This repo contains the final project for the course Scientific Computing in Python. You can run the notebook in either Binder (slower, more likely to crash the kernel) or in Google Colab (faster, works fine).
The equation is:
$$
\frac{du}{dt} - D \Delta u = 0
$$
where $u$ is the temperature field, $D$ is the thermal diffusivity, and $\Delta u$ is the heat flux.
This system is solved using the Crank-Nicolson method by defining the following matrices:
$$
A = \begin{bmatrix}
L & -rI \\
-\frac{r}{2}I & L & -\frac{r}{2}I \\
& \ddots & \ddots & \ddots \\
& & -\frac{r}{2}I & L & -\frac{r}{2}I \\
& & & -rI & L\\
\end{bmatrix}
$$
$$
L = \begin{bmatrix}
1+2r & -r\\
-\frac{r}{2} & 1+2r & -\frac{r}{2}\\
& \ddots & \ddots & \ddots\\
& & -\frac{r}{2} & 1+2r & -\frac{r}{2}\\
& & & -r & 1+2r\\
\end{bmatrix}
$$
$$
\hat{B} = \begin{bmatrix}
Q & rI\\
\frac{r}{2}I & Q & \frac{r}{2}\\
&\ddots & \ddots & \ddots\\
& & \frac{r}{2}I & Q & \frac{r}{2}\\
& & & rI & Q\\
\end{bmatrix}
$$
$$
Q = \begin{bmatrix}
1-2r & r\\
\frac{r}{2} & 1-2r & \frac{r}{2}\\
& \ddots & \ddots & \ddots\\
& & \frac{r}{2} & 1-2r & \frac{r}{2}\\
& & & r & 1-2r\\
\end{bmatrix}
$$
from which the following equation is solved:
$$
Au^{n+1} = Bu^{n}
$$
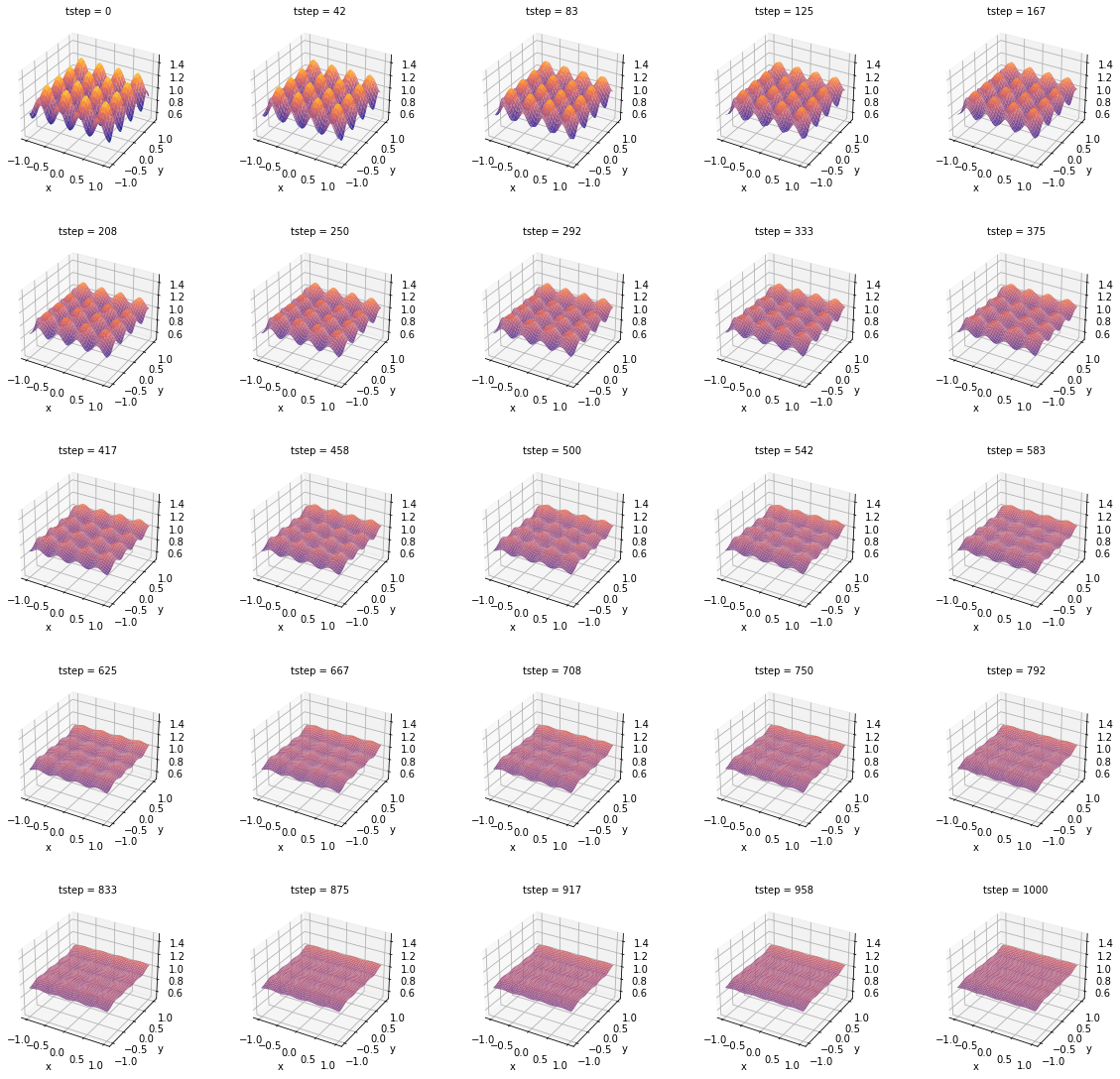
The time evolution of this system looks as follows: