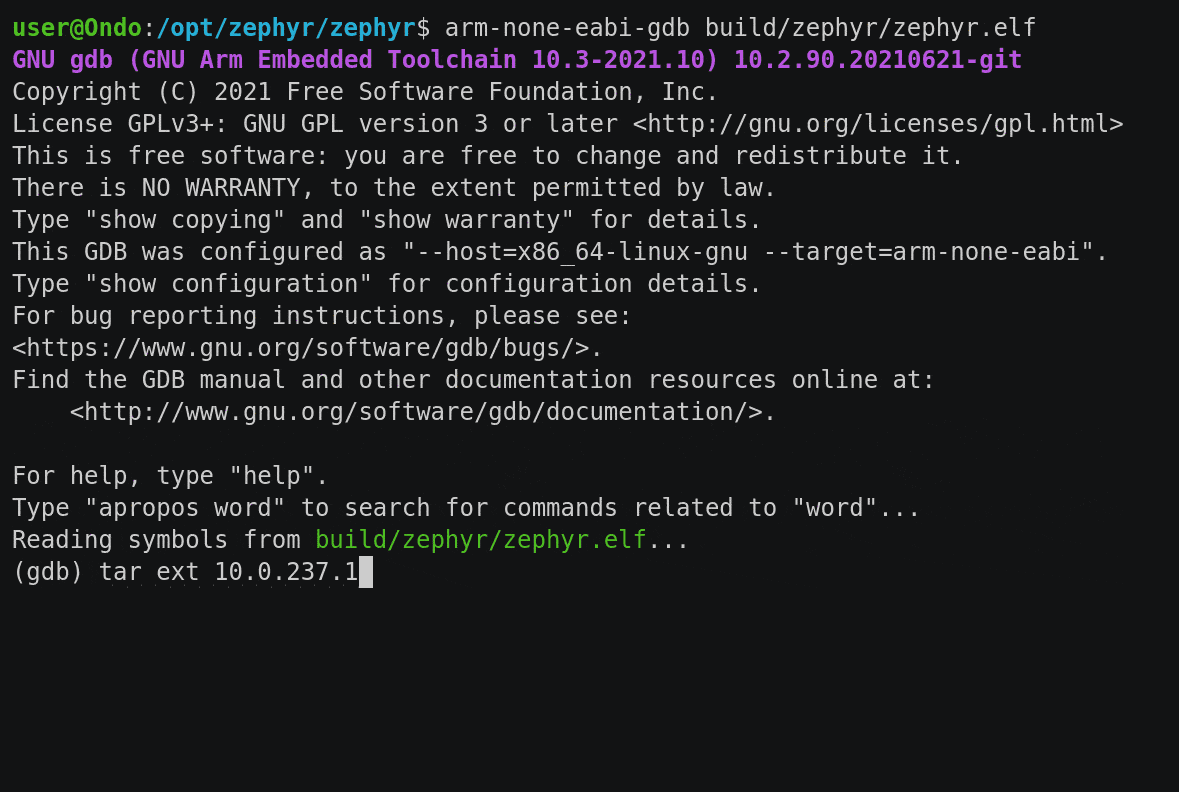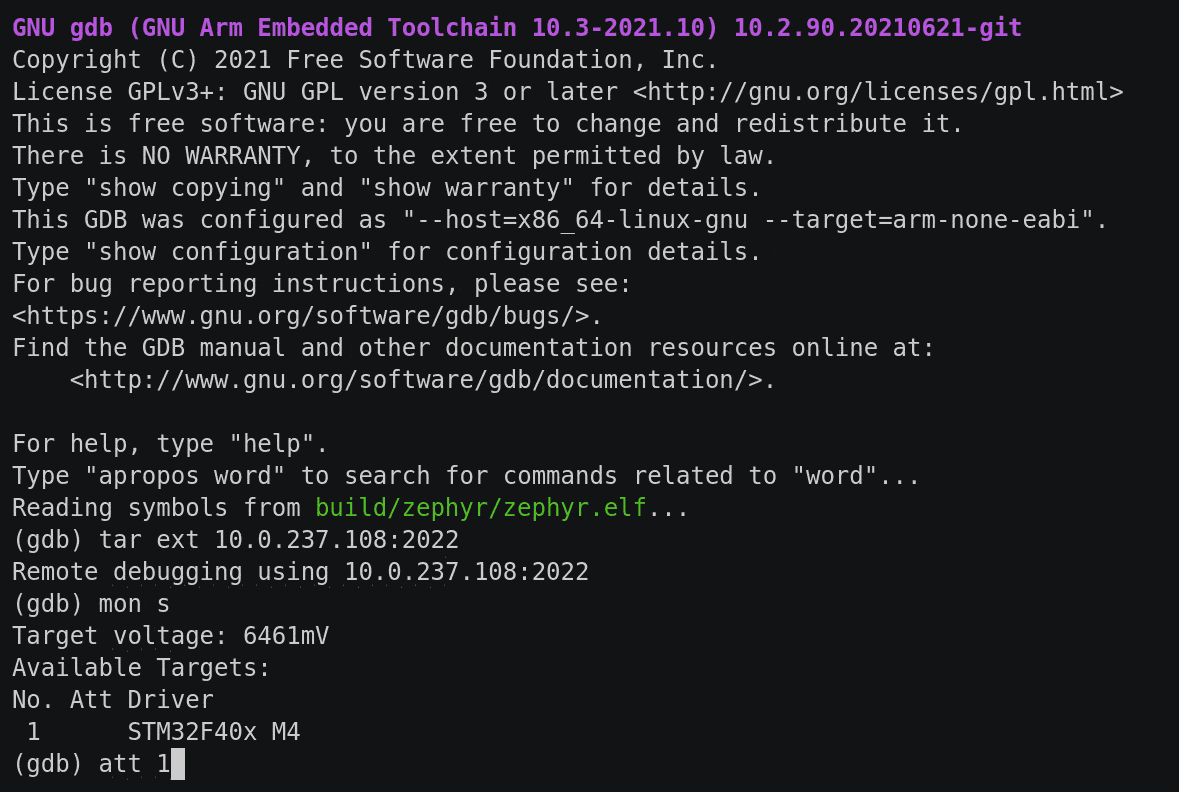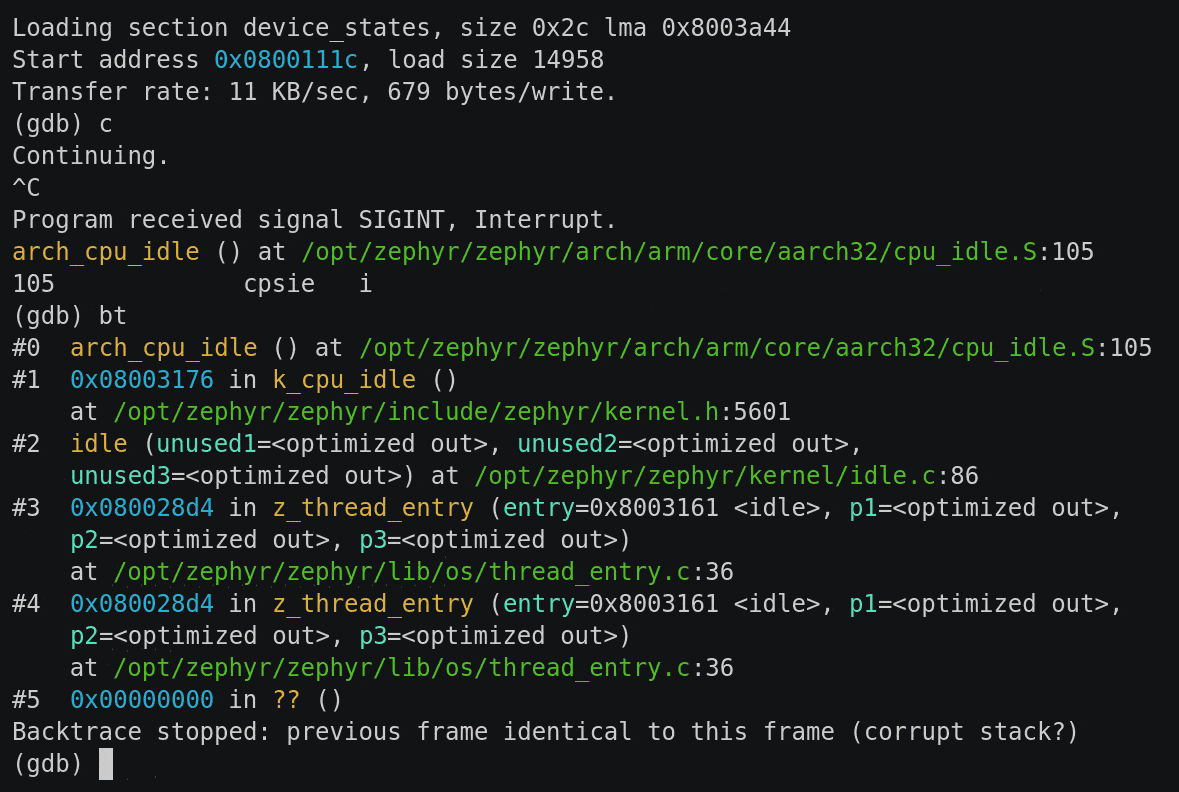
- GDB server on TCP port 2022 (configurable)
- Serial port on TCP port 23
- Wifi configuration via web interface
- OTA updates over tftp
- No drivers needed on the host PC
- All the debug features and supported targets of the blackmagic firmware:
- Targets ARM Cortex-M and Cortex-A based microcontrollers.
- Connects to the target processor using the JTAG or Serial Wire Debug (SWD) interface.
- Provides full debugging functionality, including: watchpoints, flash memory breakpoints, memory and register examination, flash memory programming, etc.
- Load your application into the target Flash memory or RAM.
- Single step through your program.
- Run your program in real-time and halt on demand.
- Examine and modify CPU registers and memory.
- Obtain a call stack backtrace.
- Set up to 6 hardware assisted breakpoints.
- Set up to 4 hardware assisted read, write or access watchpoints.
- Set unlimited software breakpoints when executing your application from RAM.
- Implements the GDB extended remote debugging protocol for seamless integration with the GNU debugger and other GNU development tools.
Supports many ARM Cortex-M and Cortex-A targets. See the list at the Blackmagic Website
ESP32 module with >= 4MB flash. It's possible to configure for other flash sizes -- see idf.py menuconfig
In order to support voltage measurement, the ADC must be connected using a voltage divider with 82k on top and 20k on the bottom. This will allow Farpatch to measure voltages with a range from 0.51V to 6.12V.
First, set your chip by running idf.py set-target [chip]. For example, idf.py set-target esp32s3.
Next, idf.py menuconfig and select Blackmagic Configuration -> Hardware Model.
If your hardware model is not listed, you can select Custom PCB and assign your
own pins, but please consider submitting a patch for your particular pinout configuration.
Hardware models only appear for the currently-selected chip target.
If you select a custom PCB, the following pinouts are set by default for ESP32:
| Pin | Use |
|---|---|
| 25 | JTAG TDI |
| 26 | JTAG TDO |
| 27 | JTAG TMS / SWD IO |
| 12 | SWD IO direction select |
| 14 | JTAG TCK / SWD CLK |
| 13 | NRST |
| 21 | LED status |
| 2 | UART TX |
| 15 | UART RX |
The following are pinout defaults for ESP32-S3:
| Pin | Use |
|---|---|
| 13 | JTAG TDI |
| 11 | JTAG TDO |
| 17 | JTAG TMS / SWD IO |
| 15 | SWD IO direction select |
| 12 | JTAG TCK / SWD CLK |
| 33 | NRST |
| 21 | UART TX |
| 10 | UART RX |
You can adjust the GPIO defaults by running idf.py menuconfig.
| Pin | Use |
|---|---|
| 3 | VREF |
| 4 | JTAG TDI |
| 5 | JTAG TDO |
| 6 | JTAG TCK / SWD CLK |
| 7 | JTAG TMS / SWD IO |
| 8 | WS2812B LED |
| 10 | NRST |
| 21 | UART TX |
| 20 | UART RX |
Connecting to serial terminal can be done using socat:
socat tcp:$FARPATCH_IP:23,crlf -,echo=0,raw,crlf
The easiest way to build is to install the Visual Studio Code extension for ESP-IDF. This will offer to install esp-idf for you. Select the master branch.
You can then build by pressing Ctrl-E Ctrl-B.
Alternately, if you have esp-idf installed, you can use idf.py to build it under Windows or Linux:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/farpatch/farpatch.git
cd farpatch
idf.py set-target esp32s3
idf.py menuconfig
idf.py buildTo flash using esptool.py, you will first need to put the board into bootloader mode:
- Apply power. For boards before DVT4, this means plugging Farpatch into a target. For newer boards, you can set the switch to
VUSB. - Plug the device into your PC via USB
- Hold down the
PRGbutton - Press and release the
RSTbutton - Release the
PRGbutton
The device should enumerate as a serial port on your computer.
The esp-idf package comes with a programmer called esptool.py. You can flash the firmware
using the command line:
idf.py flashAlternately, you can install esptool.py and flash the program that way:
python -mvenv .
. bin/activate # Mac / Linux
.\Scripts\activate.ps1 # Powershell
.\Scripts\activate.bat % cmd.exe
pip install esptool
esptool.py -p (PORT) -b 460800 --before default_reset --after hard_reset --chip esp32s3 write_flash --flash_mode dio --flash_size detect --flash_freq 80m 0x0 build\bootloader\bootloader.bin 0x8000 build\partition_table\partition-table.bin 0xd000 build\ota_data_initial.bin 0x10000 build\blackmagic.bin
If the firmware is already on the device, it is possible to flash using tftp. Make sure you have tftp-hpa package installed then run:
tftp -v -m octet $FARPATCH_IP -c put build/blackmagic.bin firmware.binPlease note that firmware.bin is required, and tells the target that you're uploading a file
called 'firmware.bin'.
There is an experimental web interface available to flashing new updates.
- Go to
http://10.10.0.1/flash/ - Select
blackmagic.binas the firmware file - Click
Update!
By default, Farpatch starts an access point that consists of its name, plus two random strings. You can connect to this to access Farpatch. This access point will always be started when the current wifi configuration does not function.
The default password is 12345678. You can change this by running make menuconfig and
selecting Component Config -> Wifi Manager Configuration -> Access Point Password.
You can configure Farpatch to connect to your existing wifi network. To do that, connect to its access point and navitage to:
This will scan your network, then ask you for a password to connect to the specified access point. When you connect, your PC will be redirected to the new address, though you may need to reconnect to your existing wifi network.
Note that /wifi.html is always available, even when connected to an existing network. Currently,
only one network can be stored at a time.
To deconfigure wifi, hold the PRG button for 5 seconds. This will clear the wifi configuration
data and start up an access point.