InfluxDB Plugin for Jenkins
Description
Collects data from various other Jenkins plugins and sends metrics to InfluxDB. It's also possible to send custom data inside pipeline jobs.
Breaking Changes
Support for InfluxDB 1.7 and lower was dropped in plugin release 3.0.
You can find all breaking changes for each version in the breaking changes documentation.
Configuration
Configuration as Code
To configure InfluxDB plugin in Jenkins add the following to jenkins.yaml:
unclassified:
influxDbGlobalConfig:
targets:
- credentialsId: "some_id"
database: "some_database"
description: "some description"
exposeExceptions: true
globalListener: true
globalListenerFilter: "some filter"
jobScheduledTimeAsPointsTimestamp: true
retentionPolicy: "some_policy"
url: "http://some/url"
usingJenkinsProxy: true
⚠️ Prior 3.0,credentialsIdneeds to swapped tousernameandpassword.
Via Jenkins UI
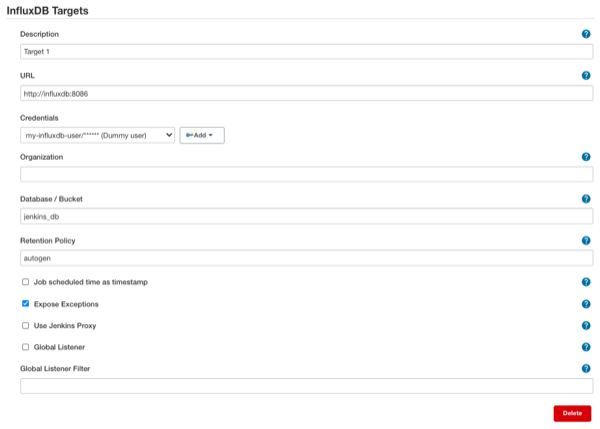
Create a database in InfluxDB and a user with access rights. In Jenkins,
go to Manage Jenkins > Configure System > InfluxDB Targets and click
"Add". Provide the database information. The "URL" parameter requires
the whole URL of the InfluxDB database, including the http(s):// and the
database port. Also, provide the retention policy you want the data to
be stored in InfluxDB (e.g. 15m or 2d). By default, it is infinite.
Exceptions generated by the InfluxDB plugin can also be
ignored by deselecting the "Expose Exceptions" checkbox.
⚠️ When you are using InfluxDB 1.x targets, leave the Organization blank. InfluxDB 2.x uses organizations and buckets instead of databases and retention policies, soorganizationfield is used as an identifier whether the target is InfluxDB 1.x or 2.x.
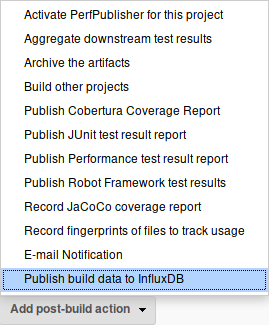
In your job, select "Publish build data to InfluxDB" from the post-build actions.
Via Jenkins Pipeline
From version 1.19 onwards, you can create and remove targets in pipelines directly.
// Get InfluxDB plugin descriptor (version < 2.0)
def influxdb = Jenkins.instance.getDescriptorByType(jenkinsci.plugins.influxdb.DescriptorImpl)
// version >= 2.0
def influxdb = Jenkins.instance.getDescriptorByType(jenkinsci.plugins.influxdb.InfluxDbStep.DescriptorImpl)
// Create target
def target = new jenkinsci.plugins.influxdb.models.Target()
// Set target details
// Mandatory fields
target.description = 'my-new-target'
target.url = 'http://influxdburl:8086'
// Not supported >= 3.0
target.username = 'my-username'
// version < 2.0
target.password = 'my-password'
// version 2.0 to 2.6
target.password = hudson.util.Secret.fromString('my-password')
// Version >= 3.0
target.credentialsId = 'my-id'
target.database = 'my-database'
// Optional fields
target.retentionPolicy = '1d' // default = 'autogen'
target.jobScheduledTimeAsPointsTimestamp = true // default = false
target.exposeExceptions = true // default = true
target.usingJenkinsProxy = true // default = false
// Add a target by using the created target object
influxdb.addTarget(target)
influxdb.save()
// Write stuff to InfluxDB
influxDbPublisher(selectedTarget: 'my-new-target')
// Remove a target by using the target description field value
influxdb.removeTarget('my-new-target')
influxdb.save()
Credentials
- InfluxDB 1.8 targets support only
Username with password. - InfluxDB 2.x supports
Username with passwordfor basic authentication andSecret Textfor authentication token authentication.
Usage
Global Listener
When globalListener is set to true for a target in which no results were published during the build, it will automatically publish the result for this target when the build is completed.
To configure the global listener, you can use environment variables prefixed with INFLUXDB_PLUGIN. The following variables are supported and all correspond to an influxDbPublisher optional parameter.
INFLUXDB_PLUGIN_CUSTOM_PROJECT_NAME->customProjectNameINFLUXDB_PLUGIN_CUSTOM_PREFIX->customPrefixINFLUXDB_PLUGIN_CUSTOM_FIELDS->jenkinsEnvParameterFieldINFLUXDB_PLUGIN_CUSTOM_TAGS->jenkinsEnvParameterTag
NOTE: The environment variables must be set on the final build object. If you are creating or updating these variables in a pipeline, you should make sure they are exported with an EnvironmentContributingAction.
Freestyle Jobs
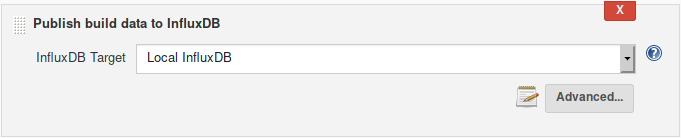
Select the InfluxDB target you wish to publish the data to.
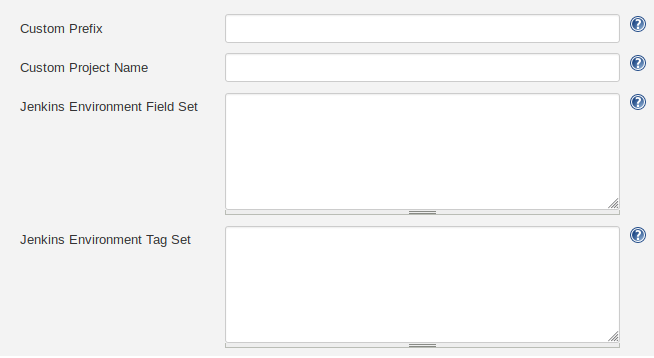
From the "Advanced" tab you can choose to set a custom prefix for your project_name field,
a custom project name to be used instead of the default job name, custom fields for your
jenkins_data metric, and custom tags for your all your metrics.
Pipelines
The plugin can be used by calling either the influxDbPublisher() or the step() function.
NOTE: The influxDbPublisher() function is only supported from version 1.21 onwards.
Pipeline syntax
The only mandatory parameter is selectedTarget, which is the "Description" for your
target in the global configuration.
influxDbPublisher(selectedTarget: 'my-target')
step([$class: 'InfluxDbPublisher', selectedTarget: 'my-target'])
Optional parameters
customProjectName(String) - custom project namecustomPrefix(String) - custom prefix for project namecustomData(Map) - custom fields in "jenkins_custom_data" measurementcustomDataTags(Map) - custom tags in "jenkins_custom_data" measurementcustomDataMap(Map) - custom fields in custom measurementscustomDataMapTags(Map) - custom tags in custom measurements (map of tags for each custom measurements)jenkinsEnvParameterField(String) - custom fields in "jenkins_data" measurement (newline-separated KEY=VALUE pairs)jenkinsEnvParameterTag(String) - custom tags in all measurements (newline-separated KEY=VALUE pairs)measurementName(String) - custom measurement name (replaces default "jenkins_data" and "jenkins_custom_data")
All customData* parameters contain custom data generated during the
build and not by the plugin, so they are not available in the snippet generator.
❗ NOTE! Up to release 1.10.3, pipeline was configured with using the url and database.step([$class: 'InfluxDbPublisher', target: 'http://127.0.0.1:8086,jenkins_db', ... ])This form of configuration is not supported from version 1.11 onwards.
Pipelines don't have post-build actions, so the build result, build
ordinal, and the build success boolean will default to "?", 5,
and false respectively, unless set manually before calling InfluxDbPublisher.
Only the build result needs to be set manually, as the boolean value and ordinal are set
based on build result. Also, the build status will appear as "?" and the build
duration might be a little off, because the build is not actually finished.
If you want to get those pieces of information you need to configure the plugin
separately on each job as a post-build action. The jobs can be run with,
for example, the Build Pipeline Plugin
to get data from all jobs to InfluxDB. Alternatively, you can insert the
information in your build manually inside your Groovy script.
try {
// Build things here
if (currentBuild.result == null) {
currentBuild.result = 'SUCCESS' // sets the ordinal as 0 and boolean to true
}
} catch (err) {
if (currentBuild.result == null) {
currentBuild.result = 'FAILURE' // sets the ordinal as 4 and boolean to false
}
throw err
} finally {
influxDbPublisher(selectedTarget: 'my-target')
}
Custom Data
You can write custom data to InfluxDB like this:
def myFields = [:]
myFields['field_a'] = 11
myFields['field_b'] = 12
influxDbPublisher(selectedTarget: 'my-target', customData: myFields)
This adds the fields field_a and field_b with values 11 and 12 respectively to a measurement called jenkins_custom_data.
You can also add tags to this measurement with the customDataTags parameter.
Alternatively, you can write custom data to InfluxDB with a higher degree of customization like this:
def myFields1 = [:]
def myFields2 = [:]
def myCustomMeasurementFields = [:]
myFields1['field_a'] = 11
myFields1['field_b'] = 12
myFields2['field_c'] = 21
myFields2['field_d'] = 22
myCustomMeasurementFields['series_1'] = myFields1
myCustomMeasurementFields['series_2'] = myFields2
myTags = ['series_1':['tag_a':'a','tag_b':'b'],'series_2':['tag_c':'c','tag_d':'d']]
influxDbPublisher(selectedTarget: 'my-target', customDataMap: myCustomMeasurementFields, customDataMapTags: myTags)
This creates 2 measurements, series_1 and series_2.
It adds the fields field_a and field_b with values 11 and 12 respectively to measurement series_1.
It adds the fields field_c and field_d with values 21 and 22 respectively to measurement series_2.
You can also add tags to your custom measurements with the customDataMapTags parameter.
You must use the same map keys as measurement names as in customDataMap.
Supported Metrics
See all available metrics from the available metrics documentation.
Contribution
Create a pull request to the development branch.
No pull requests are merged directly to master.
Comment your changes sufficiently and create appropriate tests.
For feature requests and bug reports, please use the Jenkins issue tracker.
Acknowledgements
This plugin was inspired by Jouni Rajala and Christoph Burmeister.