A complete set of tools to code games with Godot Engine in Visual Studio Code.
Warning
This plugin requires manual configuration to work with Godot 4! See the
gdscript_lsp_server_portsetting item under the Configuration section below.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Versions 1.0.0 and later of this extension only support Godot 3.2 or later.
The extension comes with a wealth of features to make your Godot programming experience as comfortable as possible:
- Syntax highlighting for the GDScript (
.gd) language - Syntax highlighting for the
.tscnand.tresscene formats - Full typed GDScript support
- Optional "Smart Mode" to improve productivity with dynamically typed scripts
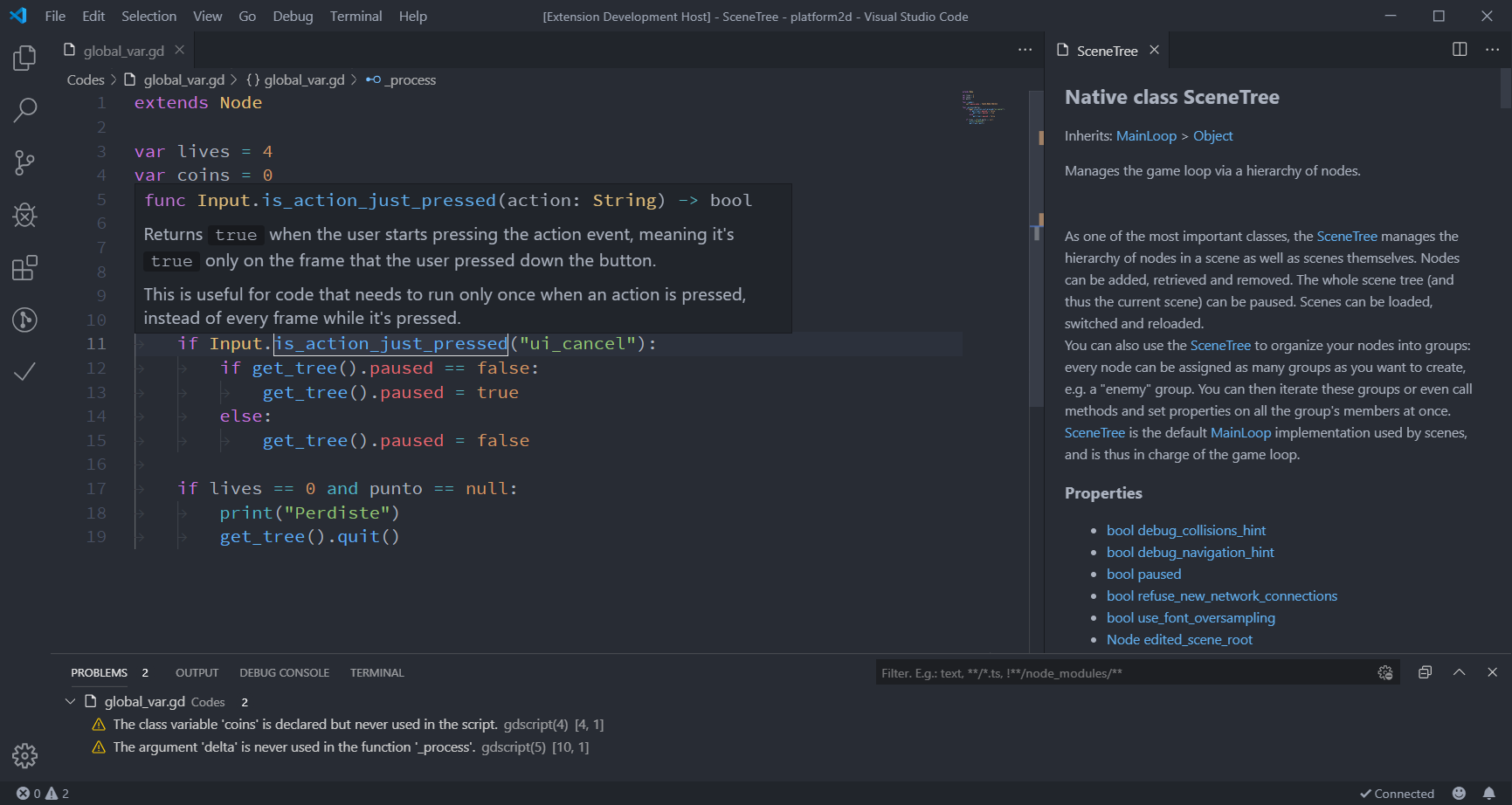
- Function definitions and documentation display on hover (see image below)
- Rich autocompletion
- Display script warnings and errors
- Ctrl + click on a variable or method call to jump to its definition
- Full documentation of the Godot Engine's API supported (select Godot Tools: List native classes of Godot in the Command Palette)
- Run a Godot project from VS Code
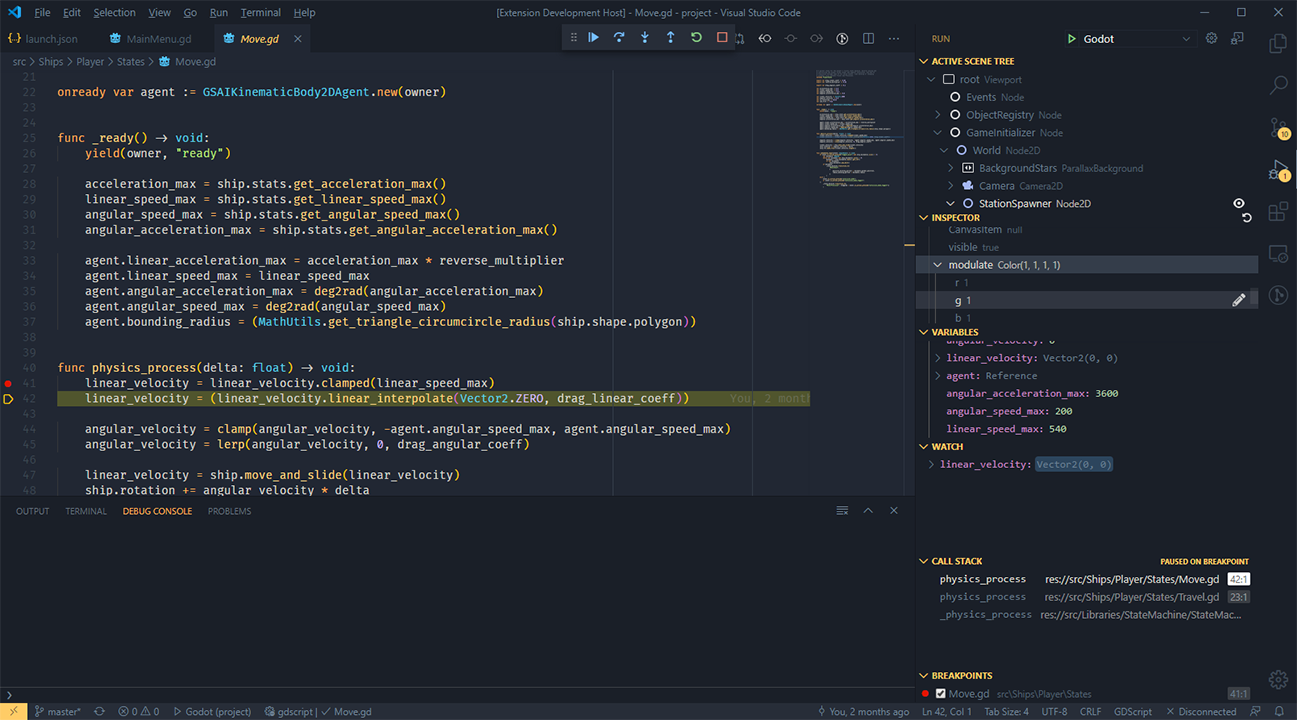
- Debug your GDScript-based Godot project from VS Code with breakpoints, step-in/out/over, variable watch, call stack, and active scene tree
- Visual Studio Marketplace (recommended)
- Stable release, with support for automatic updates.
- GitHub Releases
- Stable release, but no automatic updates. Can be useful if you need to install an older version of the extension.
- Development build (follows the
masterbranch)- Development build. Contains new features and fixes not available in stable releases, but may be unstable.
- Extract the ZIP archive before installing (it contains the
.vsixfile inside).
To install from GitHub Releases or a development build, see Install from a VSIX in the Visual Studio Code documentation.
The extension adds a few entries to the VS Code Command Palette under "Godot Tools":
- Open workspace with Godot editor
- Run the workspace as a Godot project
- List Godot's native classes
If you like this extension, you can set VS Code as your default script editor for Godot by following these steps:
- Open the Editor Settings
- Select Text Editor > External
- Make sure the Use External Editor box is checked
- Fill Exec Path with the path to your VS Code executable
- On macOS, this executable is typically located at:
/Applications/Visual Studio Code.app/Contents/MacOS/Electron
- On macOS, this executable is typically located at:
- Fill Exec Flags with
{project} --goto {file}:{line}:{col}
You can use the following settings to configure Godot Tools:
The absolute path to the Godot editor executable. Under Mac OS, this is the executable inside of Godot.app.
The WebSocket server port of the GDScript language server.
For Godot 3, the default value of 6008 should work out of the box.
For Godot 4, this value must be changed to 6005 for this extension to connect to the language server.
See this tracking issue for more information.
The debugger is for GDScript projects. To debug C# projects, use C# Tools for Godot.
To configure the GDScript debugger:
- Open the command palette:
>Debug: Open launch.json- Select the Debug Godot configuration.
- Change any relevant settings.
- Press F5 to launch.
Configurations
Required
- "project": Absolute path to a directory with a project.godot file. Defaults to the currently open VSCode workspace with
${workspaceFolder}. - "port": Number that represents the port the Godot remote debugger will connect with. Defaults to
6007. - "address": String that represents the IP address that the Godot remote debugger will connect to. Defaults to
127.0.0.1.
Optional
- "launch_game_instance": true/false. If true, an instance of Godot will be launched. Will use the path provided in
editor_path. Defaults totrue. - "launch_scene": true/false. If true, and launch_game_instance is true, will launch an instance of Godot to a currently active opened TSCN file. Defaults to
false. - "scene_file": Path relative to the project.godot file to a TSCN file. If launch_game_instance and launch_scene are both true, will use this file instead of looking for the currently active opened TSCN file.
Usage
- Stacktrace and variable dumps are the same as any regular debugger
- The active scene tree can be refreshed with the Refresh icon in the top right.
- Nodes can be brought to the fore in the Inspector by clicking the Eye icon next to nodes in the active scene tree, or Objects in the inspector.
- You can edit integers, floats, strings, and booleans within the inspector by clicking the pencil icon next to each.
The Godot Tools extension is an open source project from the Godot organization. Feel free to open issues and create pull requests anytime.
See the full changelog for the latest changes.
- Open a command prompt/terminal and browse to the location of this repository on your local filesystem.
- Download dependencies by using the command
npm install - When done, package a VSIX file by using the command
npm run package. - Install it by opening Visual Studio Code, opening the Extensions tab, clicking on the More actions (...) button in the top right, and choose Install from VSIX... and find the compiled VSIX file.
When developing for the extension, you can open this project in Visual Studio Code and debug the extension by using the Run Extension launch configuration instead of going through steps 3 and 4. It will launch a new instance of Visual Studio Code that has the extension running. You can then open a Godot project folder and debug the extension or GDScript debugger.
- Godot 3.2 or later is required.
- For Godot 4, the
gdscript_lsp_server_portsetting must be changed to6005to match the Godot editor's new default language server port number. - Make sure to open the project in the Godot editor first. If you opened the editor after opening VS Code, you can click the Retry button in the bottom-right corner in VS Code.
- GDScript is a dynamically typed script language. The language server can't infer all variable types.
- To increase the number of results displayed, open the Editor Settings, go to the Language Server section then check Enable Smart Resolve.