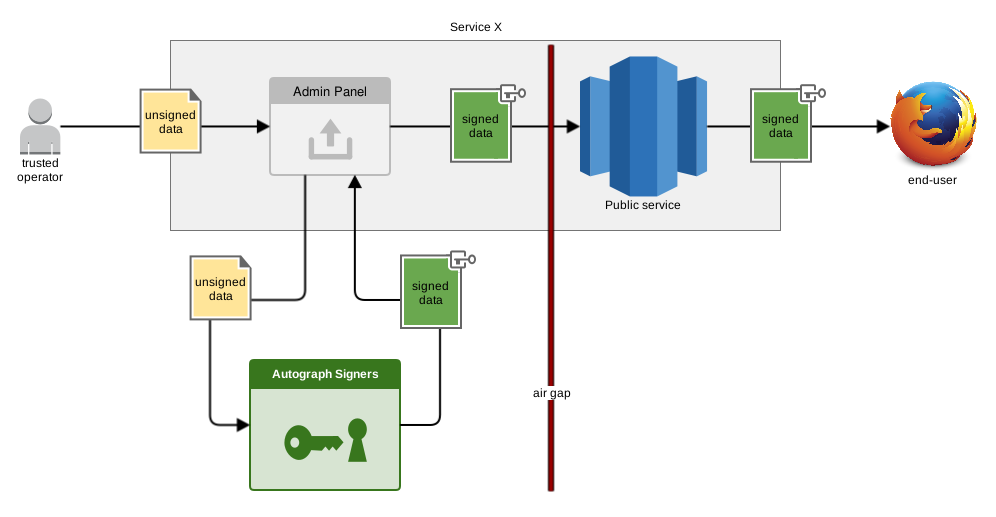
Autograph is a cryptographic signature service that implements Content-Signature, XPI Signing for Firefox web extensions, MAR Signing for Firefox updates, APK V1 Signing for Android, PGP, GPG2 and RSA.
Why is it called "autograph"? Because it's a service to sign stuff.
docker pull mozilla/autograph && docker run mozilla/autograph
This will download the latest build of autograph from DockerHub and run it with its dev configuration.
If you don't yet have a GOPATH, export one:
$ export GOPATH=$HOME/go
$ mkdir $GOPATHInstall ltdl:
- on Ubuntu: ltdl-dev
- on RHEL/Fedora/Arch: libtool-ltdl-devel
- on MacOS: libtool (NB: this might require
brew unlink libtool && brew link libtool)
Then download and build autograph:
$ go get go.mozilla.org/autographThe resulting binary will be placed in $GOPATH/bin/autograph. To run autograph with the example conf, do:
$ cd $GOPATH/src/go.mozilla.org/autograph
$ $GOPATH/bin/autograph -c autograph.yamlExample clients are in the tools directory. You can install the Go one like this:
$ go get go.mozilla.org/autograph/tools/autograph-client
$ $GOPATH/bin/autograph-client -u alice -p fs5wgcer9qj819kfptdlp8gm227ewxnzvsuj9ztycsx08hfhzu -t http://localhost:8000/sign/data -r '[{"input": "Y2FyaWJvdW1hdXJpY2UK"}]'
2016/08/23 17:25:55 signature 0 pass- Architecture
- Configuration
- Endpoints
- Content-Signature protocol
- XPI Signing protocol
- MAR protocol
- APK protocol
- HSM Support
Autograph exposes a REST API that services can query to request signature of their data. Autograph knows which key should be used to sign the data of a service based on the service's authentication token. Access control and rate limiting are performed at that layer as well.