This project is inspired by Springfox, but instead of documenting REST APIs, it documents Spring Kafka consumers.
It works by scanning the application once at runtime for methods annotated with @KafkaListener inside
@Component and @Service annotated classes, and providing a REST API to access the collected information.
A web-based UI can be added as a separate dependency.
Both the library and the UI are designed to be mostly familiar to Swagger users.
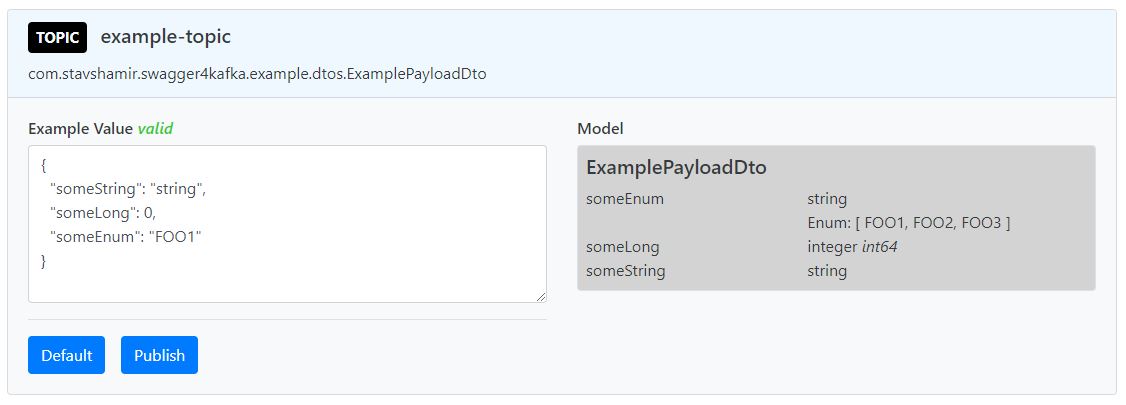
In projects using Kafka, you may often find yourself needing to manually send a message to some topic, whether if you are manually testing a new feature, debugging or trying to understand some flow. This requires serializing your payload object, and then sending it by the CLI or some other interface. swagger4kafka exploits the fact you already fully described your Kafka consumer endpoint and automatically generates an example payload object for the appropriate payload and allows you to publish it to the correct topic with a single click.
It is not another generic REST API for Kafka.
Note for springfox users - using swagger4kafka with springfox versions before 2.9.2 might raise an exception.
By applying the following instructions, methods annotated with @KafkaListener inside @Component and
@Service annotated classes will be scanned once in runtime. Of course, it is a requirement that the project is a
Spring Boot project with the spring-kafka library and its relevant configurations.
swagger4kafka is hosted on jcenter.
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
// Provides the documentation API
implementation 'io.github.stavshamir:swagger4kafka:0.0.1'
// Provides the UI - optional (recommended)
implementation 'io.github.stavshamir:swagger4kafka-ui:0.0.1'
}<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.stavshamir</groupId>
<artifactId>swagger4kafka</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.stavshamir</groupId>
<artifactId>swagger4kafka-ui</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Add a configuration class and provide a Docket bean:
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger4Kafka
public class Swagger4KafkaConfiguration {
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return Docket.builder()
.serviceName("Swagger4Kafka Example Project")
.basePackage("io.github.stavshamir.swagger4kafka.example.consumers")
.bootstrapServers("localhost:9092")
.build();
}
}The basePackage field must be set with the name of the package containing the classes to be scanned for @KafkaListener
annotated methods.
Other fields are optional, and for some sensible defaults are provided. For more info, see the Docket Javadoc.
If you have included the UI dependency, access it with the following url: localhost:8080/swagger4kafka-ui.html.
If not, try the following endpoint: localhost:8080/kafka-api/endpoints.
A default Kafka producer implementation is provided, but a custom producer with your own properties can be set in the
Docket bean like this:
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return Docket.builder()
.serviceName("Swagger4Kafka Example Project")
.basePackage("io.github.stavshamir.swagger4kafka.example.consumers")
.producerConfiguration(producerConfiguration())
.build();
}
private Map<String, Object> producerConfiguration() {
return ImmutableMap.<String, Object>builder()
.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS)
.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class)
.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, JsonSerializer.class)
.put(JsonSerializer.ADD_TYPE_INFO_HEADERS, false)
.build();
}An example project can be found here.