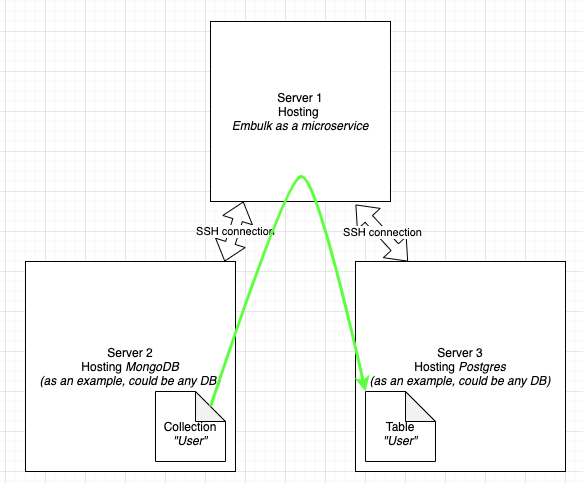
This project aims to facilitate deploying embulk as a micro-service through SSH tunneling
- Connect to your database 1
- Do a job like converting from Db1 to Db2 (as specified in the configuration_example.yml file)
- Connect to your database 2 and write the Embulk output
Every connection is done using SSH tunneling.
Example, with Mongo (database 1) and Postgres (database 2) :
Yes, you can host it on heroku for instance, or on your own server.
Pre requisite : you need Docker installed on your machine
Then, you have to :
- put your ssh key (the private part) in the .ssh folder as keyexample or default_env_SSHKEY according to your environment_variables you will define next step => this key will allow this machine to connect to the remote database so you need also to make sure the remote machines will allow the connection with a public key
- customize the environment variables in the environment_variables.txt file according to the different IP of your servers etc...
- modify configuration_example.yml according to your needs (see embulk website for more details)
- run
docker build --build-arg CONFIGURATION_FILE=configuration_example.yml --build-arg DIFF_FILE=diff.yml --tag embulk_container .to launch the build process of your docker image - run
docker run --env-file=environment_variables.txt -it embulk_container bashonly later if you want to start the process again. If you change environment_variables.txt of your configuration_example.yml you will need to run the other one in order to build again the docker image
- For better use, I suggest renaming configuration_example.yml to configuration.yml and since it is gitignored you can leave it in the repo. Another example can be found named configuration_example_2.yml
- for incremental update, we need to keep "diff.yml" (see embulk doc) from one run to another. In order to do so, we set up a Docker Volume to keep it persistent. This is donc adding
-v $PWD:/workto the dockerrun command. So here is the command:
docker run --env-file=environment_variables.txt -v $PWD:/work -it embulk_container bash - If, for some unkwnown reason, you cannot merge the first time, try to insert instead, and manually specify the primary key on your output database
- you may encounter some database error Sort operation used more than the maximum XXXXXX bytes of RAM in case of incremental_field while you haven't indexed your database on this field
- using the java:8 docker image was triggering an out of RAM problem. we switched to this image FROM fabric8/java-jboss-openjdk8-jdk:1.4.0 in order to have the ability to limit Java Ram usage
docker run -m 600m -e JAVA_OPTIONS='-Xmx300m' [...]. This issue was inherent to Java, unable to use cgroup memory limits : whatever the container Ram limit was, Java container was using all the machine ressource, causing big errors. - when running in production, don't forget to remove
-itbecause no TTY will ba available if you trigger it from a CRON job for instance
- If you still get prompt password, you have an issue with your SSH auth, It can be that your key has too wide permission. try
chmod 600 .ssh/keyexamplesee this example
see this example
see this example