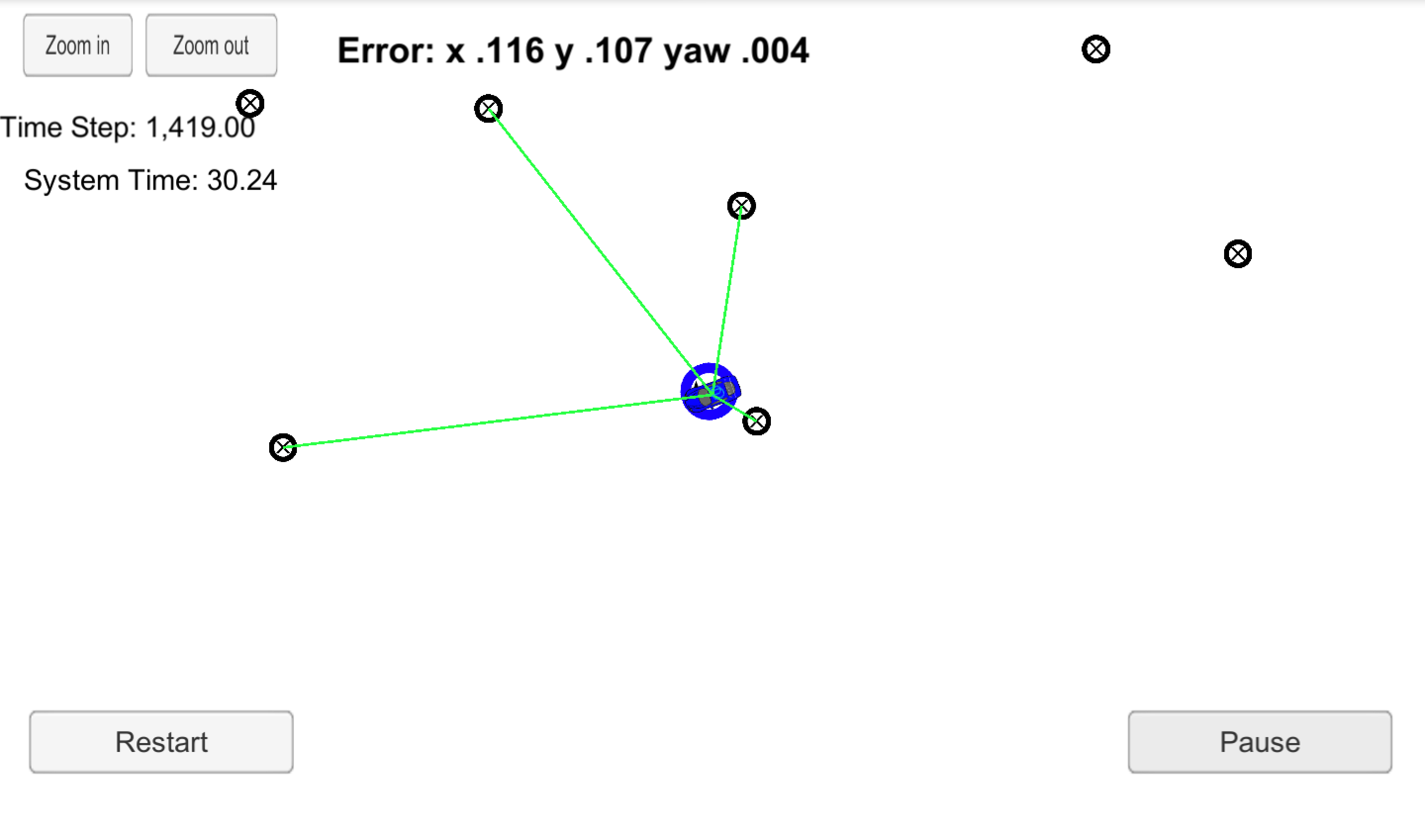
In this project we will implement a 2 dimensional particle filter in C++. To the particle filter will be given a map and some initial localization information (analogous to what a GPS would provide). At each time step the filter will also get observation and control data.
This project involves the Term 2 Simulator which can be downloaded here
This repository includes two files that can be used to set up and install uWebSocketIO for either Linux or Mac systems. For windows you can use either Docker, VMware, or even Windows 10 Bash on Ubuntu to install uWebSocketIO.
Once the install for uWebSocketIO is complete, the main program can be built and ran by doing the following from the project top directory.
- mkdir build
- cd build
- cmake ..
- make
- ./particle_filter
Alternatively some scripts have been included to streamline this process, these can be leveraged by executing the following in the top directory of the project:
- ./clean.sh
- ./build.sh
- ./run.sh
Tips for setting up your environment can be found here
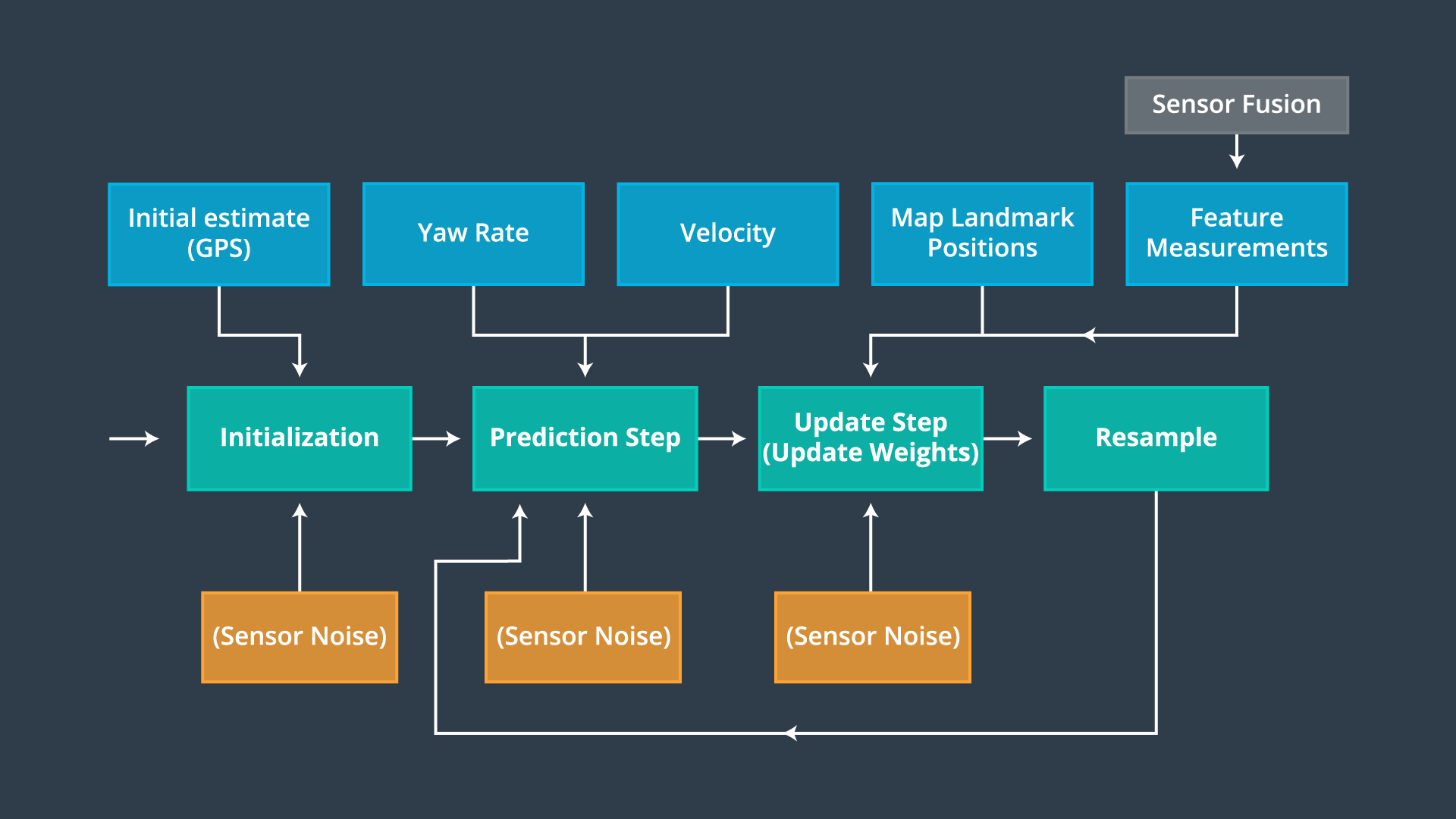
The Particle Filter algorithm will go through the following steps:
-
Initialization - At the initialization step we estimate our position from GPS input. The subsequent steps in the process will refine this estimate to localize our vehicle.
-
Prediction Step - During the prediction step we add the control input (yaw rate & velocity) for all particles.
-
Update Step (Update Weights) - During the update step, we update our particle weights using map landmark positions and feature measurements.
-
Resample - During resampling we will resample particles, drawing a particle i (i is the particle index) proportional to its weight.
void ParticleFilter::init(double x, double y, double theta, double std[]) {
// TODO: Set the number of particles. Initialize all particles to first position (based on estimates of
// x, y, theta and their uncertainties from GPS) and all weights to 1.
// Add random Gaussian noise to each particle.
// NOTE: Consult particle_filter.h for more information about this method (and others in this file).
if (is_initialized) { return; }
num_particles = 100;
double std_x = std[0];
double std_y = std[1];
double std_theta = std[2];
normal_distribution<double> normal_dist_x(x, std_x);
normal_distribution<double> normal_dist_y(y, std_y);
normal_distribution<double> normal_dist_theta(theta, std_theta);
for (int i = 0; i < num_particles; i++) {
Particle p;
p.id = i;
p.x = normal_dist_x(gen);
p.y = normal_dist_y(gen);
p.theta = normal_dist_theta(gen);
p.weight = 1.0;
particles.push_back(p);
}
is_initialized = true;
}void ParticleFilter::prediction(double delta_t, double std_pos[], double velocity, double yaw_rate) {
// TODO: Add measurements to each particle and add random Gaussian noise.
// NOTE: When adding noise you may find std::normal_distribution and std::default_random_engine useful.
// http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/numeric/random/normal_distribution
// http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/random/default_random_engine/
double std_x = std_pos[0];
double std_y = std_pos[1];
double std_theta = std_pos[2];
normal_distribution<double> normal_dist_x(0, std_x);
normal_distribution<double> normal_dist_y(0, std_y);
normal_distribution<double> normal_dist_theta(0, std_theta);
for (int i = 0; i < num_particles; i++) {
if (fabs(yaw_rate) < 0.00001) {
particles[i].x += velocity * delta_t * cos(particles[i].theta);
particles[i].y += velocity * delta_t * sin(particles[i].theta);
} else {
particles[i].x += (velocity / yaw_rate) * (sin(particles[i].theta + yaw_rate * delta_t) - sin(particles[i].theta));
particles[i].y += (velocity / yaw_rate) * (cos(particles[i].theta) - cos(particles[i].theta + yaw_rate * delta_t));
particles[i].theta += yaw_rate * delta_t;
}
particles[i].x += normal_dist_x(gen);
particles[i].y += normal_dist_y(gen);
particles[i].theta += normal_dist_theta(gen);
}
}void ParticleFilter::dataAssociation(std::vector<LandmarkObs> predicted, std::vector<LandmarkObs>& observations) {
for (int i = 0; i < observations.size(); i++) {
LandmarkObs observation = observations[i];
double min_distance = numeric_limits<double>::max();
int map_id = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < predicted.size(); j++) {
LandmarkObs prediction = predicted[j];
double distance = dist(observation.x, observation.y, prediction.x, prediction.y);
if (distance < min_distance) {
min_distance = distance;
map_id = prediction.id;
}
}
observations[i].id = map_id;
}
}
void ParticleFilter::updateWeights(double sensor_range, double std_landmark[], const std::vector<LandmarkObs> &observations, const Map &map_landmarks) {
for (int i = 0; i < num_particles; i++) {
Particle p = particles[i];
vector<LandmarkObs> landmarks_in_range;
for (int j = 0; j < map_landmarks.landmark_list.size(); j++) {
float landmark_x = map_landmarks.landmark_list[j].x_f;
float landmark_y = map_landmarks.landmark_list[j].y_f;
int landmark_id = map_landmarks.landmark_list[j].id_i;
double dx = fabs(landmark_x - p.x);
double dy = fabs(landmark_y - p.y);
if (dist(dx, dy, 0, 0) <= sensor_range) {
LandmarkObs lm = LandmarkObs{ landmark_id, landmark_x, landmark_y };
landmarks_in_range.push_back(lm);
}
}
vector<LandmarkObs> transformed_observations;
for (int j = 0; j < observations.size(); j++) {
double t_x = cos(p.theta) * observations[j].x - sin(p.theta) * observations[j].y + p.x;
double t_y = sin(p.theta) * observations[j].x + cos(p.theta) * observations[j].y + p.y;
LandmarkObs tr_ob = LandmarkObs{ observations[j].id, t_x, t_y };
transformed_observations.push_back(tr_ob);
}
dataAssociation(landmarks_in_range, transformed_observations);
particles[i].weight = 1.0;
for (int j = 0; j < transformed_observations.size(); j++) {
LandmarkObs tr_ob = transformed_observations[j];
LandmarkObs lm;
for (unsigned int k = 0; k < landmarks_in_range.size(); k++) {
if (landmarks_in_range[k].id == tr_ob.id) {
lm.x = landmarks_in_range[k].x;
lm.y = landmarks_in_range[k].y;
}
}
double std_x = std_landmark[0];
double std_y = std_landmark[1];
double dx = lm.x - tr_ob.x;
double dy = lm.y - tr_ob.y;
double weight = (1 / (2 * M_PI * std_x * std_y)) * exp(-(pow(dx,2) / (2 * pow(std_x, 2)) + (pow(dy,2) / (2 * pow(std_y, 2)))));
particles[i].weight *= weight;
}
}
}void ParticleFilter::resample() {
vector<Particle> new_particles;
vector<double> weights;
for (int i = 0; i < num_particles; i++) {
weights.push_back(particles[i].weight);
}
double max_weight = *max_element(weights.begin(), weights.end());
uniform_real_distribution<double> urdist(0.0, max_weight);
uniform_int_distribution<int> uidist(0, num_particles - 1);
auto index = uidist(gen);
double beta = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < num_particles; i++) {
beta += urdist(gen) * 2.0;
while (beta > weights[index]) {
beta -= weights[index];
index = (index + 1) % num_particles;
}
new_particles.push_back(particles[index]);
}
particles = new_particles;
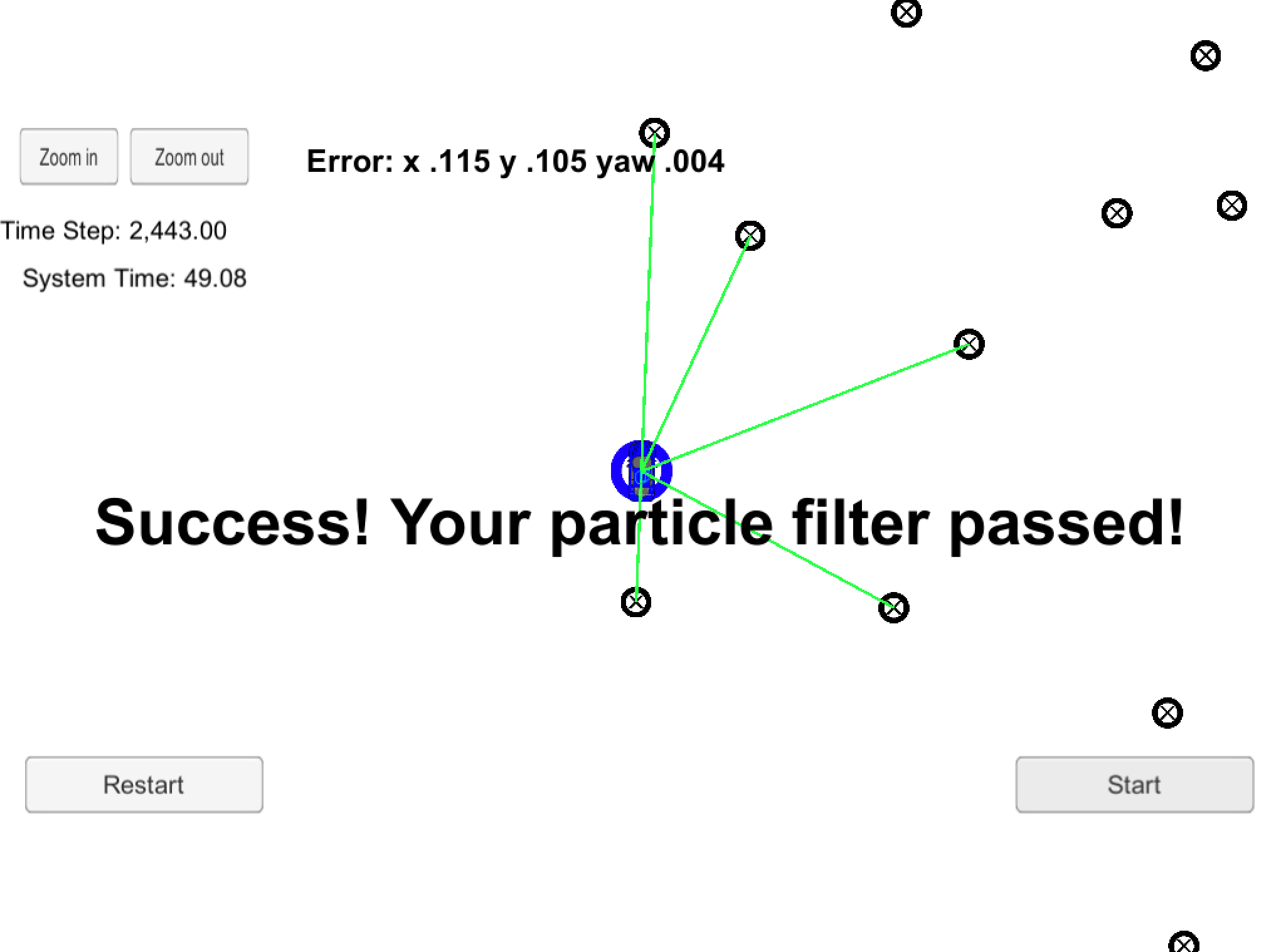
}After testing with the map provided by the simulator, the results were: